Question
Dolly the sheep was the first mammal to be cloned from an adult somatic cell.
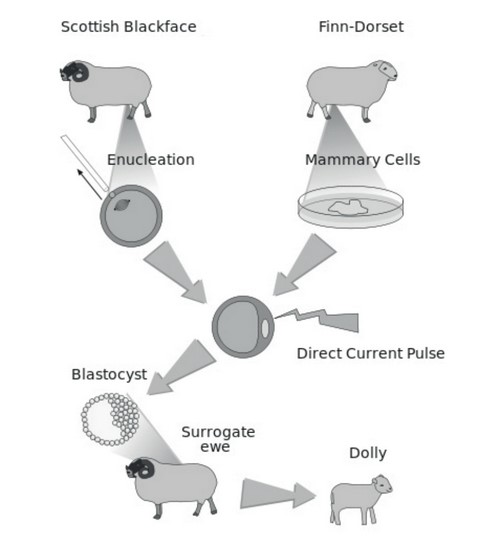
Which DNA did Dolly inherit?
A. Nuclear and mitochondrial DNA from the surrogate ewe
B. Nuclear and mitochondrial DNA from the Finn-Dorset
C. Mitochondrial DNA from the Scottish Blackface and nuclear DNA from the Finn-Dorset
D. Mitochondrial DNA from the Scottish Blackface and nuclear DNA from the surrogate ewe
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme : C
Question
a. Distinguish between the transfers of energy and inorganic nutrients in ecosystems. [2]
b. Outline the role of methanogenic archaeans in the movement of carbon in ecosystems. [2]
c. Describe how autotrophs absorb light energy [3]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
energy is lost (between trophic levels) / not all passed on / not reused / must be supplied;
nutrients are recycled/reused;
a. methane produced from organic matter;
b. in anaerobic conditions;
c. methane diffuses into atmosphere/accumulates in ground/soil;
d. oxidized/converted to carbon dioxide (in atmosphere);
a. light absorbed by (photosynthetic) pigments;
b. chlorophyll absorbs blue and red / drawing of absorption spectrum for chlorophyll;
c. photosystems are groups of pigment molecules/are light harvesting complexes;
d. photosystems are located in thylakoid membranes;
e. electrons excited/raised to higher energy level;
Question
More than 8 million different species are alive today but over the course of evolution, more than 4 billion may have existed.
a. Outline the criteria that should be used to assess whether a group of organisms is a species. [3]
b. Describe the changes that occur in gene pools during speciation. [5]
c. Discuss the process, including potential risks and benefits, of using bacteria to genetically modify plant crop species. [7]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. organisms can potentially interbreed;
b. to produce fertile offspring;
c. same sequence of genes (on chromosomes) / same types of chromosomes;
d. similar traits/phenotype/WTTE;
e. same chromosome number/karyotype;
a. gene pool is all genes/alleles in an (interbreeding) population;
b. gene pool splits/divides/separated during speciation;
c. due to reproductive isolation (of groups within a species);
d. temporal/behavioral/geographic isolation (can cause reproductive isolation);
e. divergence of gene pools;
f. allele frequencies change;
g. natural selection different (in the isolated groups so there is divergence);
h. different (random) mutations occur (in the isolated populations so there is divergence);
i. speciation has occurred when differences between populations prevent interbreeding;
Do not award both mpc and mpi for the same idea (reproductive isolation separating populations vs speciation due to interbreeding not being possible).
Process:
a. genetic modification by gene transfer between species;
b. gene/Bt gene/DNA segment transferred from bacterium to plant/crop;
c. gene/DNA codes for/responsible for desired protein/gene product;
d. bacteria have/produce plasmids / gene/DNA inserted into plasmid;
e. using restriction enzymes/endonucleases to cut DNA;
f. using DNA ligase to join DNA;
g. bacterium transfers (modified) plasmid to plant cell;
Benefits:
h. increase crop yields / more food produced / less land needed to grow food;
i. increase pest/disease resistance / use less pesticides/insecticides/fungicides;
j. improves crops to be more nutritious/increased vitamin content;
k. increased tolerance to saline soils/drought/high temperatures/low temperatures;
Risks:
l. GM organisms could spread to sites (where they will cause harm);
m. transferred gene could spread to other species / spread of herbicide resistance to weeds;
n. GM crops that produce pesticide could kill non-pest insects/monarch butterflies / insect pests could develop resistance to pesticides/insecticides/Bt toxin;