Question
The reaction that produces urea in liver cells is shown.
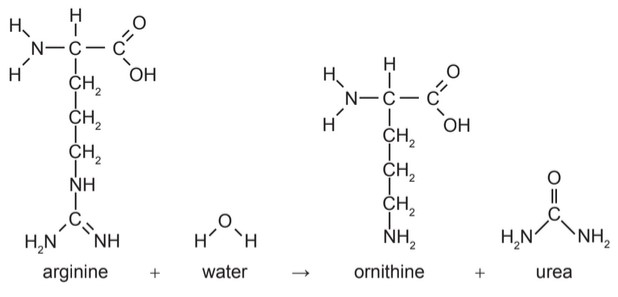
(a) Arginine and ornithine are in the same group of biochemicals. Identify this group.
(b) This reaction forms part of a metabolic cycle. Outline one feature of a metabolic cycle that distinguishes it from a chain.
(c) Predict what effect arginase has on the activation energy of this reaction.
(d) The concentration of urea in blood plasma is typically about 30mg per 100ml. In urine it can be as high as 1800mg per 100ml. Explain how this increase in concentration is achieved.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) amino acids;
(b)
a. initial molecule/substrate/intermediates are regenerated;
b. products become substrates/reactants;
(c) reduced/lowered (activation energy);
(d)
a. urea is toxic/ a (excretory) waste product removed from the body/ blood
(plasma) by the kidneys/in the urine (to be excreted in the urine);
b. urea filtered out from blood in glomerulus/Bowman’s capsule;
c. water reabsorbed from filtrate (by osmosis);
d. in proximal convoluted tubule/descending loop of Henle/collecting duct;
e. loop of Henle maintains hypertonic conditions in the medulla;
f. little/no urea reabsorbed from filtrate;
Question
The diagram shows the structure of a nephron.
Label I and II.
Outline the function of III.
Estimate the content of glomerular filtrate and urine of a healthy person by completing the following table.

Explain the role of the medulla and the collecting duct of the kidney in the maintenance of the water balance in blood.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
I: glomerulus;
II: (descending limb of) loop of Henle;
(both needed)
III: selective re-absorption of glucose/minerals/amino acids/water/ useful substances;
absorption by active transport/using ATP of glucose/minerals/ amino acids/useful substances;

Award [1] for each correct row.
collecting duct has water channels/aquaporins/is permeable to water;
high solute concentration of medulla / medulla is hypertonic;
reabsorption of water allows excretion of concentrated urine (antidiuresis);
secretion of ADH/vasopressin increases permeability of collecting duct to water / vice versa;
Question
Outline what is meant by homeostasis.
Describe how body temperature is maintained in humans.
Explain the processes occurring in the kidney that contribute to osmoregulation.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
maintaining (stable) internal environment/conditions;
within (narrow) limits;
example (e.g. body temperature / blood pH / blood glucose / water / CO2 concentration);
levels of these variables are monitored (internally);
negative feedback mechanisms / OWTTE; (reject if positive feedback included)
involves hormonal / nervous control;
maintained close to 36.7/37°C/98.6°F ;
heat is transferred/distributed in body by blood;
hypothalamus contains thermoreceptors;
hypothalamus monitors temperature/sends message to effectors/causes response;
(vaso) dilation of skin arterioles warms skin/cools body;
(vaso) constriction of skin arterioles retains body heat;
skin/sweat glands produce sweat to cool the body when overheated;
removal of heat through evaporation of sweat;
shivering generates heat / increased metabolism / hair erection to retain heat;
example of behavioural change to warm/cool the body to thermoregulate;
osmoregulation is maintenance of water balance of blood/tissues;
loop of Henle creates hypertonic conditions in the medulla;
water reabsorbed as filtrate passes through collecting duct;
hypothalamus monitors/controls water balance/content of blood;
controls secretion of ADH by (posterior) pituitary gland;
ADH is released when blood too concentrated/too little water/hypertonic;
ADH makes the collecting duct more permeable to water;
due to more aquaporins;
more water reabsorbed (in response to ADH);
less water in urine/urine more concentrated/urine hypertonic;
no/less ADH when blood too dilute/too much water/hypotonic;
collecting duct less permeable/less water reabsorption/more water in urine;