Question
The micrograph shows some onion (Allium cepa) cells undergoing mitosis.
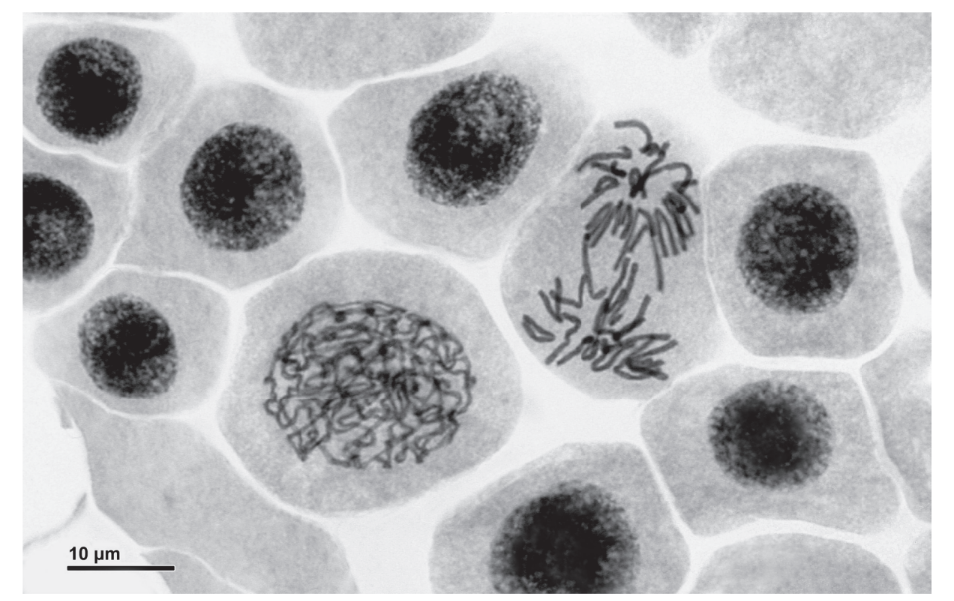
What is the mitotic index, taking into account all visible nuclei?
A. 0.1
B. 0.2
C. 0.4
D. 0.6
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
The mitotic index is a measure of the fraction of cells undergoing mitosis. It is calculated by dividing the total cells undergoing mitosis by the total cells visible
Mitotic index = number of cells with visible chromosomes ÷ total number of cells
Mitotic index = (prophase + metaphase + anaphase + telophase) ÷ total number of cell
Here 10 nuclei are visible and 2 of those are dividing, so mitotic index as per as given data will be (2 ÷10 = 0.2) or 20%.
Question
A tissue sample was examined under the microscope in order to determine a mitotic index. The number of cells in each stage of the cell cycle was determined and the data were entered into a table.
Stage of life cycle | Interphase | Prophase | Metaphase | Anaphase | Telophase | Total |
Number of cells | 120 | 20 | 10 | 8 | 2 | 160 |
What is the mitotic index?
A. 0.125
B. 0.25
C. 0.75
D. 1.00
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans B
The mitotic index is a measure of the fraction of cells undergoing mitosis. It is calculated by dividing the total cells undergoing mitosis by the total cells visible
Mitotic index = number of cells with visible chromosomes ÷ total number of cells
Mitotic index = (prophase + metaphase + anaphase + telophase) ÷ total number of cells
Here in this question, Mitotic index = [(20+10+8+2)÷(120)] = 0.25 or 25%
Which diagram(s) represent(s) processes used in asexual reproduction?
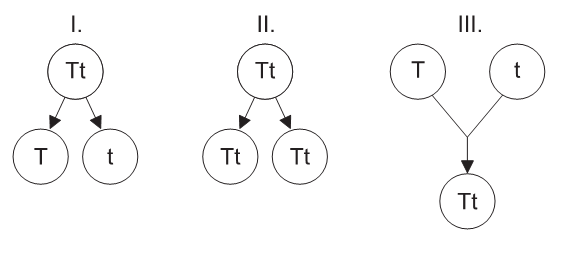
A. I only
B. I and II only
C. II only
D. I, II and III
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that does not involve the fusion of gametes or change in the number of chromosomes. The offspring that arise by asexual reproduction from either unicellular or multicellular organisms inherit the full set of genes of their single parent and thus the newly created individual is genetically and physically similar to the parent or an exact clone of the parent. When prokaryotes and eukaryotes reproduce asexually, they transfer a nearly identical copy of their genetic material to their offspring through vertical gene transfer. Although asexual reproduction produces more offspring more quickly, any benefits of diversity among those offspring are lost.
Here in option B, gene pool of parent and offspring in identical.
What occurs during meiosis but not mitosis?
A. Spindles are formed from microtubules.
B. Chromosome number is conserved.
C. Homologous chromosomes pair up.
D. Centromeres split.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
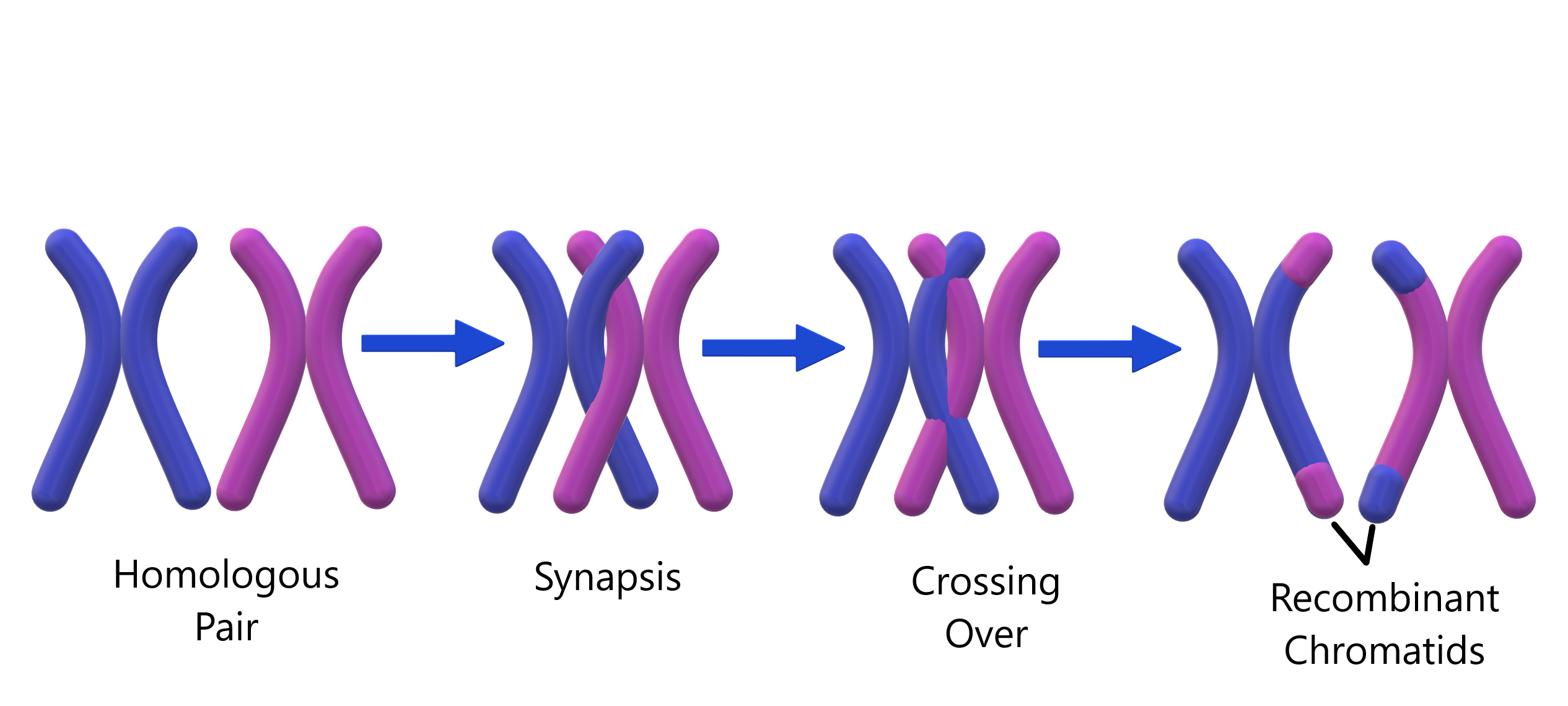
Homologous chromosomes are present in both mitosis and meiosis, but they don’t form pairs in mitosis. Rather they will form homologous chromosome pairs during meiosis, which allows for crossing over to occur. Crossing over is a cellular process that happens during meiosis when chromosomes of the same type are lined up. This can happen between multiple chromosomes or different segments of the same chromosome. Crossing over is important because it ensures genetic variability and contributes to genetic reassortment which are the key factors to genetic diversity among offspring that would otherwise lead to lot of abnormalities, genetic disorders.
In which stage of mitosis is the cell labelled X?

A. Anaphase
B. Interphase
C. Metaphase
D. Prophase
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A
The correct answer to the question “In which stage of mitosis is the cell labelled X?” is A, Anaphase. During anaphase, the sister chromatids separate and move towards opposite poles of the cell. In the image, the chromosomes are clearly separated and moving towards opposite poles, indicating that the cell is in anaphase.