Question
The graph shows the concentration of the lipid lecithin in the amniotic fluid surrounding the fetus during normal gestation. This lipid is produced in the lungs of the fetus and acts as a surfactant.
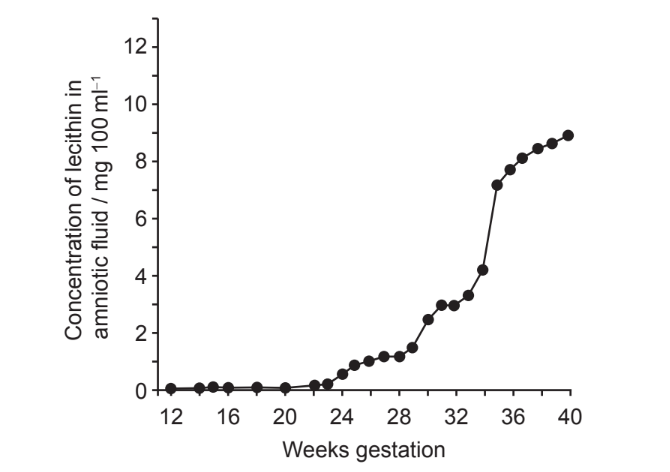
What problem may occur in a baby born before 34 weeks gestation?
A. Type I pneumocytes do not produce sufficient surfactant for lungs to inflate.
B. There are no type II pneumocytes.
C. The alveolar walls stick together.
D. The alveoli are too large.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
Pressure changes inside the thorax cause the movement of air in and out of the lung alveoli
during ventilation. Alveolar pressure correlates to thoracic pressure. The diagram shows pressure
changes in lung alveoli during ventilation in relation to normal atmospheric pressure. What causes
forced movement of air out of the lungs at T?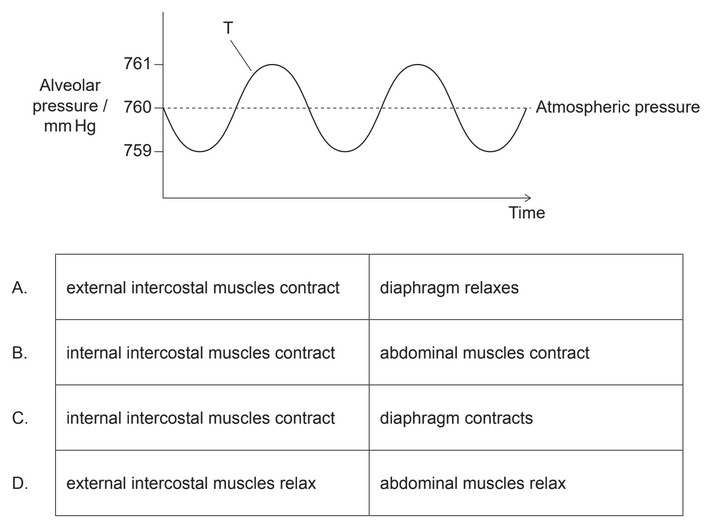
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
Where in the body are type I pneumocytes found?
Alveoli
Nephrons
Capillaries
Trachea
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
Which is an adaptation to increase rates of gas exchange in the lung?
Small surface area
Dry surface
High vascularization
Muscular alveoli
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C