IBDP Online Test Series By iitianacademy
Comprehensive Test Preparatory package targeted towards IBDP
Question
The diagrams illustrate changes in synapse density of the cerebral cortex from newborn to adult.
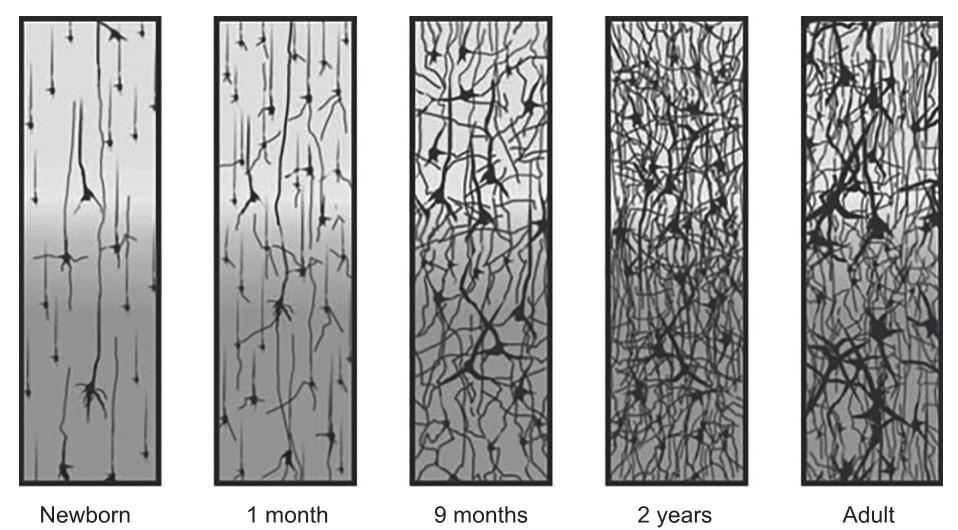
[Source: THE POSTNATAL DEVELOPMENT OF THE HUMAN CEREBRAL CORTEX, VOLUMES IVIII, by Jesse LeRoy Conel, Cambridge, Mass.: Harvard University Press, Copyright © 1939, 1941, 1947, 1951, 1955, 1959, 1963, 1967
by the President and Fellows of Harvard College. Copyright © renewed 1967, 1969, 1975, 1979, 1983, 1987, 1991.]
Explain the processes illustrated by the diagrams.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. at birth neurons are mainly unconnected
b. after birth «up to 2 years» neurons start to make synapses/connections with other neurons
OR
up to 2 years the number of synapses/connections increases
c. «increase in synapses» occurs rapidly due to learning/new experiences
d. each neuron can make multiple synapses
e. brain makes many more connections than are required
f. «after 2 years/in adults» neural pruning causes the loss of unused neurons/synapses/connections
Do not accept more neurons are made
[Max 4 Marks]
Question
The images show the early stages and completed outcome of the process of neurulation.
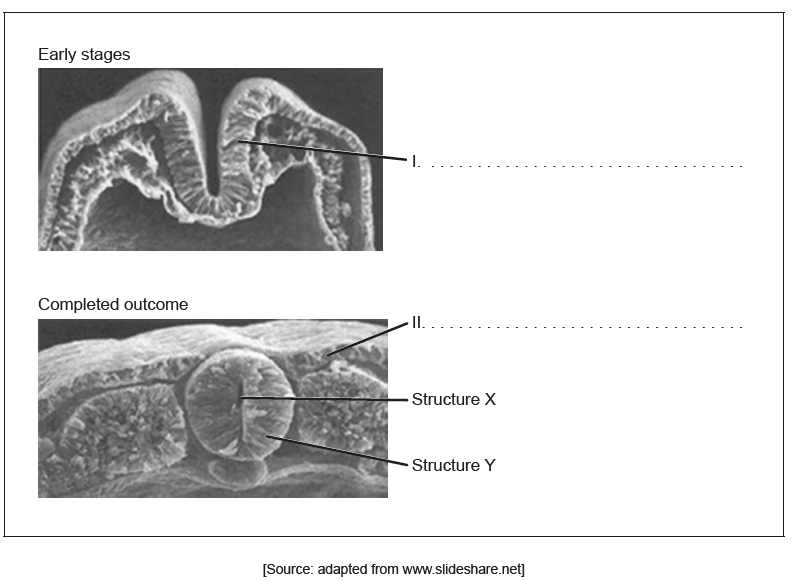
Label the parts I and II on the images.
Structure Y will eventually elongate to form two structures. State the names of these two structures.
1.
2.
State the condition that arises if the closure of structure X is incomplete during embryonic development.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
I: neural groove/plate/fold
II: ectoderm
brain
spinal cord
spina bifida
Question
The photomicrographs below show time lapse images of a migrating neuron in the grey matter of the cerebrum of an embryo. The time lapse images were taken at one hour intervals. The cell body is the rounded bright area towards the rear of the migrating neuron.
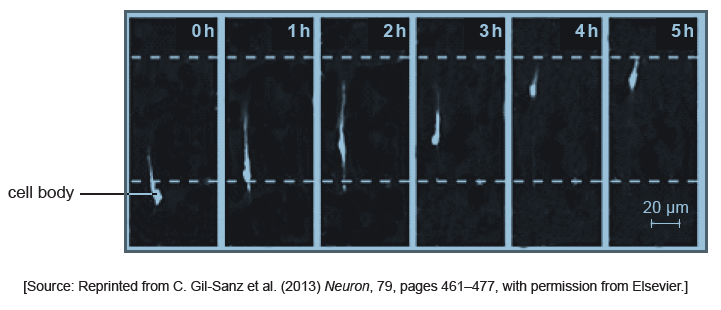
Calculate the rate of movement of the neuron cell body between 0 and 5 h. Working should be shown, giving the units.
Suggest a reason for the migration of neurons in the embryonic nervous system.
Outline neural pruning.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. cell moves 25−28mm
OR
71−93μm
b. speed range is 71−93 μm in 5 hours
c. answer in the range 14−19 μm/h or μm h−1
a. «neural migration» positions cell types from different origins into specific locations
b. «neural migration» allows formation of connections/synapses
c. allows for differentiation of cell types/types of neuron
a. neural pruning is the removal of synapses/dendrites/ neural connections
b. caused by lack of use
c. it occurs during brain development/between birth and end of puberty
d. allows new neural connections/makes nervous system more efficient /plasticity
Question
The diagram shows the early development of the nervous system in embryonic chordates.

Outline the process taking place in the diagram.
State what occurs to structure X immediately following its formation.
Outline how spina bifida could occur during embryonic development.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. infolding of the ectoderm /neural plate
“Ectoderm” is essential for the mark.
b. formation of the neural tube
OR
neurulation
“Neural tube” or “neurulation” is essential for the mark.
elongation / forms a tube
a. neural tube/structure X does not close properly
b. folic acid/folacin/folate/vitamin B9 deficiency
c. may be due to mutation / genetic condition
Question
The diagram shows an advanced stage during neurulation in humans or chicks.
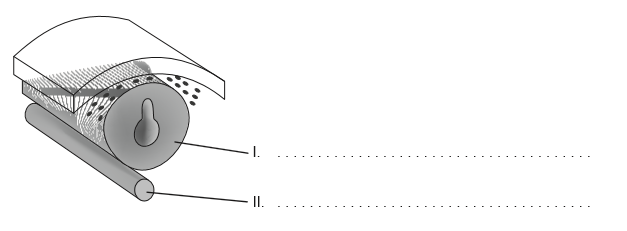
Label structures I and II
State the process by which neurons are initially produced in the embryo.
Outline the plasticity of the nervous system.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
I: neural tube
II: notochord
Differentiation/neurogenesis «in the neural tube»
Plasticity allows the nervous system to adapt «structurally»
OR
plasticity allows cortical remapping/new connections
Neurons «axons» grow in response to stimulation/experience
Unused neurons die/are lost through pruning
Accept synapses in place of neurons
