Question
The feed conversion ratio (FCR) of grouper fish, Epinephelus coioides, was compared at two different fish densities in two types of tanks over a period of 10 weeks. The recirculation tank reused the same water, which was constantly purified. The flow-water tank had a continuous flow of clean water.
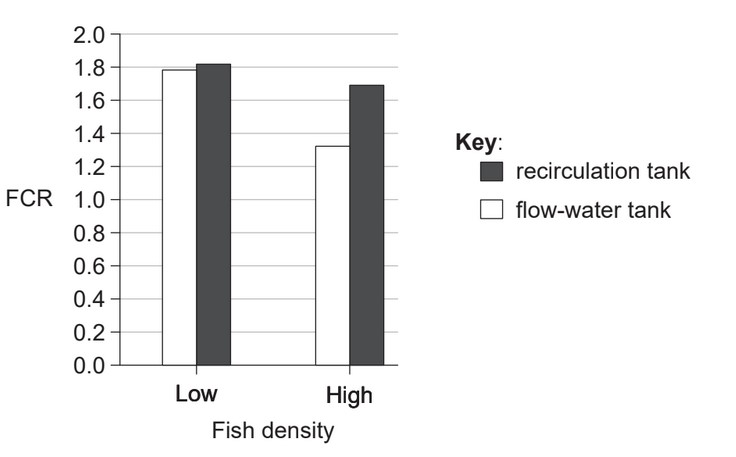
(a) State the effect of increasing fish density on feed conversion ratios.
(b) Evaluate the rearing of grouper fish as food for humans at high density using recirculation tanks rather than water-flow tanks.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) (FCRs) decrease;
(b) Pros:
a. less water is wasted (as it is purified and re-used);
b. less impure water is released to the environment;
Cons:
c. (FCR with recirculation tanks) has higher feed conversion ratio;
d. more food/energy needs to be supplied (to the fish)
OR
recirculation may cost more;
Question
Scientists examined the distribution of lichen species in Seoul, South Korea. The line graph shows the number of lichen species found on the bark of trees in green areas at different distances from the city centre.
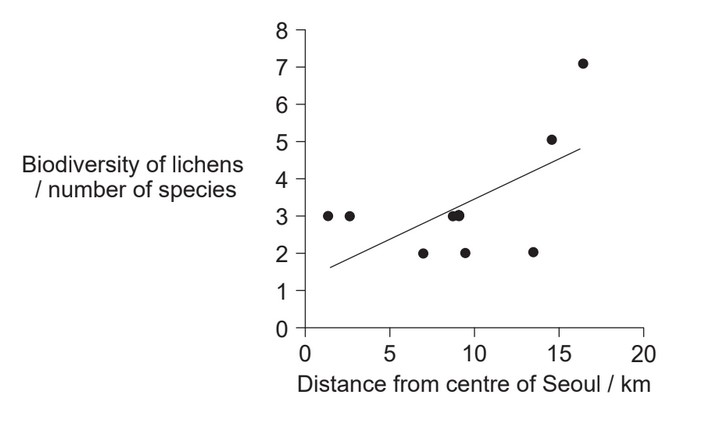
(a) Describe the trend in the distribution of lichen species.
(b) Explain how lichens can be used as indicator species.
(c) Describe a method that can be used to measure the diversity of herbaceous plants in one of the green areas at different distances from the main road.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) lichen species increase as distance from the city centre increases/positive
correlation/trend;
(b)
a. indicator species live in specific environmental conditions;
b. absence (of lichens) is an indicator or (air) pollution;
c. relative numbers of indicator species could be used to calculate biotic index;
d. biotic index can be used to monitor pollution levels over time;
e. can help evaluate antipollution actions/measures;
(c)
a. lay a line/belt transect line away from the road;
b. quadrat sampling can be used;
c. record the number of different species;
d. count the number of plants in each species;
e. calculate diversity using the (reciprocal) Simpson’s diversity index;
Question
In 1997 in South Africa, a decision was made to decrease the use of mosquito-killing pesticides due to their negative effect on the environment. Mosquitoes are known to be responsible for the spread of malaria. In 2001 the decision was reversed and the use of pesticides was increased. The graph shows the estimated numbers of people with malaria in each year.
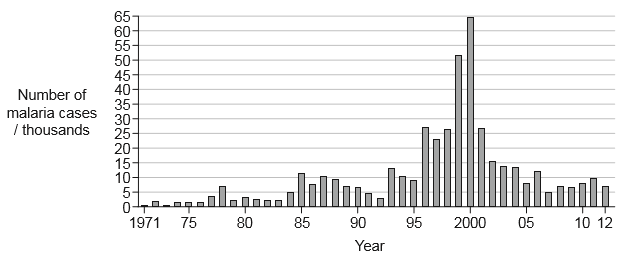
a. Outline the trend in the number of people with malaria during the period when the use of pesticides was decreased in South Africa. [1]
b. One pesticide used in killing mosquitoes was DDT. Considering its harmful effects, discuss whether the decision to reintroduce it was justified. [4]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
the number of people with malaria increase
a. choice has to be made between damage to environment or increase in malaria
b. DT may lead to biomagnification/bioaccumulation in food chains
OR
taken up by species in lower trophic levels becoming more concentrated at higher trophic levels
c. causes harm to consumers at end of food chain
OR
example «eg: thin egg shells of falcons»
d. DDT is shown to be effective in reducing malaria
e. possible partial solution to be selective in areas sprayed with DDT
f. may kill insects that are not pests
Question
Forest fires are very common in the Amazon forest. A study was performed to see the relationship between forest fragmentation, fire and management
a. Describe one method that could have been used to estimate the population size of a given tree in a forest after fire damage had occurred. [3]
b. Outline how the edge effect can affect diversity in forests. [3]
c. The number of plants in two fields of approximately the same size was counted.

Compare and contrast the richness and the evenness of the two fields. [2]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
ALTERNATIVE 1
a. transect through a given area
b. trees counted on transect
c. calculation of total population considering area
ALTERNATIVE 2
d. random sampling using quadrats
e. trees counted in quadrat
f. population calculated using area
ALTERNATIVE 3
g. GPS/Google Earth used to map individuals of a tree species
h. data base of data obtained
i. population density calculated using area
a. edge effect are the changes in community structures that occur at the boundary of two habitats
b. areas with small habitat fragments exhibit especially pronounced edge effects
c. edge species will always have a habitat
OR
edge biodiversity increases
d. if patches of forest are too small the non-edge species cannot find a habitat
e. «then» overall non-edge biodiversity is lower
a. same richness as they have the same number of species/total of individuals
b. field 1 has more evenness as more even distribution of numbers among the species
Accept correct use 2 of Simpson diversity index.