IB Biology HL (HIGHER level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 5.3 Classification of biodiversity
Topic 5 Weightage : 5%
All Questions for Topic 5.3 –Binomial System, Domains of Life, Hierarchy of Taxa, Classification, Plant Phyla, Animal Phyla, Vertebrate Classes, Dichotomous Keys, Past Nomenclatures, Archaea vs Eubacteria, Animal Complexity, Virus Classification
Question
A dichotomous key can be used to distinguish four types of plant. Which of the plants could be a bryophyte?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
An animal shows radial symmetry, has only one opening leading to a digestive cavity and is soft without a skeleton. To which phylum does this animal belong?
A. Platyhelmintha
B. Annelida
C. Mollusca
D. Cnidaria
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
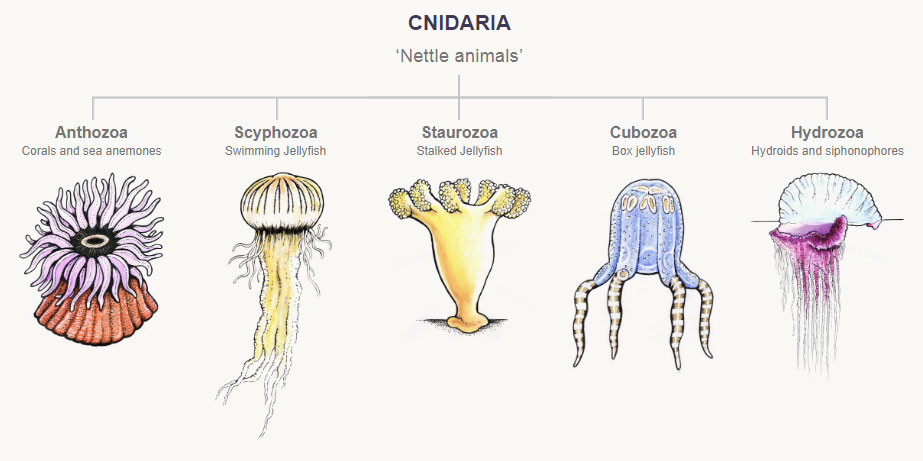
The animal with radial symmetry, only one opening leading to a digestive cavity, and is soft without a skeleton belongs to the phylum Cnidaria. Cnidarians are a group of aquatic animals that include jellyfish, corals, and sea anemones. They have radial symmetry, meaning that their bodies are organized around a central axis, and they have tentacles armed with stinging cells called cnidocytes. The single opening in their body leads to a central cavity that serves as both a mouth and an anus. Cnidarians do not have a true digestive system or a skeleton, and they rely on water flow to circulate nutrients and oxygen throughout their bodies.
The scientific name of the great egret has recently been changed from Casmerodius albus to Ardea alba.

What is a possible reason for the reclassification of egrets?
A. Allopatric speciation
B. Discovery of different ancestry
C. A change in the mating behaviours
D. Change in habitat and geographic range
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
The scientific name of the great egret was changed from Casmerodius albus to Ardea alba because of the discovery of different ancestry. The reclassification was based on a more accurate and objective measure of evolutionary relationships, using DNA sequences rather than morphological characteristics. DNA sequences provide a more precise way to determine how closely related different organisms are to one another. The DNA analysis showed that the great egret was more closely related to other species in the genus Ardea than to those in the genus Casmerodius. As a result, the great egret was reclassified into the genus Ardea. This reclassification reflects a better understanding of the evolutionary relationships among different bird species and allows for more accurate and consistent classification of organisms.
To which domain does Carcharodon carcharias, a shark, belong?
A. Eukaryote
B. Consumer
C. Fish
D. Chordata
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A
Carcharodon carcharias, the great white shark, belongs to the domain Eukarya. The domain Eukarya includes all organisms with eukaryotic cells, which are cells that have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. This domain includes all animals, plants, fungi, and protists. Sharks, including the great white shark, are part of the animal kingdom, which is one of the four major groups within the domain Eukarya.
How can molluscs and platyhelminthes be distinguished?
A. Molluscs are unsegmented but platyhelminthes are segmented.
B. Molluscs have a mouth and an anus but platyhelminthes do not.
C. Molluscs are smooth but platyhelminthes have bristles.
D. Molluscs remain attached to rock but platyhelminthes move around in water.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
Mollusks and Platyhelminthes can be distinguished by several characteristics. Mollusks have a mouth and an anus because they have a complete digestive system with two openings, one for ingestion and one for elimination. Platyhelminthes, on the other hand, have a simple digestive system with only one opening that serves as both the mouth and anus, which means that they do not have a separate anus.
The photograph shows an animal of the species Eisenia fetida.

Which phylum does it belong to?
A. Cnidaria
B. Platyhelminthes
C. Annelida
D. Arthropoda
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
Eisenia fetida belongs to the phylum Annelida. Annelids are characterized by their segmented bodies, which are divided into repeating units called metameres. Eisenia fetida, commonly known as the red wiggler or red worm, is a type of earthworm that has a segmented body and a well-developed digestive system. Annelids also have a closed circulatory system, a ventral nerve cord, and a hydrostatic skeleton.
Question
The foxglove, Digitalis purpurea, was once classified in the figwort family. The figwort family has been reclassified and is now much smaller.

Why were species such as the foxglove moved into other families?
A. The appearance was too dissimilar.
B. The plants are found in different locations.
C. The genera were different.
D. The DNA sequences indicated different ancestry.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
The foxglove, Digitalis purpurea, was once classified in the figwort family based on its morphological characteristics. However, when DNA sequences were analyzed, they indicated a different ancestry for the foxglove, which suggested that it should be placed in a different family. This is because DNA sequences provide a more accurate and objective measure of evolutionary relationships than morphological characteristics alone. By comparing the DNA sequences of different organisms, scientists can determine how closely related they are and use this information to classify them into different taxonomic groups. In the case of the foxglove, the DNA sequences suggested that it was more closely related to other plants in a different family, and this led to its reclassification.
