Question
The image shows human red blood cells.

a. Outline what will happen to human red blood cells if transferred to distilled water. [1]
b. Stem cells can be used to treat Stargardt’s disease. State one other condition treated using stem cells. [1]
c. Explain the propagation of nerve impulses along the membrane of a neuron. [3]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
cells absorb water by osmosis and swell/increase in volume
OR
cells burst/lyse;
leukemia/other diseases of the hematopoietic system / skin burns;
a. depolarization of part of axon/membrane triggers/causes depolarization of next part;
b. local currents;
c. diffusion of sodium ions between depolarized part and next/polarized part (of axon);
d. resting potential reduced/polarization of membrane becomes less /change from -70 to -50mV;
e. sodium channels open when -50mV/threshold potential reached;
f. entry of sodium ions causes depolarization;
g. saltatory conduction in myelinated neurons/axons;
Allow answers in an annotated diagram
Question
(a) Outline four types of membrane transport, including their use of energy. [4]
(b) Draw the structure of a dipeptide. [3]
(c) ADH (antidiuretic hormone) is a peptide hormone that is produced in the hypothalamus. Explain its action in the human body. [8]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
a
a. simple diffusion is passive movement of molecules/ions along a concentration gradient
b. facilitated diffusion is passive movement of molecules/ions along a concentration gradient through a protein channel «without use of energy»
c. osmosis is the passage of water through a membrane from lower solute concentration to higher
d. active transport is movement of molecules/ions against the concentration gradient «through membrane pumps» with the use of ATP/energy
e. endocytosis is the infolding of membrane/formation of vesicles to bring molecules into cell with use of energy OR exocytosis is the infolding of membrane/formation of vesicles to release molecules from cell with use of energy mpa, mpb and mpc require reference to concentration. OWTTE Active transport requires mention of the use of energy.
f. chemiosmosis occurs when protons diffuse through ATP synthase «in membrane» to produce ATP
b
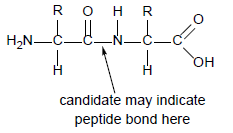
a. two amino acids, one with NH2/NH3 + end and one with COOH/COO– end
b. peptide bond between C=0 and N—H correctly drawn
c. «chiral» C with H and R group on each amino acid
d. peptide bond labelled/clearly indicated between C terminal of one amino acid and N terminal of the second amino acid
c
a. ADH plays a role in osmoregulation/regulating blood solute concentration
b. acts on the collecting ducts of the kidney
c. acts in «late» distal convoluted tubule
d. hypothalamus detects plasma/blood osmolarity/solute concentration
e. if plasma/blood is too concentrated/hypertonic, «posterior» pituitary
releases ADH OWTTE for all mp.
f. ADH stimulates insertion of aquaporins/water channels / increases permeability of collecting duct
g. water moves «through aquaporins» by osmosis into the medulla/blood
h. urine becomes more concentrated/smaller volume
i. negative feedback occurs
j. if blood is hypotonic no ADH is released OWTTE for negative feedback acceptable.
k. water is not reabsorbed from the collecting ducts/permeability of the collecting duct decreases
l. urine becomes more dilute/less concentrated / higher volume