IB Biology HL (HIGHER level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 3.1 Genes
Topic 3 Weightage : 5%
All Questions for Topic 3.1 –Genes and Loci, Alleles, Mutations, Genome, Gene Comparisons, Types of Mutations, Sickle Cell versus Malaria, Genome Structure, Pseudogenes
Question
Which genotype would be normally found in a gamete?
Rr
RS
rStt
TUt
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
An allele is a specific variation of a gene, or specific segment of DNA. Different alleles produce slightly different proteins, which function in different ways. In dominant/recessive relationships, the recessive allele produces a non-functional protein. The dominant allele produces a functioning protein. Therefore, if RS is a recessive allele, it will only show its effect if the individual has two copies of the allele (also known as being homozygous).
Note: Due to the information in the question is insufficient so we cant predict so far than the given explaination.
What is the effect of dominant alleles?
I. They mask the effect of recessive alleles.
II. They become more frequent than recessive alleles in a population.
III. They have a joint effect with recessive alleles when characteristics are co-dominant.
A. I only
B. I and II only
C. I and III only
D. I, II and III
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
We say that a dominant allele masks the effect of a recessive allele because the dominant allele produces a phenotype that is visible even when only one copy of it is present, while the recessive allele produces a phenotype that is hidden unless two copies of it are present. For example, in pea plants, the allele for round seeds is dominant over the allele for wrinkled seeds. A plant with one copy of R and one copy of r (Rr) will have round seeds, because the R allele masks the effect of the r allele. Only a plant with two copies of r (rr) will have wrinkled seeds.
What is the effect of dominant alleles?
I. They mask the effect of recessive alleles.
II. They become more frequent than recessive alleles in a population.
III. They have a joint effect with recessive alleles when characteristics are co-dominant.
A. I only
B. I and II only
C. I and III only
D. I, II and III
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Different versions of a gene are called alleles. Alleles are described as either dominant or recessive depending on their associated traits¹. A dominant allele is one that shows its effect even if the individual only has one copy of the allele (also known as being heterozygous). A recessive allele is one that only shows its effect if the individual has two copies of the allele (also known as being homozygous).
For example, the allele for brown eyes is dominant, therefore you only need one copy of the ‘brown eye’ allele to have brown eyes. The allele for blue eyes is recessive, therefore to have blue eyes you need to have two copies of the ‘blue eye’ allele.
Dominance is not inherent to an allele or its traits (phenotype). It is a strictly relative effect between two alleles of a given gene of any function. A dominant allele always suppresses the recessive allele. A dominant allele or factor can form complete polypeptide or enzyme for expressing its effects.
Question
What is a feature of the human genome?
Plasmids
Messenger RNA
Transfer RNA
Mitochondrial DNA
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Mitochondrial DNA is the circular chromosome found inside the cellular organelles called mitochondria. Mitochondria are the site of the cell’s energy production and other metabolic functions¹. Mitochondrial DNA is not transmitted through nuclear DNA, which contains most of the genetic information of a cell². In humans, as in most multicellular organisms, mitochondrial DNA is inherited only from the mother’s ovum². Human mitochondrial DNA was the first significant part of the human genome to be sequenced. This sequencing revealed that the human mitochondrial DNA includes 16,569 base pairs and encodes 13 proteins. The human mitochondrial genome is the entirety of hereditary information contained in human mitochondria.
Question
What is a difference between two alleles of a gene?
A. Their positions on homologous chromosomes
B. Their amino acid sequence
C. The characteristic they influence
D. Their base sequence
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
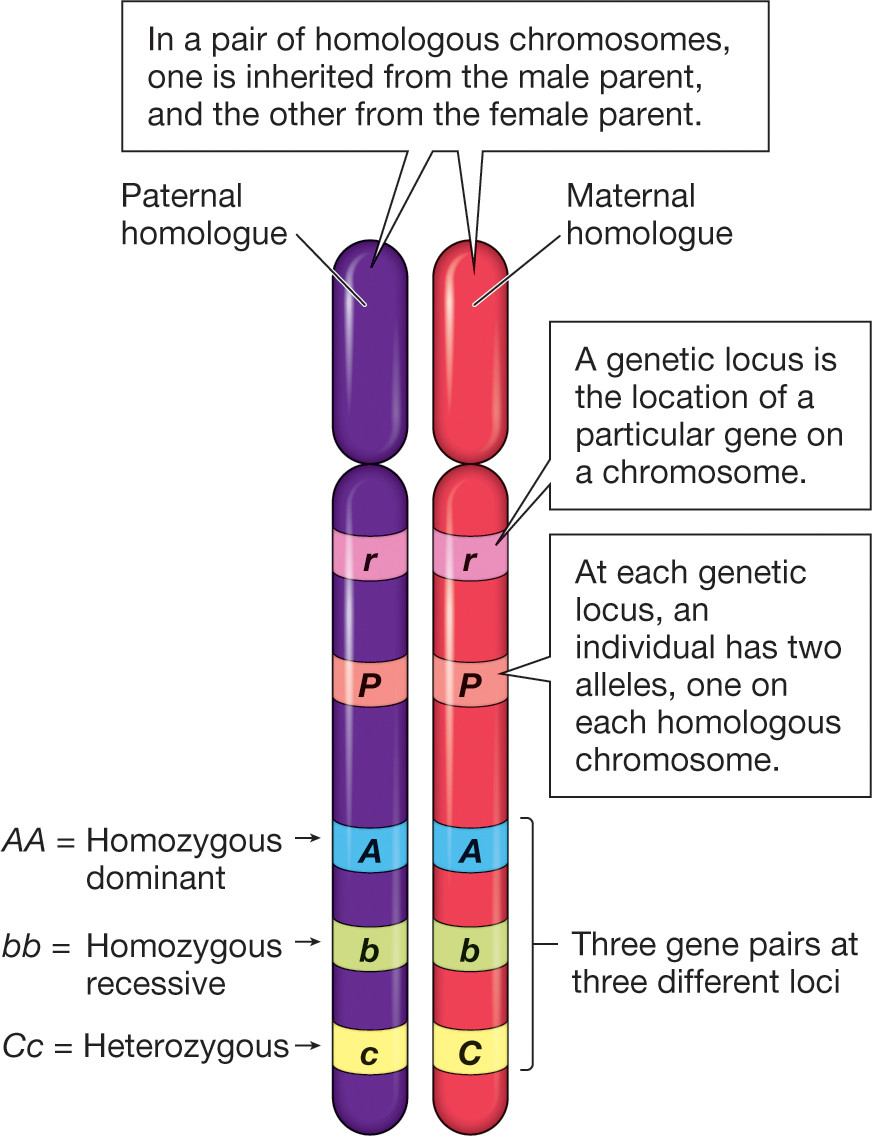
A gene is a unit of hereditary information that codes for a certain trait. An allele is a variant form of a gene that may have different effects on the trait. For example, eye color is a trait that is determined by a gene, but there are different alleles of that gene that can produce blue, brown, green or other eye colors.
Each organism has two alleles for every gene, one on each chromosome. If the two alleles are the same (e.g., both coding for blue eyes), they are called homozygotes. If they are different (e.g., one for blue eyes and one for brown eyes), they are called heterozygotes. Some alleles are dominant, meaning they override the effects of other alleles, and some are recessive, meaning they are masked by dominant alleles. Some alleles are codominant, meaning they both contribute to the trait equally.
