IB Biology HL (HIGHER level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 11.1 Antibody production and vaccination
Topic 11 Weightage : 8%
All Questions for Topic 11.1 – Self versus Non-Self, Pathogenesis, Clonal Selection, Antibodies, Immunity, Allergens, Vaccination, Monoclonal Antibodies, Lymphatic System, Immune Pathways, Types of Immunity, Immune Disorders
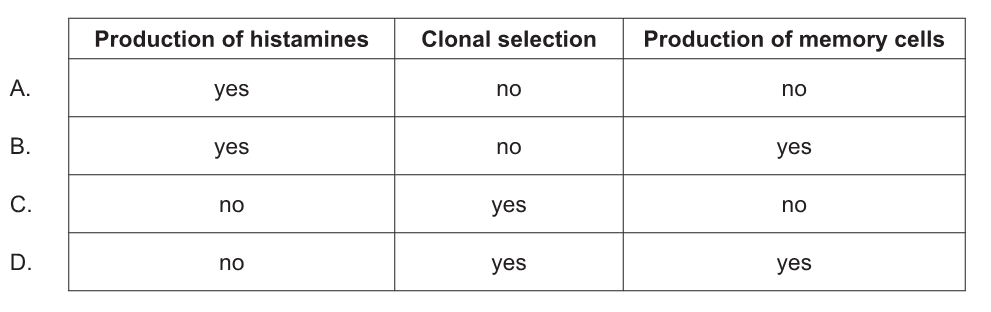
What forms the basis of immunity after vaccination?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
Clonal selection and the production of memory cells form the basis of immunity after vaccination because they allow the immune system to respond more quickly and effectively to a pathogen upon subsequent exposure. When a vaccine is administered, it contains a weakened or dead version of the pathogen or a piece of it, which triggers the immune system to produce a response. This response includes the activation and proliferation of B cells and T cells that are specific to the pathogen. During clonal selection, only the B cells and T cells that are specific to the pathogen are selected for further proliferation and differentiation. This leads to the production of a large number of identical cells, or clones, that are all specific to the pathogen. Some of these cells differentiate into plasma cells, which produce and secrete antibodies that can recognize and neutralize the pathogen. Other cells differentiate into memory cells, which can survive for a long time and quickly respond to a subsequent exposure to the pathogen.
Therefore, the production of memory cells and clonal selection form the basis of immunity after vaccination because they allow the immune system to produce a more rapid and effective response to a pathogen upon subsequent exposure.
A secondary immune response occurs when an antigen is encountered on a second occasion, due to exposure to a pathogen that previously caused infection. Which property of some viruses explains the lack of a secondary immune response?
A. Viruses fail to induce a primary response.
B. Viruses can have a high mutation rate.
C. B cells do not interact with viruses.
D. Antibodies cannot interact with viruses.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
The correct answer is B, viruses can have a high mutation rate.
Some viruses have a high mutation rate, which allows them to quickly evolve and change their surface proteins, making it difficult for the immune system to recognize and respond to them. As a result, the immune system may not be able to mount a secondary immune response to the virus upon subsequent exposure.
This is why some viruses, such as the influenza virus, require annual vaccination to keep up with the changing strains.
What is required for a skeletal muscle to exert force?
A. Extensor and flexor muscles
B. Synovial joints
C. Attachment to bones
D. Ligaments
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
The correct answer is C, attachment to bones.
Skeletal muscles are attached to bones via tendons, which allows them to exert force and generate movement. When a skeletal muscle contracts, it pulls on the bone to which it is attached, causing movement at the joint.
Extensor and flexor muscles are types of skeletal muscles that work together to produce movement at a joint, but they are not required for a skeletal muscle to exert force. Synovial joints and ligaments are also important for movement, but they are not directly involved in the force production of skeletal muscles.
What is directly responsible for allergic symptoms, including a runny nose or itchy eyes?
A. Pathogens
B. Histamine
C. T-lymphocytes
D. Antigens
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
The correct answer is B, histamine.
Histamine is a chemical mediator that is released by mast cells and basophils in response to an allergen. It is directly responsible for many allergic symptoms, including a runny nose, itchy eyes, and hives.
When histamine is released, it causes an increase in blood flow and permeability of blood vessels, leading to swelling and inflammation. It also stimulates nerve endings, causing itching and pain.
Pathogens, T-lymphocytes, and antigens are all involved in the immune response, but they are not directly responsible for allergic symptoms.
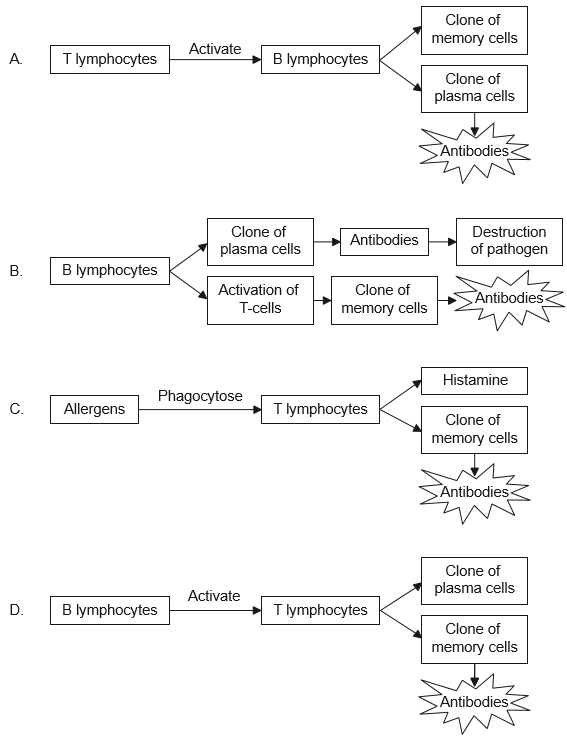
Which sequence of events leads to the production of antibodies?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A
The correct answer for the question “Which sequence of events leads to the production of antibodies?” is A.
The correct sequence of events leading to the production of antibodies is:
1. Antigen presentation: Antigen-presenting cells (APCs) such as dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells present the antigen to T helper cells (Th cells).
2. Activation of T helper cells: The Th cells recognize the antigen presented by the APCs and become activated.
3. T helper cells activate B cells: The activated Th cells stimulate B cells to become activated.
4. Clonal expansion: The activated B cells undergo clonal expansion, producing a large number of identical B cells that can recognize the antigen.
5. Differentiation: Some of the B cells differentiate into plasma cells, which produce and secrete antibodies that can bind to the antigen.
6. Antibody production: The antibodies produced by the plasma cells can bind to the antigen and neutralize it, marking it for destruction by other immune cells.
This sequence of events is known as the humoral immune response and is a key component of the adaptive immune system’s response to pathogens.
What first happens to a B lymphocyte when it becomes activated?
A. It divides by mitosis producing a clone of cells.
B. It begins transcription and produces antigens.
C. It differentiates into memory cells.
D. It produces antibodies using its extensive rough endoplasmic reticulum (rER).
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A
When a B lymphocyte becomes activated, it first divides by mitosis producing a clone of cells.
This process is known as clonal expansion and is a key step in the immune response. The activated B cells undergo clonal expansion to produce a large number of identical B cells that can recognize the antigen. These B cells then differentiate into plasma cells, which produce and secrete antibodies that can bind to the antigen.
Option A is therefore the correct answer.
