Very soon after fertilization, parental epigenetic methylation is reversed in the DNA.
Later, tissue-specific epigenetic modifications are made to the embryonic DNA. The graph follows the degree of methylation from different sources during embryonic development.
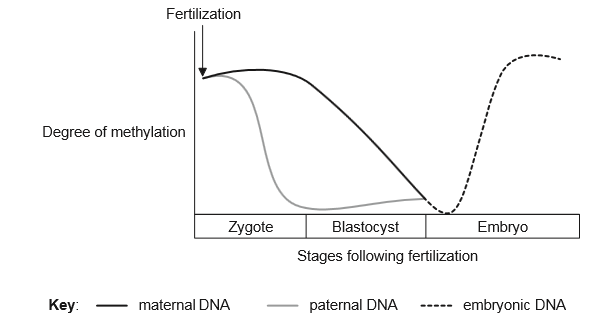
According to the graph, what are the changes in DNA methylation during embryonic development?
A. Only the paternal DNA becomes demethylated.
B. The maternal DNA becomes demethylated first.
C. The methylation patterns of the parents’ DNA are erased before fertilization.
D. The methylation patterns of both parents are erased after fertilization.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
What is a feature of transcription?
A. Both strands of a DNA molecule act as a template for mRNA.
B. Nucleoside triphosphates become nucleotides by losing three phosphates.
C. RNA polymerase binds to the promoter region.
D. The sense strand acts as a template for mRNA.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
What happens during transcription in eukaryotes?
A. Polysomes move.
B. Nucleosomes are phosphorylated.
C. RNA polymerase separates DNA strands.
D. Okazaki fragments are produced.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C