Question
The drawing shows a flower of red valerian, Centranthus ruber.
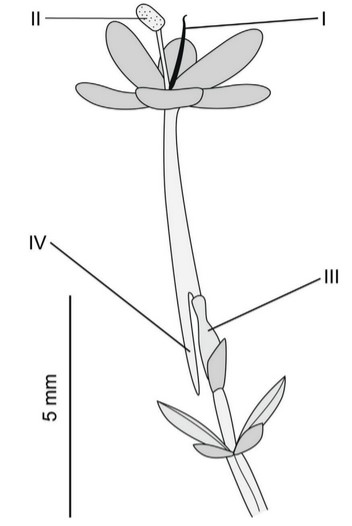
(a) State the name and function of structures I and II.
Structure I name and function: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Structure II name and function: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
(b) Structure III is the ovary. Outline the processes that occur in the ovary.
(c) Structure IV contains a gland that secretes a sugary liquid. Suggest a benefit to the plant of secreting this liquid.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a)
a. I is the stigma which receives the pollen/where pollen lands/is captured (during pollination);
b. II is the anther and produces/contains/releases pollen;
(b)
a. female gamete/ovule is produced/meiosis to produce ovules/ovule develops;
b. Fertilisation occurs
OR
fusion/union of male and female gametes/nuclei;
c. development of seed (from fertilised ovule);
d. development of fruit (from the whole ovary);
(c)
a. attracts an insect/animal/which pollinates the flower;
b. attracts a pollinator;
Question
Feedback mechanisms are used in living organisms both to promote and respond to change.
(a) Outline the role of ADH in osmoregulation.
(b) Explain the regulation of metabolic pathways by end-product inhibition.
(c) Describe the hormone feedback mechanisms that help to prepare a woman’s body for
pregnancy, sustain the pregnancy and then give birth.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a)
a. ADH (secreted by pituitary) if body/blood is dehydrated/hypertonic/has high solute concentration;
b. more aquaporins / aquaporins open (in collecting duct);
c. collecting duct more permeable to water/reabsorbs more water (from filtrate/urine);
d. water reabsorbed by osmosis/water reabsorbed because medulla is hypertonic;
e. (reabsorbed) water passes (from filtrate) to blood / blood solute concentration reduced;
f. less water lost in urine / smaller volume of (more concentrated) urine;
g. negative feedback / less/no ADH secreted when blood solute concentration returns to normal;
(b)
a. final product in pathway acts as an inhibitor/blocks (reaction)/slows (reaction);
b. first/early/earlier enzyme (in pathway is inhibited);
c. non-competitive / binds at allosteric site / causes active site to change;
d. production of end-product reduced/paused when there is an excess;
e. isoleucine inhibits enzyme using threonine as substrate at start of pathway to isoleucine;
f. negative feedback / production restarts when end-product used up/concentration drops;
(c) Preparing the woman’s body for pregnancy
a. FSH stimulates estrogen secretion (by the developing follicle);
b. estrogen increases FSH receptors so boosting estrogen production/so causing positive feedback;
c. estrogen stimulates repair/thickening of the endometrium/uterus lining;
d. high levels of estrogen stimulate LH production/inhibit FSH secretion (negative feedback);
e. LH (surge/peak) stimulates ovulation; Sustaining pregnancy
f. LH stimulates the development of corpus luteum / corpus luteum secretes progesterone;
g. progesterone inhibits FSH/LH secretion (negative feedback);
h. progesterone maintains lining of uterus/endometrium (for pregnancy/implant of embryo);
i. progesterone inhibits uterine contractions;
j. HCG (secreted by embryo) stimulates maintenance of corpus luteum; Childbirth
k. oxytocin stimulates uterine/myometrial contractions which stimulate oxytocin secretion;
l. positive feedback (mechanism used to stimulate childbirth);
Question
Outline the process of spermatogenesis in humans.
Explain the structure and function of the placenta during pregnancy.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
production of sperm/spermatozoa in the testes/seminiferous tubules;
first stage of sperm production requires divisions by mitosis;
cells then undergo a period of growth;
future sperm cells then undergo two meiotic divisions;
cells then differentiate to form sperm cells;
nourished by Sertoli cells number becomes haploid / chromosome number halved / 46 to 23 chromosomes;
embryonic/disc shaped structure that nourishes the developing embryo;
starts forming at implantation of the blastocyst/embryo;
embryonic tissue invades/grows into the uterine wall;
fetal capillaries exchange material with maternal blood/lacunae;
allows exchange of food/oxygen/antibodies from mother’s blood to fetus;
allows exchange of carbon dioxide/waste products from fetal blood to mother;
connected to the embryo/fetus by an umbilical cord;
placenta takes over hormonal role of ovary;
indication of time this happens / at approximately 12 weeks;
secretes estrogen/progesterone;
hormone secretion maintains pregnancy;
expelled from uterus after childbirth;
Question
The drawing shows part of a Thunbergia grandiflora plant. It has been widely cultivated as an ornamental garden plant.

The drawing shows a section through a T. grandiflora flower, which contains a honeybee (Apis mellifera).

a. Using the drawing, deduce which plant phylum T. grandiflora belongs to, giving one visible recognition feature of this phylum. [1]
b.i. Identify the structure labelled X. [1]
b.ii. Outline the relationship the bee has with the T. grandiflora flower. [2]
c. After fertilization, seeds of T. grandiflora form in a small pod. If you were provided with Petri dishes, absorbent cotton balls and seeds, suggest how one variable affecting germination of these seeds could be investigated.
 [3]
[3]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Angiospermophyta/Angiosperms
AND
flowers «as reproductive organs» ✔
Both required.
ovule ✔
a. mutualistic relationship
OR
bee gets nectar/pollen «as food» AND flower is pollinated/fertilized ✔ Both needed.
b. when bee enters, pollen from anther sticks to it ✔
c. pollen is picked up by stigma «of same or other flower» ✔
a. different values for the named independent variable ✔ Name of the independent variable must be included, eg temperature.
b. large / equal number of seeds in each Petri dish ✔
c. control of other variables «than seeds» ✔
d. mentions how germination will be determined eg appearance of radicle.
OR
how germination rate/percentage will be measured ✔ eg number germinated over time/in a set time. Do not accept measurement of growth of stem/number of leaves.
e. includes a control giving seeds all factors needed ✔
Possible factors include water, oxygen, temperature, pH, light, salt concentration