Question
Hums Athletics (HA)
Hums Athletics (HA) manufactures running shorts, sweat shirts, and sports bras. Operating only in the secondary sector, HA has a head office and three manufacturing facilities, one for each product. These are located in its home country in Europe. Labour costs are high. The quality of labour is excellent.
HA produces goods under its own HA brand, which it sells to wholesalers. HA also manufactures for other sportswear companies. HA puts the other sportswear companies’ logos on the running shorts, sweat shirts, and sports bras. Sales to other sportswear companies are an important revenue stream for $H A$.
HA has many levels of hierarchy. Managers at each level have a narrow span of control, and the company is organized by product. HA’s management believe that these features of organizational structure ensure product quality, which they view as essential for brand loyalty.
The sportswear manufacturing industry is becoming more competitive. Some foreign manufacturers have begun using penetration pricing to gain market share. For three years, none of HA’s revenue streams have increased, despite increasing unit sales. HA’s gross and net profit margins have declined. However, its sales have increased for the last three years. HA has had to raise additional external finance to increase production.
In response to the increasing competition, $H A$ is considering two options:
- Option 1: Outsourcing some of its manufacturing overseas.
- Option 2: Entering the rapidly growing online business-to-consumer (B2C) retail market.
Market research has shown that consumers increasingly expect to buy online.
a. State two ways in which market share can be measured.[2]
b. Draw an organization chart for $H A$.
c.i. Explain the impact of price changes by foreign competition on HA’s break-even point.[2]
c.ii.Explain why $H A$ had to raise additional external finance to increase production.[2]
d. Recommend whether HA should choose Option 1 or Option 2.$[10]$
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
a. The term market share refers to the percentage of a sales that one company has within a particular market, such as athletic gear.
Ways that market share can be measured include:
- by revenue (value), in terms of currency $(\$, €, ¥$, etc.).
- by unit sales (volume).
N.B. candidates are not being asked how to calculate market share, and, thus, they are not expected to provide a definition. For [2], they have to convey the idea that two ways exists to measure it.
Award [1] for each correct way of measuring market share up to [2]. Maximum award: [2].
b.
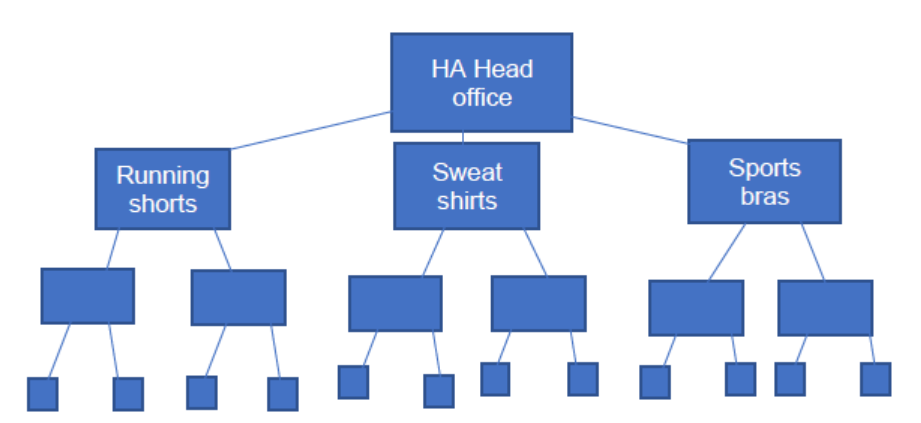
The chart does not have to be drawn exactly as above.
Award [1] for drawing an organizational chart and additional [1] for each of:
information that conveys some understanding of “by product”
information that conveys some understanding of hierarchy (must have at least four levels)
information that conveys some understanding of a narrow span of control (two or three reporting units per manager).
Maximum award: [4].
N.B. to convey the idea of organized by product, candidates may use the actual products (running shorts, sweat shirts, and sports bras) or generic products (product A, product B, product C) as long as they have exactly three products.
ci. HA is selling more units of product, but sales revenue has not been rising as foreign competitors, using penetration pricing, have driven prices down. Thus, the average sales price per unit is falling. Further, the gross profit margin has been declining, which means that HA has not been able to reduce per unit cost as much as sales price per unit. With a declining contribution per unit, HA has seen its break-even point move to the right on the X-axis.
Award [1] for stating that the break-even point moves to the right, and an additional [1] for an explanation with application to the stimulus.
c.ii.Candidates may answer this question in one of three ways:
1. One way puts emphasis on the word external in the question. If a candidate chose this emphasis, they need to say something like “Because foreign competitors have used penetration pricing to gain market share, $H A$ has had to lower its prices, which is why gross and net profit margins have declined. As a result, HA has not been able to generate sufficient internal finance to support increased production and has had to turn to external finance.”
Both of the other ways candidates can answer this question emphasize the increase in production:
2. Candidates may believe that $H A$ needs more working capital to support increased trading activity. $H A$ has had increased unit sales volume, which means that it has been manufacturing and selling more product, even if at lower margins. For most companies, increased trading means increased inventory and accounts receivable. The asset accounts must be financed. Increased accounts payable will fund some of that increased trading activity, but probably not all of it. With margins declining, HA probably cannot fund this need internally and, thus, has had to turn to external sources of finance.
3. Candidates may believe that HA needs property, plant, and equipment to support increased production. However, because of contracting margins, in the past few years, HA probably has generated insufficient funds internally to finance long-term assets. Thus, they have obtained finance externally.
Award [1] for some understanding of one of the three issues above and an additional [1] for application to the stimulus. Up to a maximum of [2].
N.B. In all three cases, the key is for candidates to link contracting margins or lower prices (which is why HA’s margins are lower) to external finance (rather than internal) or to increased production (increased working capital requirements or more property, plant, and equipment).
d. Refer to Paper 2 markbands for 2016 forward, available under the “Your tests” tab > supplemental materials.
Reasons for outsourcing include:
- Lower costs, which is usually why companies outsource overseas.
- Lower investment in fixed assets: no need to expand current manufacturing facilities and some possibility of selling off existing facilities.
- Lower fixed costs, which can be an advantage were sales to fall in the highly competitive market.
Reasons against outsourcing include:
HA relies on high-quality manufacturing, which overseas manufacturers may not be able to deliver.
HA exposes itself to additional risks, such as political risk of the home countries where the new manufacturers are located.
Depending on where most of HA’s sales occur, it may lose the advantage of saying manufactured in the home country or in Europe.
Outsourcing, if to developing countries, may raise ethical and environmental concerns.
Accept any other relevant reason for or against outsourcing.
Reasons for setting up online business-to-consumer (B2C) retail stores include:
The online retail market is rapidly growing.
Consumers have increasing expectations that goods will be available online.
B2C eliminates links in the downstream supply chain that erode profit margins.
Reasons against setting up online retail stores include:
HA has only operated in the secondary sector and has no experience in retail.
Though capital outlays will be less than if HA started to build brick-and-mortar stores, setting up an online presence will require capital outlays at a time when the business is having to turn to external finance just to fund manufacturing operations.
The online market is no less competitive than traditional approaches.
Accept any other relevant reason for or against setting up online retail stores.
Award marks as follows:

N.B. A balanced argument is one that has a reason for and a reason against the options.
Marks should be allocated according to the Paper 2 markbands for 2016 forward.
Question
Willow Enterprises (WE)
Willow Enterprises (WE) was founded in 1989 originally as a small manufacturer of carpeting for high-end commercial and institutional office space. In 1997 the management made several strategic decisions:
- change from the use of cheap man-made materials to more expensive natural fibres in its carpets
- change legal status from a private to a public limited company
- use profits to increase production capacity and expand the sales force
- diversify by taking over other regional businesses, including a retail chain, and transform them into environmentally friendly businesses.
Because of its appeal to environmentally conscious customers, WE became the regional market leader and, by 2008 , was an important carpet manufacturer at a national level.
At this time, Chief Executive Officer Simon Dee decided that WE would adopt a far-reaching programme of corporate social responsibility (CSR). Every year, WE committed more resources to various forms of corporate social responsibility (CSR), such as charitable contributions and fair payments to employees and suppliers. By 2018, WE had diverse revenue streams and a brand identity strongly associated with corporate social responsibility (CSR).
For the last few years, WE’s gross and net profit margins have been falling slightly but steadily. Simon has attributed the declining profitability to diseconomies of scale and one-off (one-time) expenses associated with each takeover. The Chief Financial Officer, Ruth Croft, disagreed. She gave Simon a copy of a 1970 article by the economist Milton Friedman entitled “The Social Responsibility of Business is to increase its Profits”.
a. Define the term revenue streams.[2]
b. Explain one advantage and one disadvantage of WE changing its legal status to a public limited company.
c. With reference to $W E$, distinguish between internal and external growth.
d. Discuss whether WE should retain its programme of corporate social responsibility (CSR).
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
a. Revenue streams refer to the different sources of sales revenue that a firm may have. Often, as firms grow, they attempt to diversify revenue streams as a way to find sales growth in saturated markets or as a way to offset risk (if sales revenue from one revenue stream declines, perhaps it can be offset by sales growth in another revenue stream).
Award [1] for a partial answer that conveys some understanding and [2] for a complete response that shows full understanding. Candidates do not have to word exactly as above. Simple exemplification is insufficient for a second mark. There must be some definition or description.
b.
Advantages of changing legal status to a public limited company include:
Access to greater sources of finance, either debt or equity, which WE may well want given its plan to grow externally through acquisition.
Greater prestige and name recognition, which may help WE as it approaches and acquires additional business.
Disadvantages of changing legal status to a public limited company include:
The initial and ongoing cost of being a public company, which requires extensive paperwork and filings with the government, as well as regular communication with shareholders. As WE is struggling to maintain margins, having additional expenses may further contribute to lower profitability.
Public disclosure to shareholders and media prevent WE from being more private in how it operates. Greater privacy with respect to strategy and direction could help WE more easily implement its strategies.
Accept any other relevant advantage or disadvantage.
Mark as 2 + 2.
For [2], candidates must identify an advantage or disadvantage, explain it, and apply it to the stimulus.
c.
Internal growth occurs when a business increases sales revenue through expansion of current operations, typically by building more capacity, hiring more sales people, or having more channels of distribution. WE’s growth, up until it decided on a programme of external growth, was always internal and in the carpet industry.
External growth occurs when business grows through some activity related to another business external to the original one. When WE decided to purchase additional companies, it was acquiring revenue streams and operations from other firms, which allowed for rapid growth.
Accept any other relevant advantage or disadvantage.
Mark as 2 + 2.
For [2], candidates must identify an advantage or disadvantage, explain it, and apply it to the stimulus.
d.
Refer to Paper 2 markbands for 2016 forward, available under the “Your tests” tab > supplemental materials.
Much debate exists around the question of CSR. Some companies advocate it, arguing that CSR is a way to balance corporate power with corporate responsibility despite the fact that having a programme of CSR increases costs in the short term and that there is no certainty that it will enhance business performance in the long run (though a slight positive correlation appears to exist).
Others argue that a company’s only responsibility, other than obeying the law, is increasing profits for shareholders. CSR makes a company less efficient. If all businesses in an economy are operating at less than optimal efficiency, the economy as a whole will suffer (just as each individual business will).
In the case of WE, the question of CSR is complicated. On the one hand, the brand identity of WE was built first on ecological sustainability and, later, on a full programme of CSR (thus economic and social sustainability as well). To suddenly change focus and adopt a totally profit-oriented mentality, as Milton Friedman argues, could hurt WE’s brand identity in the marketplace.
On the other hand, WE has experienced a steady erosion in margins (and, thus, profitability). Were the company to continue to allow this to occur, in the long run, WE would put itself at risk. Some disagreement internally exists, with the CEO believing the issue is the costs of expansion while the CFO has suggested that it is the costs of CSR.
WE should undertake a full marketing audit to determine the impact of CSR on its brand identity, as well as a thorough financial and managerial costing analysis to determine the true source of declining profitability. Without that investigation, WE will have difficulty knowing whether it should continue with CSR.
For a balanced argument, a candidate must have two arguments for and two arguments against CSR. At least one of the arguments for and against can be purely theoretical, while at least one argument for and one argument against must be based upon application to the stimulus. If the candidate does not make judgments on conclusions, maximum award: [6].
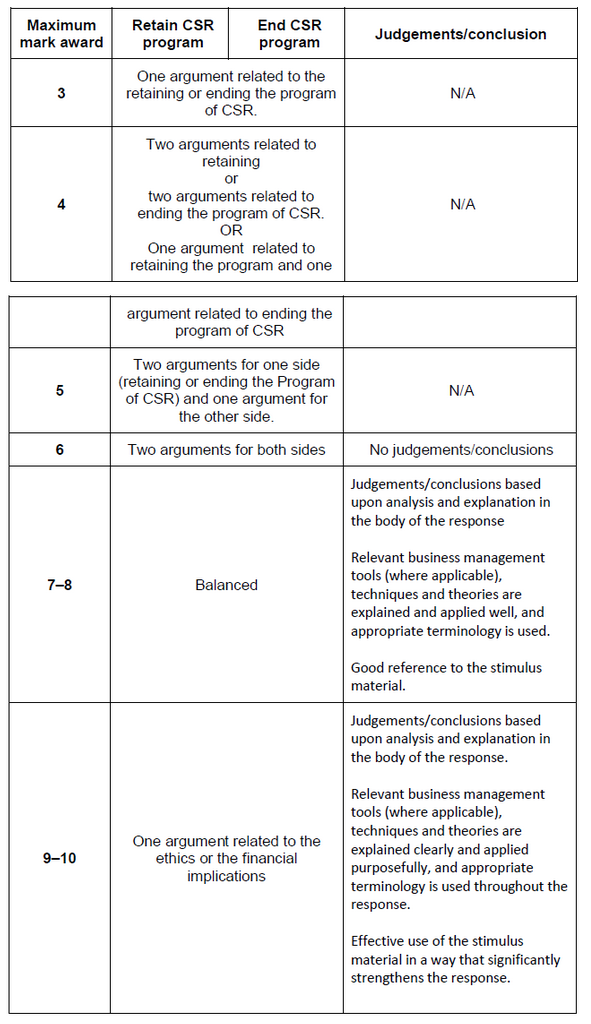
Marks should be allocated according to the paper 2 markbands for May 2016 forward.