Question
Movement of insects requires muscles in antagonistic pairs. The diagram shows an insect leg with muscles labelled $\mathrm{X}$ and $\mathrm{Y}$.
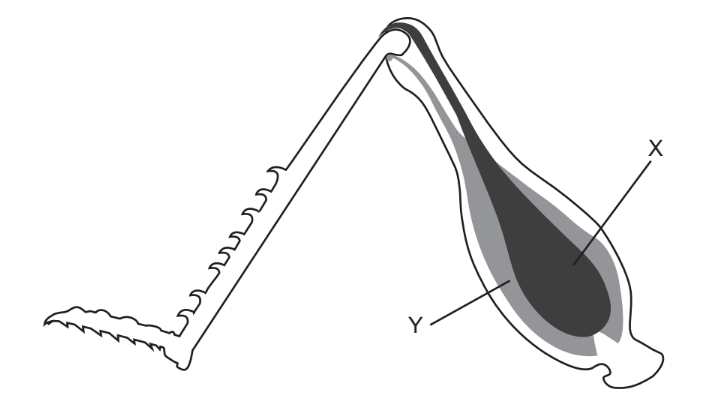
What actions in the human arm are equivalent to muscle X contracting and muscle Y relaxing?
A. triceps contracts, biceps relaxes, arm extends
B. biceps contracts, triceps relaxes, arm flexes
C. triceps contracts, biceps relaxes, arm flexes
D. biceps contracts, triceps relaxes, arm extends
Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question
The electron micrograph shows sarcomeres in myofibrils of striated muscle during muscle contraction. The lines P–Q and R–S show two regions of one sarcomere.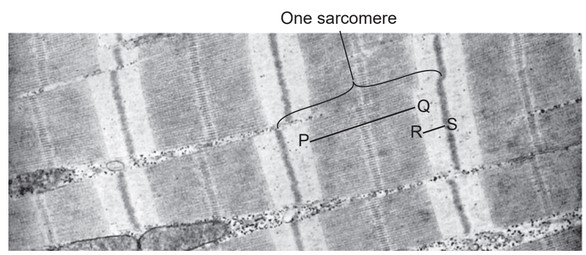
How would regions P–Q and R–S change when the muscle relaxes?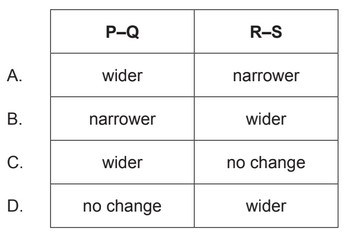
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
The diagram shows the side view of the human elbow. Which structure is the radius?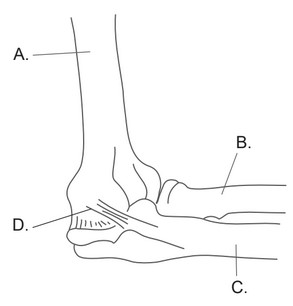
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B