Question
The diagram shows the structure of a cell in the pancreas that secretes digestive enzymes.
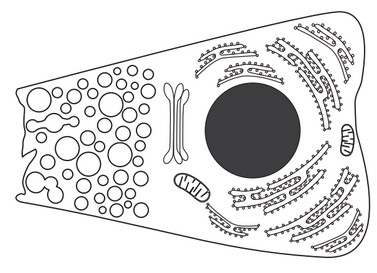
(a) Explain how the pancreas cell carries out its function, with reference to three organelles visible in the diagram.
(b) The pancreas secretes lipase into the small intestine.
(i) Outline the function of lipase.
(ii) State one other enzyme secreted by the pancreas.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a)
a. genes for digestive enzymes are transcribed in the nucleus;
b. rough ER/ribosomes produces/synthesizes enzymes/proteins;
c. mitochondrion produces ATP to provide energy for protein/enzyme production;
d. Golgi apparatus/body processes enzymes/proteins
OR
Golgi apparatus/body packages enzymes into vesicles;
e. vesicles carry enzymes to (plasma) membrane
OR
vesicles secrete enzymes by exocytosis;
(b)
(i) digestion/hydrolysis/break down of lipids/fats/triglycerides (into fatty acids and
glycerol);
(ii) amylase / endopeptidase / trypsin / trypsinogen / protease;
Question
Pastry cream or confectioners’ custard is made with a combination of milk (rich in casein and lactose), egg yolks, sugar, starch and a flavouring such as vanilla.
(a) Describe the structure of starch. [5]
(b) Explain how amino acids in casein could reach the liver, starting from the moment when the person takes a bite of pastry cream pie. [7]
(c) Congenital lactase deficiency is a type of lactose intolerance that occurs in infants. It is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern. Calculate the chance of congenital lactose intolerance in a child whose parents are both carriers for the disorder, showing fully how you reached your answer. [3]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
a
a. starch is a carbohydrate
b. starch is formed by carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
c. it is a polymer/chain/polysaccharide
d. formed from monosaccharides/simple sugars/glucose
e. linked together by condensation/dehydration
f. consists of amylose and amylopectin
g. amylose is a long chain/unbranched
h. amylopectin is branched
b
a. food is mechanically/physically digested in the mouth through mastication/chewing
b. mixed with saliva (to form the bolus) in mouth
c. moved through esophagus/peristalsis
d. proteins digested in the stomach (pepsin)
e. pancreas secretes enzymes into lumen of small intestine OR (endo)peptidases/trypsin) are secreted by pancreas
f. enzymes digest macromolecules to monomers OR endopeptidases digest polypeptides to peptides/amino acids
g. villi of small intestine absorb amino acids
h. amino acids carried to blood capillaries
i. blood (capillaries) carry amino acids to (hepatic portal) vein/blood vessel going to liver
j. amino acids absorbed by active transport/protein pumps in the villi
c
a. gametes of both parents shown as a capital and small letter (eg L and l)
b. possible F1 genotypes
c. 25% lactose intolerant, 50% carriers, 25% lactose tolerant OR 75% tolerant and 25% intolerant OR child has 25%/1:4/ chances of inheritance of intolerance
Question
Humans ingest food which provides energy and nutrients to carry out life processes.
(a) Outline how starch in the diet is modified for absorption in humans.[3]
(b) Describe how the small intestine is adapted for efficient absorption of nutrients.[5]
(c) Blood transports nutrients to all tissues of the body. Explain the initiation of the heartbeat and how blood flow is controlled in the heart.[7]
▶️Answer/Explanation
a a. starch is broken down by the enzyme amylase;
b. (amylase) secreted by the pancreas/salivary glands;
c. acts in the duodenum/small intestine/mouth;
d. starch is broken down into monomers/maltose/glucose;
e. products of digestion are smaller/more soluble molecules for absorption
b a. small intestine is very long;
b. small intestine contains villi/microvilli;
c. the epithelial cells of villi have microvilli
d. these increase the surface area for absorption;
e. the cells of the small intestine contain (a large number of) mitochondria;
f. these provide energy for active transport;
g. the walls contain proteins for active transport/ facilitated diffusion
h. the villi have a rich blood supply/ lacteals;
i. the walls of the villi are thin so less distance for diffusion;
c a. the contraction of the heart is myogenic / heart beat initiates within the heart tissue itself;
b. heart beat initiates in the sinoatrial node
OR
SA acts as a pacemaker;
c. the SA node is located in the right atrium;
d. electrical impulses pass over the atria then the ventricles;
e. nerves from the medulla can control the rate of heart beat/ blood flow;
f. epinephrine/adrenaline can increase the rate of the heart/blood flow;
g. contraction of heart/cardiac muscle causes blood to flow;
h. ventricles send blood to the organs/cells of the body
i. the direction of flow is controlled by valves/valves prevent backflow
OR
when the heart/named chamber contracts the valves/named valve open.
j. AV valves prevent backflow from ventricles/into atria
k. semilunar valves prevent blood returning/backflow to the heart/ventricles
