IB Biology HL (HIGHER level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 5.4 Cladistics
Topic 5 Weightage : 5%
All Questions for Topic 5.4 – Clades, Cladograms, Molecular Evidence, Structural Evidence, Clade Reclassification, In Situ Hybridisation, Mitochondrial DNA
Question
The cladogram shows some of the groups in the three domains.
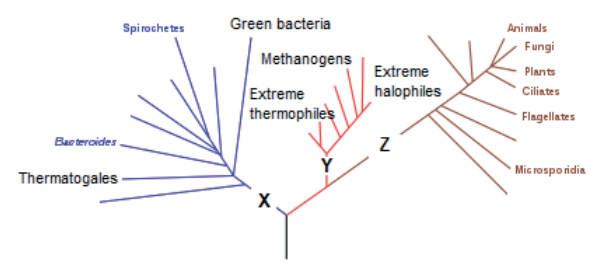
What domains do X, Y and Z represent?
Domains | |||
| X | Y | Z |
A | prokaryote | archaea | eukaryote |
B | archaea | eubacteria | prokaryote |
C | eubacteria | archaea | eukaryote |
D | eubacteria | prokaryote | eukaryote |
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
X, thermatogales and spirochetes are both groups of bacteria that are classified under the domain Bacteria. They are both considered part of the larger group Eubacteria, which encompasses all bacteria except for the Archaea. Eubacteria are characterized by their cell walls, which contain peptidoglycan, and by their ability to carry out aerobic or anaerobic respiration. While Thermatogales and spirochetes have different shapes and structures, they share many of these fundamental characteristics that define the Eubacteria.
Y, Methanogens, extreme halophiles, and thermophiles are all groups of microorganisms that are classified under the domain Archaea. Archaea are distinct from bacteria in that they have unique genetic and biochemical characteristics. For example, the cell walls of Archaea lack peptidoglycan, which is a defining feature of bacterial cell walls. Methanogens are a group of Archaea that produce methane as a byproduct of their metabolism. Extreme halophiles are a group of Archaea that are adapted to living in extremely salty environments. Thermophiles are a group of Archaea that thrive in high-temperature environments. These three groups of Archaea are classified together because they share many genetic and biochemical characteristics that distinguish them from both bacteria and eukaryotes.
Z, animals, fungi, plants, ciliates, and flagellates are all groups of organisms that are classified under the domain Eukarya. Eukaryotes are characterized by their cells, which contain a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. This distinguishes them from prokaryotes, such as bacteria, which lack these structures. Animals, fungi, and plants are three of the main kingdoms of eukaryotes, and they are characterized by their different modes of nutrition and reproduction. Ciliates and flagellates are two groups of protists, which are eukaryotic organisms that are not classified as animals, fungi, or plants. Ciliates are characterized by the presence of cilia, which are hair-like structures that they use for movement and feeding. Flagellates are characterized by the presence of one or more flagella, which are whip-like structures that they use for movement. Despite their differences, all of these groups of eukaryotes share many fundamental genetic and biochemical characteristics that distinguish them from prokaryotes.
Question
What information can be deduced from the sequence of nodes in a cladogram?
The geological period in which the species in the clade diverged from their common ancestor
The probable sequence of divergence among the species in the clade
The number of characteristics the species have in common
The number of mutations that have occurred since the species shared a common ancestor
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
The sequence of nodes in a cladogram represents the order in which the species diverged from a common ancestor. The species that diverged first will be located closer to the root of the tree, while the species that diverged more recently will be located closer to the tips of the branches. Therefore, by examining the sequence of nodes in a cladogram, we can infer the probable sequence of divergence among the species in the clade.
Question
What is a recognition feature for both of the plant phyla indicated?
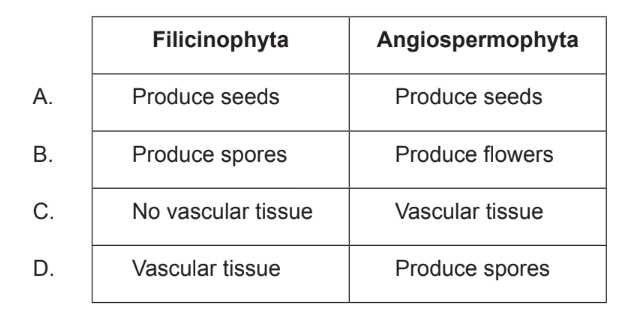
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Angiosperms produce flowers, which are reproductive structures that contain both male and female parts. The male parts produce pollen, which is transferred to the female parts to fertilize the ovules and produce seeds. Filicinophytes, on the other hand, produce spores instead of flowers. These spores are produced in structures called sporangia, which are located on the undersides of the leaves. The spores are released into the air and can grow into new plants under the right conditions.
