Question
Multicellular organisms benefit from cell specialization and division of labour.
(a) Outline the processes occurring during interphase in the cell cycle.[4]
(b) Describe what occurs in a neuron when an action potential is propagated along the axon. [4]
(c) Explain how cells in the bloodstream cause a specific immune response.[7]
Answer/Explanation
a a. growth/increase in cell size;
b. division of mitochondria/chloroplasts/production of more organelles/number of organelles doubled;
c. replication of DNA/amount of DNA is doubled;
d. transcription of genes/production of mRNA;
e. protein synthesis;
f. cell respiration/production of ATP;
b a. sodium ions/Na+ enter/diffuse in;
b. depolarization/membrane potential/voltage changes from negative to positive;
c. potassium channels open AND potassium ions/K+ exit/diffuse out;
d. repolarization/membrane potential/voltage changes back from positive to negative;
e. local current due to diffusion of sodium ions along the neuron;
f. (local currents) cause next sodium channels to open/next part of axon to depolarize;
g. opening of sodium channels triggered when threshold potential/-50mV reached;
c a. (specific immune response is) production of antibodies in response to a particular pathogen;
b. antibody is specific to/binds to a specific antigen;
c. macrophages/phagocytes engulf/present antigens from pathogens/viruses/bacteria;
d. T lymphocytes activated by antigens/antigen presentation/antigens presented by macrophage;
e. (activated) T lymphocytes activate B lymphocytes;
f. only B lymphocytes that produce antibodies against the antigen/pathogen are activated;
g. (activated) B lymphocytes clone/divide by mitosis to form plasma cells;
h. plasma cells then secrete (large quantity) of an antibody/secrete antibodies of same type;
i. some B lymphocytes/plasma cells form memory cells;
j. memory cells give long lasting immunity/faster response to a disease/pathogen;
Question
(a) The onion (Allium cepa) root cells shown in the micrograph are in different stages of mitosis.
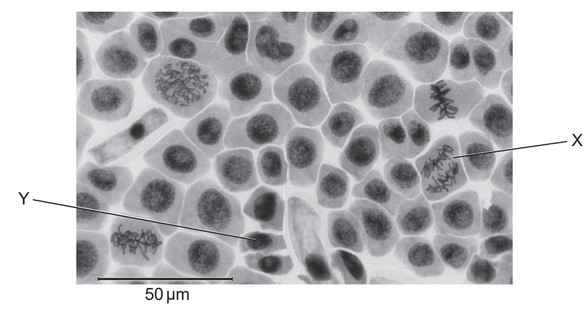
(i) Identify, with a reason, the stage shown at X.
(ii) Calculate the length of the entire cell labelled Y, showing your working.
(iii) State the role of cyclins in the cell cycle.
(b) (i) Distinguish between the structure of chromosomes in prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
(ii) Explain Cairns’s technique to measure the length of the DNA molecule.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
a) i. a. anaphase;
b. the (replicated) chromosomes/chromatids are separating/moving to opposite poles of the
cell;
ii. 50 μm = 27/28/29 mm, Y = 8/9/10 mm
OR
50 x 9 /27
OR
16.7 μm (accept answers in the range of 14.8 μm to 17.2 μm)
iii. a. (group of regulatory proteins that) control/regulate the cell cycle;
b. activate cyclin-dependent kinases (which control cell cycle processes);
b) i. a. prokaryotes (usually) have one chromosome while eukaryotes have numerous
chromosomes;
b. prokaryotes have a circular chromosome while eukaryotes have linear ones;
c. eukaryotes’ chromosomes are associated with histones/proteins but
prokaryotes/Eubacteria have naked DNA vs eukaryote DNA associated to
proteins/histones;
ii. a. Cairns grew prokaryotes/E. coli in radioactive thymidine/thymine/thymine containing
tritium;
b. contents of cell put on photographic film/surface (for several weeks) / used
autoradiography and electron microscopes;
c. measured the length of the DNA molecule and photographed it / produced image of DNA;
d. could show the new strands were all labelled with thymidine/thymine;