Question
Refer to the Accord case study
Problems are continuing with Enrich drinks. Aran is becoming increasingly frustrated with the lack of growth of sales. He always wants to succeed and is driven by the need to get tasks completed. The Enrich part of his life is not a success. He blames the workforce. The workforce does not share his vision. Employees are mainly part-time workers and parents who value jobs that enable them to fit work around school hours. As Aran has become more autocratic in his leadership style, labour turnover has increased. Last month, from a workforce of twelve, one retired and two left for what they called “better jobs”.
There are also increasing problems with the quality of Enrich drinks, as batches of Enrich are rejected by the quality control department. Elsie, the manager of the production department, blamed suppliers, saying that Aran had damaged business relations with them due to his impatience. Elsie also blamed Aran for poor stock management. She has proposed total quality management (TQM) as a solution to these problems.
Detox
Accord decided to start the production and marketing of Detox, the green tea drink that helps athletes to relax. Detox proved to be very successful. Encouraged by the success and boosted cash inflow, Kayla is considering producing a range of snack bars based on Enrich and Detox flavours and recipes. Accord would use the Enrich brand name for the snack bars. The market for healthy snack bars is very competitive and dominated by a few large companies who spend large amounts of money on advertising. The market is growing rapidly – some market researchers estimate by 34 % per annum. There are many examples of small businesses entering the market successfully on a small scale. Kayla estimates that the proposal would involve an investment of $100 000, with forecast net returns of $80 000 for four years. Aran thinks that the money could be better spent on marketing Enrich drinks.
Accord have not yet made a decision about producing a range of snack bars.
Kayla is certain that there is a market for the snack bar products. The snack bars would complement Accord’s product portfolio. The investment required, according to Kayla’s estimate (see Section B), is acceptable and she is certain that it is the right time for the business to grow. Her information on the market (see Appendix 1) is very positive. In contrast, she believes that it is too difficult to grow in the beverage market because of competition, so she would prefer to switch from drinks to snack bars. She likes owning the business and has very clear objectives for the future.
Aran is becoming increasingly frustrated. His idea of targeting a mass market for Enrich and Detox has been rejected by Kayla and other managers at Accord. His efforts to introduce total quality management (TQM) failed because employees resisted the change. He is interested in performance and not relaxation, so he does not like Detox as an idea for a product.
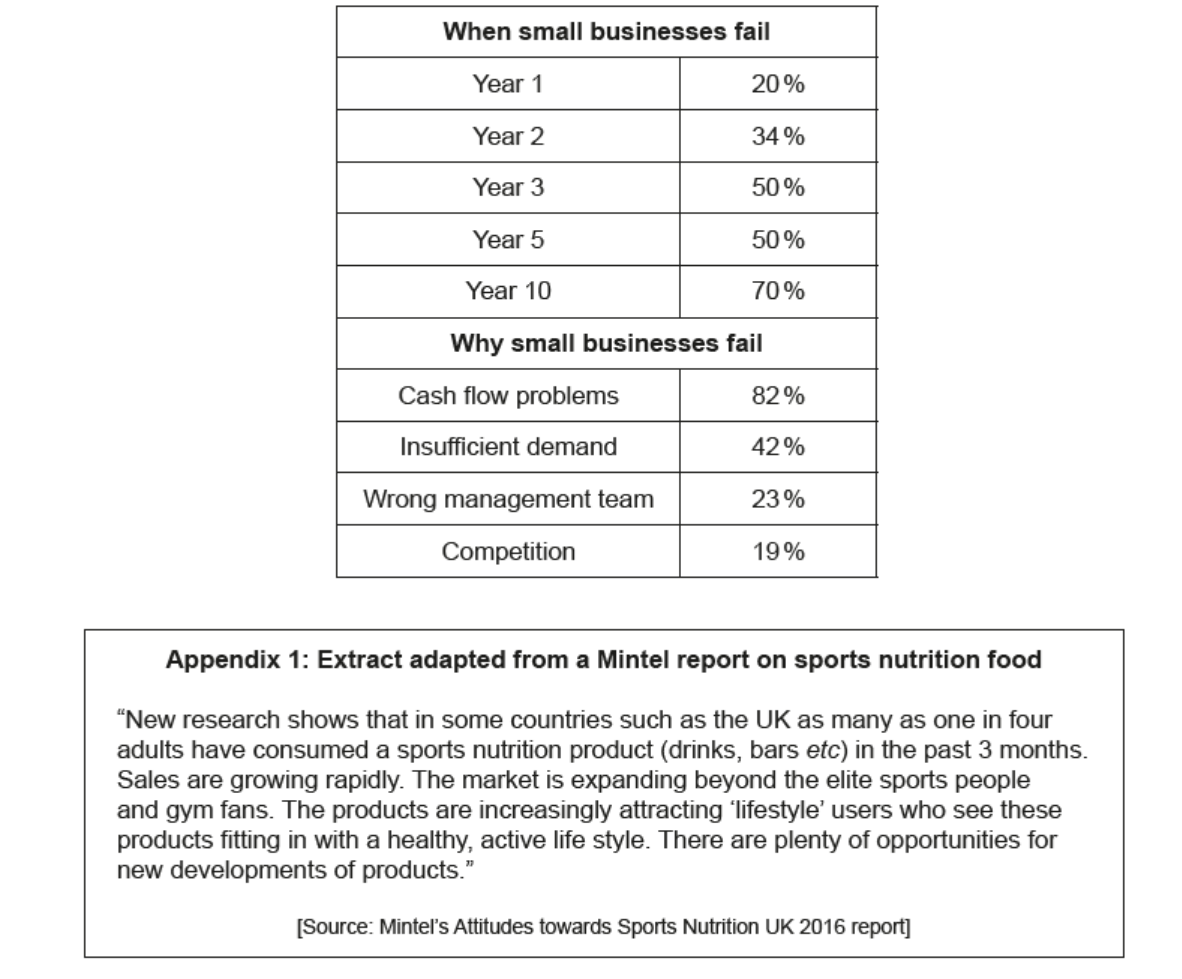
Aran has been approached by Star Food (SF), a multinational company (MNC) that produces a range of food products including soft drinks. SF are interested in the Enrich brand name and Accord’s contracts with sports centres. SF have offered to buy Accord for $5 million. This is approximately five years of earnings for Accord. Kayla and Aran would keep the Detox part of the business. Aran would be happy to accept the offer, particularly given the risk that Accord may not survive (Table 1). Aran likes the certainty that the sale would bring. He would accept a small payment from Kayla to sell his share of the Detox business to her.
Table 1: Survival rates of small businesses (based on a survey of local businesses)
Using the case study and the resources, recommend whether Accord should start making and selling snack bars or whether Kayla and Aran should sell Accord to SF. A force field analysis of the options could help you in your answer.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Refer to Paper 1 markbands for May 2016 forward, available under the “Your tests” tab > supplemental materials.
Making and selling snack bars:
Forces for the change to snack bars:
Kayla is certain there is a market
Fits in with existing product portfolio
Payback and ARR are OK
Business is in a good position to grow
The Mintel report is very positive
Snack bars are better than drinks because of competition.
Forces restraining the change:
Aran thinks it better to target the mass drinks market
There are still quality issues to overcome first
Detox does not fit in with his ideas for the product/market.
Selling Accord to SF:
Forces for the selling SF:
Offer is for 5 years’ worth of earnings
Detox remains
Aran is frustrated with the current business and would accept the offer
There are threats to Accord’s survival
Certainty
Kayla would buy Detox, which she likes.
Forces restraining the change:
It would end the partnership
Would Aran later regret it?
Do not penalize candidates who do not consider the “do nothing” option.
Marks should be allocated according to the paper 1 markbands for May 2016 forward section C
Criterion A: Is about the choice of theories/tools made by the candidate to try and solve the problem. Possible theories, planning tools and techniques include: FFA, Investment appraisal, SWOT, Risk (candidates need not refer to Ansoff but it might be useful), takeovers, product portfolios, market data, ownership and control issues, eg partnership, market research the importance of assumptions.
In this instance, as compared with previous sessions, the emphasis is likely to be on choosing relevant theories and ideas and not so much on business tools.
No understanding of FFA max [3]. FFA could be presents as a table or a discussion of driving/restraining forces
For [4]: FFA plus at least one other tool, technique or theory understood and developed well with some relevance to the additional stimulus material.
For [2]: some understanding of at least two tools, techniques or theories, but not developed.
Criterion B: Is about the use of the stimulus, tools, techniques, theories in solving the problem. Application will be judged by the use of the stimulus material, in particular the extra material, especially Table 1, Appendix 1.
For [4]: relevant tools, techniques and theories are applied well to the case study (including OFR) context and additional stimulus material, the application is convincing and relevant.
If only one option considered max [3].
Limited use of Table 1 or Appendix 1 max [3].
For [2]: some limited context/application but not developed. Use of tools limits candidate’s ability to make reasoned arguments.
Criterion C: Is about the process of making a decision and the strength of the recommendation. Options discussed in balanced way, conclusions drawn as to whether they work. Remember, “do nothing” can be a recommendation.
It is always worth reflecting on the piece of work as a whole (the entirety of the answer) when deciding on the mark for this criterion.
There can be some flexibility about the chose option: Option A, Option B, both options, neither option.
For [4]: There needs to be a comparison between the two options using Section C and other material and a recommendation (Option 1, option 2 or do nothing) made and supported.
For [2]: Only one option considered or some limited arguments but not justified. No comparison, limited analysis, but candidate arrives/draws a reasoned conclusion.
Criterion D: Structure. This criterion assesses the extent to which the student organizes his or her ideas with clarity, and presents a structured piece of writing comprised of:
an introductory paragraph
logical structure
a concluding paragraph
fit-for-purpose paragraphs. This means: not too long, focused on distinct issues, sequenced well, guides the reader.
Beware of under-rewarding weak scripts that, nonetheless, have some or all of the elements. The candidate will lose marks in the other criteria so they should not be doubly penalized.
For [4]: all four elements present, clearly organized and there is clarity in the student’s answer.
For [2]: No logical structure, but other elements present or logical structure with other elements missing.
Criterion E: Is about the extent to which stakeholders (both groups and individuals)
are considered.
Individuals: Aran and Kayla (these hold different views so can be considered as different individuals).
Groups: Managers, employees, customers, communities, governments, stakeholders at SF.
For [4]: two or more individuals and groups are considered in a balanced way.
For [2]: one group or individual considered appropriately, or several individuals or groups considered superficially.
[1] could be awarded if there is mention of stakeholders but with little development.
[3] could be awarded if there is a range of stakeholders but little balance.
Question
Refer to the Radeki de Dovnic Manufacturing case study
If RDM builds a new production facility in Europe, an immediate consequence will be an increase in capacity. At current levels of output this would lead to a reduction in capacity utilization. The current output of RDM’s factory is 20 000 units a year, with a productive capacity of 21 000 units a year before the new facility is built. If the new production facility is built, the greater capacity for the whole business will, at current levels of output, result in the capacity utilization falling to 50 % until production at the new facility starts.
Xi, the marketing manager, suggests that this increased capacity provides the opportunity for market development to be achieved by entering the United States (US) market.
The US market has similarities with Europe, with an aging population and low birth rate. Demand for customized healthcare devices is high. However, the healthcare system in the US is very different, with a much greater role for private sector healthcare compared to Europe, where much of the healthcare is state funded. In the US, 18 % of gross domestic product (GDP) is spent on healthcare compared with an average of 11 % in Europe. Advertising spend in the US is very high for the typical healthcare equipment business, which uses TV and the internet to reach individuals, whereas in Europe healthcare equipment businesses typically negotiate with government organizations. Average incomes in the US are higher than in Europe. Competition in the US is very high, although some major healthcare equipment businesses dominate the market. Industrial/ employee relations in the US are generally more decentralized than in Europe, with a lower level of unionization.
To assess the best way to enter the US market, some senior managers may have to move to the US and Xi may need to recruit some new staff in the US with specialized knowledge of US laws and regulations, as well as some additional marketing employees. Xi is aware that industrial/ employee relations are different in the US. Existing staff will have to get used to new ways of working and are concerned about having to work with new staff in the US.
Jan is considering two options for the long-term development of the business: market development and diversification.
Option 1: Market development
Although Jan, with his strong associations with the US, likes the idea of developing the US market, he has concerns about it. Over the last four years, the exchange rate has fluctuated between ![]() . There is some evidence that the US wants to discourage imports and prefers foreign businesses to invest directly in the US. Jan thinks there are other markets in and closer to Europe that could be developed more easily without significant changes to the distribution channels or the culture of the business. He has suggested the United Kingdom (UK) market as an alternative, which has a health service similar to those in other European countries. In most other respects the UK market is similar to other European markets. The main worry is that the UK market would be difficult to enter, as established suppliers are likely to be preferred by the health service and there may be financial constraints on the health service.
. There is some evidence that the US wants to discourage imports and prefers foreign businesses to invest directly in the US. Jan thinks there are other markets in and closer to Europe that could be developed more easily without significant changes to the distribution channels or the culture of the business. He has suggested the United Kingdom (UK) market as an alternative, which has a health service similar to those in other European countries. In most other respects the UK market is similar to other European markets. The main worry is that the UK market would be difficult to enter, as established suppliers are likely to be preferred by the health service and there may be financial constraints on the health service.
Option 2: Diversification
Jan is also considering a proposal by Heinrik Langer, a business analyst. Heinrik’s idea is for diversification. He thinks that RDM should develop a service role. RDM’s directors and workforce have all of the skills and experience needed to help other businesses convert from traditional production methods to automated robotic production processes. This service (known as a consultancy) would require recruitment of more engineers and computer specialists as well as highly skilled and experienced consultants. Heinrik’s proposal is based on:
the likely low long-term growth prospects for RDM’s healthcare products. Population trends in Europe due to the low birth rates (Table 1) will lead to an aging population in the short and medium term. However, in the long term there could be economic and demographic problems arising from the eventual decline in population that is predicted to occur when the birth rate is less than 2.1
his view that every business should have a service role
possible financial pressures on European governments, potentially reducing healthcare spending
his data market research results on robots and robotics (Table 2).
Table 1: Population birth rates

Table 2: Market research on robotics

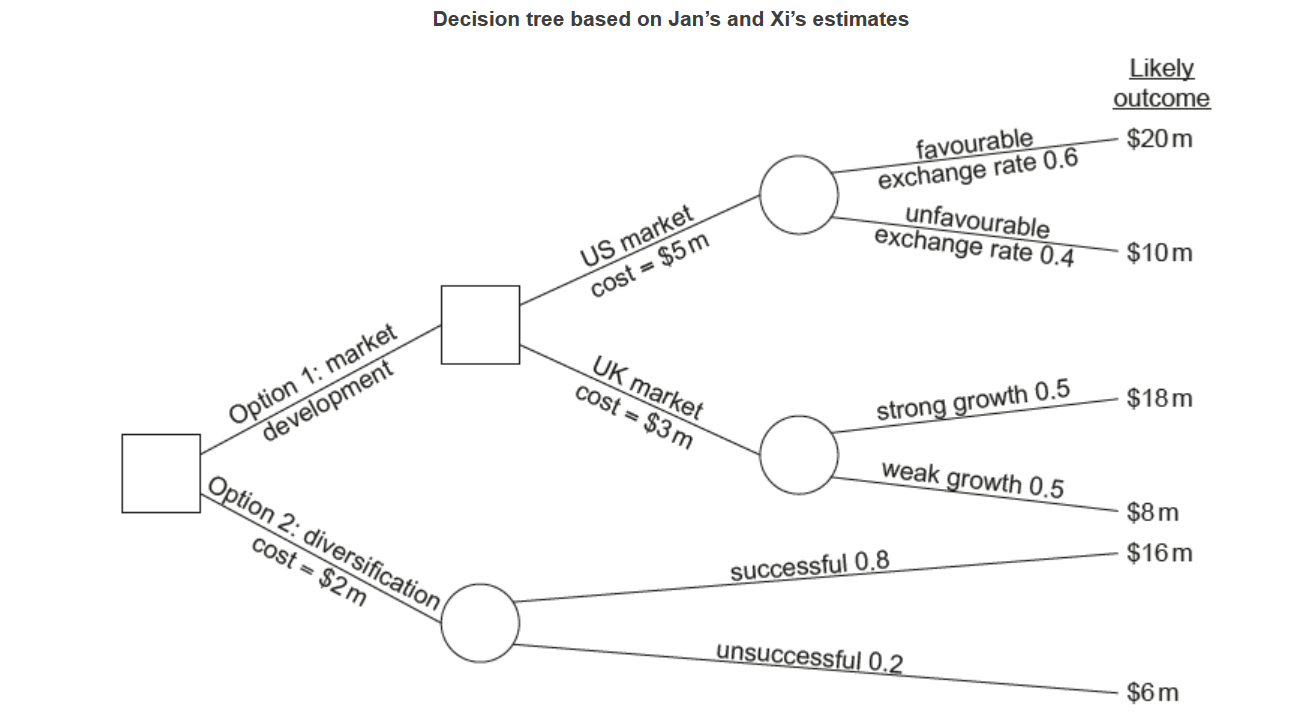
Nikita, RDM’s director of corporate strategy, has asked both Jan and Xi to provide data on each option to help her construct a decision tree to present at the next board meeting. The decision tree below summarizes the issues involved in the decision.
Using the case study and the resources, recommend whether RDM should choose Option 1 or Option 2
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Refer to Paper 1 markbands for May 2016 forward, available under the “Your tests” tab > supplemental materials.
Option 1: Market development
Arguments for:
Good use of capacity.
Looks good on decision tree. EV US=$11m; EV UK=$10m
US high cost($5m), UK lower cost ($3m), both more than Option 2
UK market similar to those in other European countries.
UK market close
UK market would not need major changes to distribution channels
Lower risk in Ansoff
Birth rates high in US, UK so possible aging population
The following points are in the resource so are not necessary for an answer but can be rewarded:
US is a massive market with wealthy customers.
Spending on health in US is higher, incomes in US are high.
Likely long-term decline in Europe.
Lower union power in US.
Arguments against:
Fluctuating exchange rates make planning especially pricing difficult
US likely to discourage imports and prefers direct investment
No experience of either market.
Difficult to enter the UK market
Possible decline in healthcare markets especially US, UK
There are already established suppliers in the UK market
Reduced healthcare spending in Europe
The following points are in the resource so are not necessary for an answer but can be rewarded:
US is highly competitive, dominated by multinationals.
Recruiting could be expensive.
Different rules and regulations in US may mean changes to product designs.
Option 2: Diversification
Arguments for:
Existing product may go into decline phase of product life cycle.
Rapidly growing and new market. (Table 2)
RDM has wide experience.
Possible reduction in Europe health care markets because of reductions in government spending.
Importance of service industries, healthcare opportunities likely to decline especially in Europe
Lowest cost ($2m) Highest chance of success (0.8)
Decision tree gives best EV ($12m)
Arguments against:
No experience.
Higher risk in Ansoff.
Recruitment may be difficult (high skills, experience needed)
Allow discussion of any reasonable related issue. Discussion of Brexit in the UK may help a candidate reach a conclusion but is not to be rewarded as the issue is external to the case.
Marks should be allocated according to the paper 1 markbands for May 2016 forward section C.
Criterion A: Knowledge and understanding of tools, techniques and theories
Decision tree and data from case, the 7Ps, diversification, interpretation of data, stakeholder differences, pace of change, Ansoff, Risk. Force Field and SWOT, but both often misunderstood in which case not rewarded. Be careful, mention of market development/diversification does not necessarily show knowledge of Ansoff – the candidate could be quoting from the case.
For [4] Good understanding of a range appropriate tools/techniques/theories
For [2] Satisfactory understanding of a limited number of tools/techniques/theories
Criterion B: Application judged by use of stimulus, in particular the extra material.
Remember, understanding has been rewarded in Criterion A. So B is about USE
For [4]: relevant tools, techniques and theories are applied well to the case study context and additional stimulus material, the application is convincing and relevant.
For [2]: some limited context/application but not developed. Use of tools limits candidate’s ability to make reasoned arguments.
Criterion C Reasoned arguments
Options discussed in balanced way, conclusions drawn and recommendation made/supported.
For [4]: There needs to be a clear recommendation supported by the data and analysis.
For [2]: Some limited arguments but not justified. Or limited analysis (e.g. one-sided argument) but candidate arrives/draws a reasoned conclusion.
Criterion D: Structure: This criterion assesses the extent to which the student organizes his or her ideas with clarity, and presents a structured piece of writing comprised of:
an introduction, which could be scene setting, or an executive summary (e.g. presenting/stating the recommendation)
a concluding paragraph. Please note this can be different from the concept of a conclusion/recommendation shown in Criterion C. Criterion D can be rewarded without a recommendation. Also please note that if there is an executive summary at the beginning (e.g. presenting/stating the recommendation) then the concluding paragraph should be more than simply a repeat of the executive summary (i.e. more than simply re presenting/restating the recommendation)
fit-for-purpose paragraphs. This means: not too long, each focused on distinct issues,
structure. This means whether there is a clear flow to guide the reader through the discussion, how the paragraphs are sequenced.
For [4]: all four elements present, clearly organized.
For [2]: No logical structure but other elements present or logical structure with other elements.
Criterion E: Individuals: Heinrik, Jan, Xi; Groups: Directors; shareholders; employees; customers; competitors. Likely issues include what the individuals want, the impact on employees, whether employees/managers have right skills, etc.
For [4 Individual(s) and group(s) are named and considered in a balanced way. I.e needs 1 or more of both individuals and groups developed
For [2]: one individual or one group considered appropriately, or several individuals and/or groups considered superficially.
For [1] one individual and/or one group considered superficially
Question
Benno

Benno is a soft drinks manufacturer. Its mission statement is “to produce healthy drinks without damaging the environment”.
Competition in the healthy soft drinks market is fierce. Benno uses a competitive pricing strategy. However, sales of Benno’s drinks have fallen significantly over the last five years, particularly in the 12-18 age group. The business has no accumulated retained profits.
Benno is committed to innovation and corporate social responsibility (CSR). Its research and development division has recently invented a new biodegradable drink pack ring that starts to break down within two hours of contact with sea water. It dissolves fully in 48 hours. Currently, $98 \%$ of pack rings are made of plastic and when dumped in the sea are responsible for the death of many sea creatures.
A focus group of loyal customers used regularly by Benno’s marketing department is wholeheartedly in favour of the new drink rings. However, the marketing director has read recent studies that suggest:
- purchases of green products are not increasing, despite the positive attitude of many consumers towards sustainability and biodegradable products
- consumers continue to prioritize price when purchasing soft drinks.
To manufacture the new drink rings, machinery costing $\$ 5$ million would be needed. Drink ring production unit costs would rise from 10 cents to 15 cents and prices of a six-pack of Benno soft drinks would have to increase by $5 \%$. Benno’s net profit margin on a six-pack is $10 \%$.
Benno’s director of corporate social responsibility favours the change to the new drink rings but is opposed by both the finance director and marketing directors.
a. Define the term innovation.[2]
b. Explain two roles of Benno’s mission statement.$[4]$
c. Explain one advantage and one disadvantage for Benno of using a focus group of loyal customers.$[4]$
d. Recommend whether Benno should replace its plastic drink rings with the new biodegradable drink rings.[10]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Innovation is about putting a new idea or approach into action. It can be described as the process of translating an idea/invention into a service/good that creates value. Innovation can be achieved by improving existing goods, processes or services
Candidates are not expected to word the definition exactly as above. Award [1] if the candidate recognizes that innovation is the creation or invention of something original. Award [2] marks if the candidate also recognizes that the new invention or process has value [2].
N.B.: no application required. Do not credit examples on their own.
Award [1] for a basic definition that conveys partial knowledge and understanding.
Award [2] for a full definition.
b.The roles of a mission statement include:
communicating the purpose of the organization to stakeholders
informing decision making and strategy development
developing the measurable goals and objectives by which to gauge the success of the organization’s strategy.
For Benno, the mission statement has provided a way for the business to differentiate itself from its competitors, especially at a time when competition in the healthy soft drinks market is intense.
The mission statement is also a way to attract new investors who may have empathy with the direction of Benno. This is an important role given the need for Benno to be committed to innovation and CSR.
Award [1] for a basic answer that shows an understanding of a role of a mission statement.
Award [2] for an answer that shows an understanding of two roles of a mission statement.
Award [3] for an answer that shows a good understanding of two roles of a mission statement and one of these is suitably applied to Benno.
Award [4] for an answer that shows a good understanding of two roles of a mission statement and both of these is suitably applied to Benno.
Do not reward marks for describing/defining a mission statement.
c.Advantages of a focus group of loyal customers:
Can obtain detailed information about your own customers about their feelings, perceptions and opinions.
Are cheaper than performing individual interviews.
Provide an opportunity to clarify any issues or problems.
Disadvantages of a focus group of loyal customers:
They can be hard to control and manage.
You are only getting the views of loyal customers – it tells you nothing about consumers who prefer rival brands and why they prefer them to your soft drink.
The results are difficult to analyse, especially if the focus group provides qualitative feedback.
Members may not reveal their own feelings but are swayed by the majority view.
May not be representative of the target market as a whole.
Possible application:
For Benno, an advantage of using a regular focus group is that they will be aware of the company’s products and mission. This will reduce the amount of statistical noise and save time in the discussions when looking at new product ideas, such the biodegradable rings.
However, having a regular group for Benno increases bias and reduces objectivity of the data researched. It might be a useful exercise for Benno to ask customers who are not overly familiar with their products to achieve a more balanced qualitative view.
Accept any other relevant advantage / disadvantage.
Accept any other relevant explanation.
Mark as 2 + 2.
Award [1] for a basic answer that shows an understanding of an advantage of using a focus group.
Award [2] for an answer that shows an understanding of an advantage and disadvantage of using a focus group.
Award [3] for an answer that shows an understanding of an advantage and disadvantage of using a focus group of loyal customers and one of these is suitable applied to Benno.
Award [4] for an answer that shows an understanding of an advantage and disadvantage of using a focus group of loyal customers and both of these is suitable applied to Benno.
d.Refer to Paper 2 markbands for May 2016 forward, available under the “Your tests” tab > supplemental materials.
For:
It fits in well with its mission statement “to produce healthy drinks without damaging the environment” and this may be important in maintaining customer loyalty.
It fits into its belief in corporate social responsibility, as the current drink rings damage the environment and harm creatures in the seas, such fish.
Competition in this drinks market is very intense – this could act as a strengthening of its USP for Benno and retain loyal customers and attract customers from rivals. It will strengthen its image as a business that has “green” credentials.
Sales of Benno’s drinks have fallen significantly over the last five years– so it is important that Benno does something to stem this tide.
Accept any other reasoned arguments.
Against:
It will cost $5m to buy the machinery to produce the new rings and the business has no accumulated retained profits – therefore the funds will need to be raised, probably externally via a bank loan, which will lead to interest charges and an increase in operating costs. It may take time to find a suitable angel investor to help finance this project. Will the angel investor wish to exert some control over Benno’s operations?
The unit cost increase is 50 %, a rise from 10 cents to 15 cents per ring, and the business only has a net profit margin of 10 %. As the market is competitive and reports suggest that consumers are price sensitive, a price rise – passing on the cost of the new rings – is probably not going to be possible. The result is that Benno’s net profit margin will fall.
Sales are falling, particularly to the 12–18 age group – are they going to be energized into buying a product that is more environmentally friendly, particularly when reports suggest purchases of green products are not increasing?
In terms of a new way forward for Benno, the introduction of the new rings has a great deal of merit. There are a large number of marketing opportunities available in a competitive market and this idea will strengthen Benno’s brand. However, the forecasted financial implications of this idea are not ideal and if sales volumes do not increase significantly then Benno may find itself financially worse off if profits do not increase. One solution may be to wait until some more objective market research via a new untested focus group have given their thoughts on the new ring.
Accept any other reasoned arguments.
Marks should be allocated according to the paper 2 markbands for May 2016 forward with further guidance below.
A balanced response is one that provides at least two arguments for and two arguments against the option.
For one relevant issue that is one-sided, award up to [3]. For more than one relevant issue that is one-sided, award up to a maximum of [4]. Award a maximum of [6] if the answer is of a standard that shows balanced analysis and understanding throughout the response with reference to the stimulus material but there is no judgement/conclusion.
Candidates cannot reach the [7–8] markband if they give judgement/conclusions that are not based on analysis/explanation already given in their answer.
Mark as 2 + 2.
