Question
DNA samples of a child, his mother and three males were studied in order to determine paternity. The diagram is a simplified version of the DNA profiles obtained in the study.

(a) State
(i) where the DNA of each individual could be taken from.
(ii) how the DNA is amplified.
(b) Deduce with a reason the identity of the father.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a)
(i) from blood sample/hair/cheek/saliva/semen;
(ii) PCR/polymerase chain reaction
OR
using Taq polymerase;
(b)
a. male 2;
b. each band in the child’s DNA must be the same as a band in either the mother
or the father
OR
any band in the child’s profile that is not present in the mother’s profile must be
present in the father’s;
Question
a. Describe the structure of the DNA molecule. [5]
b. Outline the role of three enzymes used in the replication of DNA. [3]
c. Insulin is produced in β cells of the pancreas and not in other cells of the human body. Explain how differentiation of cells and regulation of gene expression allow proteins such as insulin to be produced in only certain types of body cell. [7]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. two stranded/double helix ✔
b. antiparallel / strands running in opposite directions
OR
one strand organized 5’ to 3’ and the other 3’ to 5’ ✔
c. sugar-phosphate backbone ✔
d. each strand formed by chains of nucleotides ✔
e. each nucleotide is formed by a phosphate, a deoxyribose and a base / annotated diagram of a nucleotide clearly indicated as a nucleotide ✔
f. the bases are adenine, guanine, cytosine and thymine ✔
g. strands held together by hydrogen bonds (between complementary base pairs)
OR
A pairs with T and C pairs with G ✔
Both helix and two strands needed for mp a. Double helix is sufficient for the mark.
Points can be awarded to annotated diagrams.
For mp c, the explicit label sugar phosphate backbone is required.
To award mp d from a diagram, at least three pairs of nucleotides should be shown.
For mp e, the diagram would need to be labelled as a nucleotide.
For mp e, expect deoxyribose not just sugar.
The written names of the bases are required for mp f.
Do not penalize twice for mp f and g for using letters.
If they only ever use the symbols A,T,C and G they are ineligible for mp f. If however, they say A pairs with T and C pairs with G, then they would get mp g. If they wrote adenine pairs with thymine and cytosine pairs with guanine, then they would obtain both mp f and mp g.
a. helicase to separate/unwind DNA strands ✔
b. gyrase / toposiomerase to relax the tension as bacterial DNA is being uncoiled / prevent supercoiling ✔
c. primase to synthesise primers ✔
d. polymerase (I) removes primers and replaces with nucleotide ✔
e. polymerase (III) adds nucleotides (in a 5′ to 3′ direction) ✔
f. ligase joins (Okazaki) fragments together ✔
Accept the enzyme name without ‘DNA’ included; e.g. ‘DNA ligase’ or ‘ligase’ can both be accepted.
a. insulin production is determined by a gene ✔
b. gene for insulin (is found in all cells), but only activated in (β cells of) pancreas ✔
c. stem cells differentiate into specialized cells/(into pancreatic β) ✔
d. during differentiation some genes are turned on and others off ✔
e. insulin is a hormone that regulates the amount of glucose/sugar in blood ✔
f. pancreatic β cells have sensors that detect glucose level in blood ✔
g. an increase in glucose will increase transcription of mRNA of insulin ✔
h. the site of transcription of insulin is in the pancreatic β cells ✔
i. gene transcription is regulated by proteins that bind to specific base sequence in DNA/ enhancers/silencers/promoter proximal elements ✔
j. regulatory sequences/proteins are specific to the gene they regulate / insulin regulator proteins are only found in in the pancreatic β cells ✔
k. (DNA) methylation (usually) inhibits gene expression / (histone) acetylation promotes gene expression / tightness of coiling of DNA around histones affects gene expression ✔
Accept sugar as equivalent to glucose.
Question
Angiospermophyta are vascular flowering plants.
a. Describe the transport of organic compounds in vascular plants. [4]
b. The flowers of angiospermophyta are used for sexual reproduction. Outline three processes required for successful reproduction of angiospermophyta. [3]
c. Growth in living organisms includes replication of DNA. Explain DNA replication. [8]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. phloem transports organic compounds/sucrose
b. from sources/leaves/where produced to sinks/roots/where used
c. through sieve tubes/columns of cells with sieve plates/perforated end walls
d. loading of organic compounds/sucrose into /H+ ions out of phloem/sieve tubes by active transport/using ATP
e. high solute concentration causes water to enter by osmosis (at source)
f. high (hydrostatic) pressure causes flow (from source to sink)
g. companion cells help with loading / plasmodesmata provide a path between sieve tubes and companion cell
h. translocation/mass flow
a. meiosis / production of male and female gametes
b. pollination / transfer of pollen from anther to stigma
c. fertilization happens after pollination / fertilisation is joining of gametes
d. seed dispersal / spread of seeds to new locations
Reject fruit dispersal.
a. helicase unwinds the double helix
b. gyrase/topoisomerase relieves strains during uncoiling
c. helicase separates the two strands of DNA/breaks hydrogen bonds
Accept unzips here but not for mark point a.
d. each single strand acts as a template for a new strand / process is semi-conservative
e. DNA polymerase III can only add nucleotides to the end of an existing chain/to a primer
f. (DNA) primase adds RNA primer/short length of RNA nucleotides
g. DNA polymerase (III) adds nucleotides in a 5’ to 3’ direction
h. complementary base pairing / adenine to thymine and cytosine to guanine
Do not accept letters.
i. DNA polymerase (III) moves towards the replication fork on one strand and away from it on the other strand
j. continuous on the leading strand and discontinuous/fragments formed on the lagging strand
k. DNA polymerase I replaces primers/RNA with DNA
l. ligase joins the fragments together/seals the nicks
Question
a. The Hershey and Chase experiment supported DNA as the hereditary material. Describe the experiment. [3]
b. Some regions of DNA act as telomeres or produce tRNA. State one other function of DNA sequences that do not code for protein. [1]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. radioactive isotopes used to label viruses/bacteriophages/phages
b. proteins labelled with radioactive sulphur/35S and DNA labelled with radioactive
phosphorous/32P
c. phage infects bacterium
d. only viral DNA enters bacterium «viral coat/capsid/shell do not»
e. parts of phage remaining outside bacterial cell are removed
OR
bacteria are separated from phage parts «by centrifuge»
f. bacteria contain the labelled/radioactive DNA
a. regulate gene expression
b. act as promoter
c. role in chromosome pairing/crossing over/recombination
d. introns
Question
a.Draw a labelled diagram of the molecular structure of DNA including at least four nucleotides.[5]
b.A small DNA sample found at a crime scene can be used in an investigation. Describe the steps taken in the processing of this small sample of DNA.[6]
c. Discuss the relationship between one gene and one polypeptide.[7]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
The diagram must show four nucleotides shown with two on each side showing phosphate-sugar backbones and nitrogen base pairs bonded between them.
a.Award [1] for each of the following clearly drawn and correctly labelled.
phosphate – shown connected to deoxyribose;
deoxyribose – shown connected to phosphate;
(nitrogenous) bases – shown bonded to deoxyribose;
base pairs – shown with labels adenine/A bonded to thymine/T and cytosine/C bonded to guanine/G;
hydrogen bonds – shown connecting bases;
covalent bonds – shown connecting deoxyribose to phosphates;
nucleotide – clearly identified by the candidate;
Award [4 max] if diagram is not shown double stranded.
DNA samples are taken from crime scene, suspects and victims;
polymerase chain reaction/PCR used to increase the amount of DNA;
restriction enzymes used to cut DNA;
electrophoresis involves electric field/placing sample between electrodes;
used to separate DNA fragments according to size;
creating DNA profiles/unique patterns of bands;
comparison is made between the patterns;
criminals/victims can be identified in this way;
DNA is (quite) stable / DNA can be processed long after the crime;
c.
DNA codes for a specific sequence of amino acids/polypeptide;
the DNA code for one polypeptide is a gene;
DNA is transcribed into mRNA;
mRNA moves to a ribosome;
where mRNA is translated into a polypeptide;
originally it was thought that one gene always codes for one polypeptide;
some genes do not code for a polypeptide;
some genes code for transfer RNA/tRNA/ribosomal RNA/rRNA;
some sections of DNA code for regulators that are not polypeptides;
antibody production does not follow this pattern (of simple transcription-translation); (allow other examples)
change in the gene/mutation will affect the primary structure of the polypeptide;
Question
The electron micrographs show mitosis in a cell at an early stage and an intermediate stage.
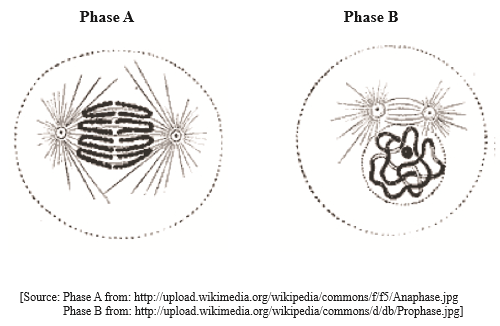
State the name of each phase shown, recording whether each phase has taken place at an early or intermediate stage of mitosis.
Phase A: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .occurs at an. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . stage
Phase B: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .occurs at an. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . stage[2]
a (i). Outline the events occurring in phase A.[2]
b. State what results when there is an uncontrolled division of cells in living organisms.[1]
c. DNA in chromosomes undergoes replication before mitosis. Outline how complementary base pairing is important in this process.[2]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a (i).
phase A: anaphase (occurs at an) intermediate (stage); (both needed)
phase B: prophase (occurs at an) early (stage); (both needed)
a (ii).
centromeres split/break;
(sister) chromatids/chromosomes separate;
dragged/pulled/movement to separate poles;
by shortening of spindle microtubules;
Do not allow events other than those in anaphase
b.
tumours / cancer
c.
conservation of the base sequence of DNA;
adenine pairs with thymine and cytosine pairs with guanine; (do not accept initials only)
both (daughter) cells/DNA strands produced have identical genetic information;
Question
Thrombophilia is a human genetic condition where the blood has an increased tendency to clot. The condition is caused by a single base substitution mutation in DNA. If a person is homozygous for the gene, they are at greater risk for developing a blood clot than an individual who is heterozygous. The pedigree chart shows the inheritance of thrombophilia in a family.
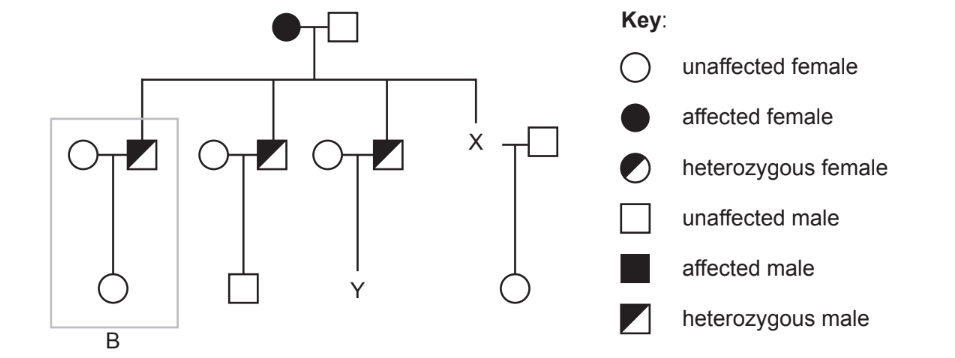
(a) Draw the symbol for individual X on the diagram. [1]
(b) Calculate the probability of male Y having an allele for the disorder. [1]
(c) Explain how the information in the box labelled B indicates that the gene is not sex-linked. [2]
(d) Explain how a single base substitution mutation in DNA can cause a change to a protein. [2]
▶️Answer/Explanation
a
![]()
b 50%/ 0.5/ 1/2;
c a. if it was sex-linked it would be on the x chromosome;
b. there cannot be a heterozygous male if the trait is sex-linked
c. males would pass the allele to their daughter;
d. daughter is not shown as heterozygous so it is not sex linked;
d a. sequence of DNA bases determines the amino acid sequence of a protein;
b. changing one base (on the DNA) can cause the triplet /mRNA to code for a different amino acid;
c. changing one base (on the DNA) causes a different protein to be made (during translation);