Question
An experiment on aerobic respiration was performed using a plant in a pot containing fertile soil. The apparatus was set up as shown in the diagram. Sodium hydroxide and limewater (calcium hydroxide) are both alkaline solutions. Limewater goes cloudy when carbon dioxide is bubbled into it.

(a) State the purpose of lime water in flask B.
(b) Suggest a reason that the pot was covered with a plastic bag.
(c) Suggest a suitable control for this experiment.
(d) The same apparatus was used in another experiment, but the potted plant was exposed to light. Predict with a reason the results for lime water in flask C after one hour.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) to check there is no carbon dioxide (left in the air)/show any carbon dioxide
present;
(b) soil releases \(CO_2\) from microorganisms/decomposers/bacteria/fungi
OR
respiration by microorganisms may affect the result;
(c) using the same apparatus without a plant
OR
cover the whole plant with a plastic bag;
(d) no change/limewater stays clear
OR
because plant takes in carbon dioxide by photosynthesis;
Question
a.Describe the genetic code and its relationship to polypeptides and proteins.[5]
b.Outline the role of proteins in active and passive transport of molecules through membranes.[5]
c. Many cell functions, like synthesis of macromolecules and transport, require energy in the form of ATP. Explain how ATP is generated in animal cells.[8]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a.)
Remember, up to TWO “quality of construction” marks per essay.
a. (the genetic code is based on) sets of three nucleotides/triplets of bases called codons;
b. bases include adenine, guanine, cytosine and thymine in DNA / adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil in RNA; (do not accept ATCG)
c. each codon is code for one amino acid;
d. some codons are (start or) stop codons;
e. DNA is transcribed into mRNA by base-pair matching/complementary base pairing;
f. mRNA is translated into a sequence of amino acids/polypeptide;
g. each gene codes for a polypeptide;
h. polypeptides may be joined/modified to form proteins;
b.)
Remember, up to TWO “quality of construction” marks per essay.
a. channel proteins allow diffusion/osmosis/passive transport;
b. large/polar molecules cannot cross the (hydrophobic) membrane freely;
c. facilitated diffusion involves moving molecules through proteins down their concentration gradient/without requiring ATP;
d. aquaporins (specific integral membrane proteins) facilitate the movement of water molecules/osmosis;
e. some proteins (for facilitated diffusion) are specific to molecule/ions;
f. active transport involves moving molecules through proteins against their concentration gradient/requiring ATP;
g. (some) proteins in the membrane are pumps / pumps perform active transport / sodium potassium pump;
c.)
Remember, up to TWO “quality of construction” marks per essay.
a. ATP is a form of energy currency/immediately available for use;
b. ATP is generated in cells by cell respiration (from organic compounds);
c. aerobic (cell respiration) requires oxygen;
d. anaerobic (cell respiration) does not require oxygen;
e. glycolysis breaks down glucose into pyruvate;
f. glycolysis occurs in cytoplasm;
g. (by glycolysis) a small amount of ATP is released;
h. ADP changes into ATP with the addition of a phosphate group/phosphoric acid / accept as chemical equation;
i. in mitochondria/aerobic respiration produces large amount of ATP / $38 \mathrm{mols}$ (for the cell, per glucose molecule);
j. oxygen/aerobic respiration is required for mitochondrial production of ATP;
k. in mitochondria/aerobic respiration pyruvate is broken down into carbon dioxide and water;
Question
a. State the functions of the following organelles of a eukaryotic animal cell: lysosome, Golgi apparatus, free ribosomes, plasma membrane, rough endoplasmic reticulum.[5]
b. Distinguish between anaerobic and aerobic cell respiration in eukaryotes.[4]
c.Explain the mechanism of ventilation in the lungs in order to promote gas exchange for cell respiration.[9]
lysosome:
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
a.
a. (from Golgi apparatus) with digestive enzymes / break down food/organelles/ cell;
Golgi apparatus:
b. site that processes/modifies/packages and releases proteins;
free ribosomes:
c. site of synthesis of proteins (released to cytoplasm);
plasma membrane:
d. controls entry and exit of materials/substances in cell;
rough endoplasmic reticulum:e. synthesis and transport of proteins; (both needed)
b.)
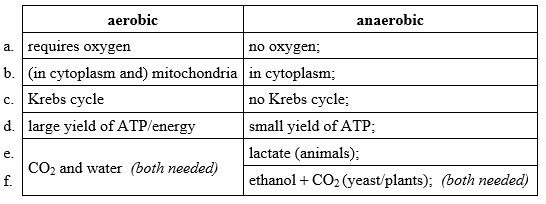
Award [1] for each contrasting characteristic.
Table format is not necessary for the marks.
c.
a. inspiration/inhalation brings air into lungs;
b. external intercostal muscles contract;
c. and move rib cage upwards and outwards;
d. diaphragm flattens/contracts;
e. increasing thoracic volume;
f. pressure decreases from atmospheric pressure so air rushes into lungs;
g. expiration/exhalation forces air out;
h. internal intercostal muscles contract / external intercostal muscles and diaphragm relax;
i. abdominal/abdomen wall muscles contract and push diaphragm upwards;
j. decreasing thoracic volume;
k. increasing pressure in lungs so air is forced out;
l. a concentration gradient between air sacs and blood needs to be maintained;
Question
a. Explain how materials are moved across membranes of cells by active transport.[2]
b. Explain the effects of pH on enzyme catalysed reactions.[3]
c.Distinguish between the process of anaerobic respiration in yeast and humans.[2]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a.transport against a concentration gradient / from low to high concentration; through protein pumps; uses energy/ATP;
b.enzymes have a pH optimum; active site works best at this $\mathrm{pH}$; activity decreases above and below the optimum; by interfering with $\mathrm{H}$-bonding/active site structure; denaturing by extremes of $\mathrm{pH}$ so enzyme activity/reaction stops;
c. yeast: pyruvate to ethanol and carbon dioxide; humans: pyruvate to lactic acid; Award [1 max] if products are appropriately linked to organisms without the mention of pyruvate.
Question
a. Distinguish between ventilation, gas exchange and cell respiration.[4]
b.Outline the process of aerobic respiration.[6]
c. Respiration and other processes in cells involve enzymes. Explain the factors that can affect enzymes.[8]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a.ventilation is moving air into and out of lungs/inhalation and exhalation;
involves (respiratory) muscle activity;
gas exchange involves movement of carbon dioxide and oxygen;
between alveoli and blood (in capillaries) / between blood (in capillaries) and cells;
cell respiration is the release of energy from organic molecules/glucose;
(aerobic) cell respiration occurs in mitochondria;
To award [4 max] responses must address ventilation, gas exchange and cell respiration.
b. during glycolysis glucose is partially oxidized in the cytoplasm;
(small amount/yield of) ATP produced;
(two) pyruvate formed by glycolysis;
pyruvate absorbed into/broken down in the mitochondrion;
requires oxygen;
carbon dioxide is produced;
water is produced;
large amount/yield of energy/ATP molecules (per glucose molecule);
C. collisions between enzyme/active site and substrate;
enzyme activity increases as temperature rises;
more frequent collisions at higher temperatures;
each enzyme has an optimum temperature / enzymes have optimal temperatures;
high temperatures (above optimum) denature enzymes;
each enzyme has an optimum pH / enzymes have optimal pHs;
increase or decrease from optimum $\mathrm{pH}$ decreases rate of reaction/activity;
extreme $\mathrm{pH}$ alters/denatures the tertiary/3D protein/enzyme structure;
increasing substrate concentration increases the rate of reaction;
higher substrate concentration increases chance of collision;
until plateau;
when all active sites are busy;
Accept clearly annotated graph.