Question
Between 1900 and 2020 the Earth’s average surface air temperature increased by about 1°C.
Temperature affects many biological processes.
(a) Explain how temperature affects enzymes.
(b) Outline the role of the thyroid gland in helping to control body temperature in humans.
(c) Describe how human activities have caused average surface air temperatures on Earth to increase.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a)
a. speed of reaction/catalysis increases as temperature rises;
b. faster molecular motion so more collisions between substrate and active site;
c. denaturation at higher temperatures;
d. (denaturation causes) shape/conformation/structure of enzyme/active site
altered/damaged;
e. an enzyme works fastest at its optimum temperature;
f. inactivation at lower temperatures (due to very few collisions);
g. sketch graph to model the effect of temperature on enzyme activity;
(b)
a. secretes thyroxin;
b. thyroxin causes the metabolic rate to rise;
c. heat released by metabolism;
d. thyroxin increases generation of body heat;
e. thyroxin stimulates shivering/stimulates brown adipose tissue (to release heat);
f. more thyroxin secreted if body temperature too low/converse;
(c)
a. release of carbon dioxide;
b. combustion of fossil fuels produces carbon dioxide;
c. forest fires (caused by humans) produce carbon dioxide;
d. deforestation reduces carbon dioxide uptake by photosynthesis;
e. release of methane;
f. from cattle/sheep/ruminant digestive systems / other verified source of
anthropogenic methane;
g. greenhouse effect / carbon dioxide/methane is a greenhouse gas;
h. carbon dioxide/methane allow short wave radiation in sunlight to pass through
the atmosphere;
i. longer wave/infra-red radiation emitted by the warmed Earth’s surface;
j. carbon dioxide/methane absorbs/reflects back longer wave/infra-red radiation;
Question
a. Outline how greenhouse gases interact with radiation and contribute to global warming. [4]
b. Outline how plants make use of the different wavelengths of light.[4]
c. Explain how organic compounds are transported within plants. [7]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas
b. methane/nitrogen oxide/water vapour is a greenhouse gas
c. sunlight/light/(solar) radiation passes through the atmosphere (to reach the Earth’s surface)
d. CO2 in atmosphere/greenhouse gases absorb/trap/reflect back some radiation/heat (emitted by the Earth’s surface)
e. CO2 in atmosphere/greenhouse gases allow short wave radiation to pass (through atmosphere) but absorb long wave/infra-red
f. solar radiation/sunlight is (mostly) short wave
g. radiation/heat emitted by the Earth is long wave/infra-red
Allow answers presented in a clearly annotated diagram.
a. light used in photosynthesis/light-dependent reactions/photolysis/photosystems/photophosphorylation/excitation of electrons/switch to flowering
b. chlorophyll absorbs red AND blue light (more)
c. chlorophyll/leaf/plant reflects/does not absorb/does not use green light
d. absorption spectrum of chlorophyll has peaks in the red and blue/sketch graph to show this
e. action spectrum shows which wavelengths plants use in photosynthesis/sketch graph of action spectrum showing peaks in the blue and red
f. accessory/other (named) photosynthetic pigments absorb different wavelengths/colours
g. violet is the shortest wavelength and red the longest
h. red light and far red/infra-red absorbed to measure length of light/dark periods
a. transported in/translocated in/loaded into phloem
b. in sieve tubes
c. by mass flow
d. from sources to sinks
e. from leaves/other example of source to roots/other example of sink
f. loading (of sugars/organic compounds) by active transport
g. cause high concentration of solutes (in phloem/sieve tubes)
h. water uptake (in phloem/sieve tubes) by osmosis/water diffuses into phloem
i. rise in (hydrostatic) pressure at source (in phloem)
j. creates a (hydrostatic) pressure gradient/higher pressure in source than sink
k. flow can be in either direction/bidirectional
Question
Describe the structure and function of starch in plants.
Outline the production of carbohydrates in photosynthesis.
Discuss the processes in the carbon cycle that affect concentrations of carbon dioxide and methane in the atmosphere and the consequences for climate change.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Structure:
a. «starch» is a polysaccharide/is composed of glucose molecules
b. contains amylose which is a linear/helical molecule
c. contains amylopectin which is a branched molecule
Function:
d. storage of glucose/energy in plants
e. storage form that does not draw water
a. light is absorbed by chlorophyll
OR
chlorophyll absorbs more red and blue light
b. «absorbed» light energy is converted to chemical energy
c. some of the energy is used for production of ATP
d. water molecules are split/photolysis
e. produces oxygen «as waste product»/hydrogen/NADPH
f. plants absorb/fix CO2 «from air or water»
g. ATP/energy is needed to produce carbohydrates/starch
a. CO2 is produced from respiration in organisms/combustion of biomass/fossil fuels
b. CH4 is produced by anaerobic respiration of biomass/«methanogenic» bacteria
c. CH4 is oxidized to CO2 and water
d. CO2 is converted into carbohydrates/organic compounds by autotrophs/producers/photosynthesis
e. CO2 can be converted to calcium carbonate/fossilized into limestone
f. «partially» decomposed organic matter/biomass can be converted into peat/coal/oil/gas/fossil fuels
g. CO2 and CH4 are both greenhouse gases/increase greenhouse effect
h. both absorb long-wave radiation from the earth and retain the heat in the atmosphere
i. increased CO2 concentrations in the atmosphere correlate with increased combustion of fossil fuels
j. rising average global temperatures correlate with more greenhouse gases in the atmosphere
k. cattle production/rice paddy/defrosting of tundra increase CH4 in the atmosphere
OR
increasing CO2 leads to acidification of marine/aquatic environments
l. the global temperature increase influences/disrupts climate patterns
OWTTE
Question
The diagram shows the greenhouse effect.
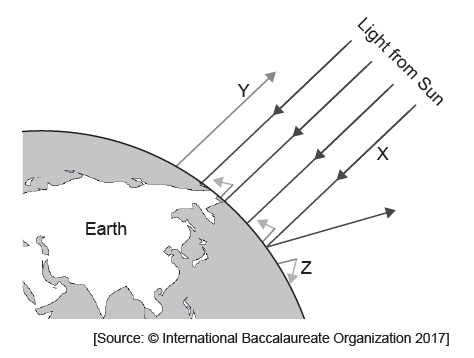
State the type of wavelength of the radiation labelled X and Y.
X:
Y:
Outline reasons for the change occurring at Z.
The short-tailed albatross (Phoebastria albatrus) nests and breeds on remote low-lying coral islands in the Pacific Ocean. Predict how global warming may threaten the survival of such an ocean bird.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
X: short-/ultraviolet/UV/visible/EMR/electromagnetic radiation
Y: long-/infrared/IR
a. greenhouse gases present (at Z)
b. greenhouse gases «CO2, methane, nitrous oxide, water vapour» absorb long-wavelengths/infrared
OR
long wavelengths/infrared waves blocked from leaving the atmosphere
c. (long-wavelengths/infrared absorbed and) reradiated/re-emitted (heat Earth)
a. rising ocean levels/more extreme weather «due to global warming» may destroy breeding/nesting sites
OR
rising sea level may put island underwater causing young birds/chicks to drown
b. populations may not find/adapt to new colony sites
c. warming seas may affect the food supply