Question
Imperial Falls (IF)
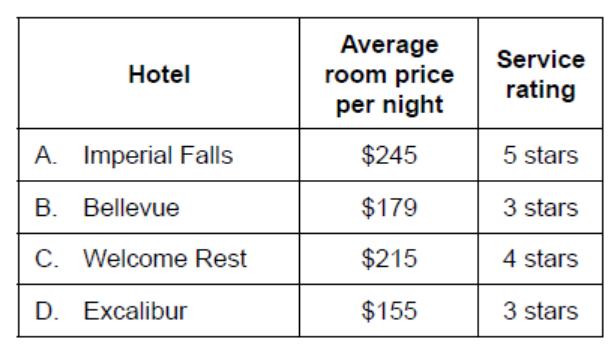
Imperial Falls (IF) is a luxury hotel in a city centre. The hotel is an old palace, elegantly furnished and overlooking the harbour. Of the highest quality, for decades IF has been the preferred hotel for business travellers to the city. Relying on reputation and word of mouth, IF does little promotion. Its facilities include a swimming pool and a high-quality restaurant. Table 1 shows information about the principal hotels located in this city centre in 2018.
Table 1: Selected information about the principal hotels in the city centre in 2018
In 2019, bookings at IF have begun to decline because of a new hotel, Guest Rooms (GR), which is part of a global chain. Many businesses have employees who travel to major cities, where most business meetings occur. Hotels in city centres are usually luxurious and expensive. GR is different. It offers clean, small rooms with Wi-Fi, a small desk and a double bed. Room prices at $\mathrm{GR}$ are significantly lower than most city-centre hotels. The new $G R$ is located near the airport, 6 kilometres (3.72 miles) from the city centre.
GR uses a fee-based membership model and member companies require employees to stay at a $G R$ hotel when on business. Employees may also stay there when on personal travel. Guests use self-service check-in machines (similar to those used at airport check-ins), which issue electronic keys. GR electronically bills the company directly. Service is minimal. GR relies heavily on social media marketing. It also uses above-the-line promotion.
a. State two types of above-the-line promotion.[2]
b. Using Table 1, construct a product position map/perception map for all four hotels prior to the opening of $G R$.
c. Explain two ways in which $G R$ is able to offer rooms at a lower price than IF.[4]
d. Discuss possible changes to IF’s marketing mix to reduce the loss of customers to GR.[10]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
a.
Appropriate types of above-the-line promotion include:
newspapers
magazines
radio advertisements
television advertisements.
Accept any other relevant answer, including “advertising on the Internet” or “the Internet.”
Award [1] for each appropriate type of above the line promotion up to [2].
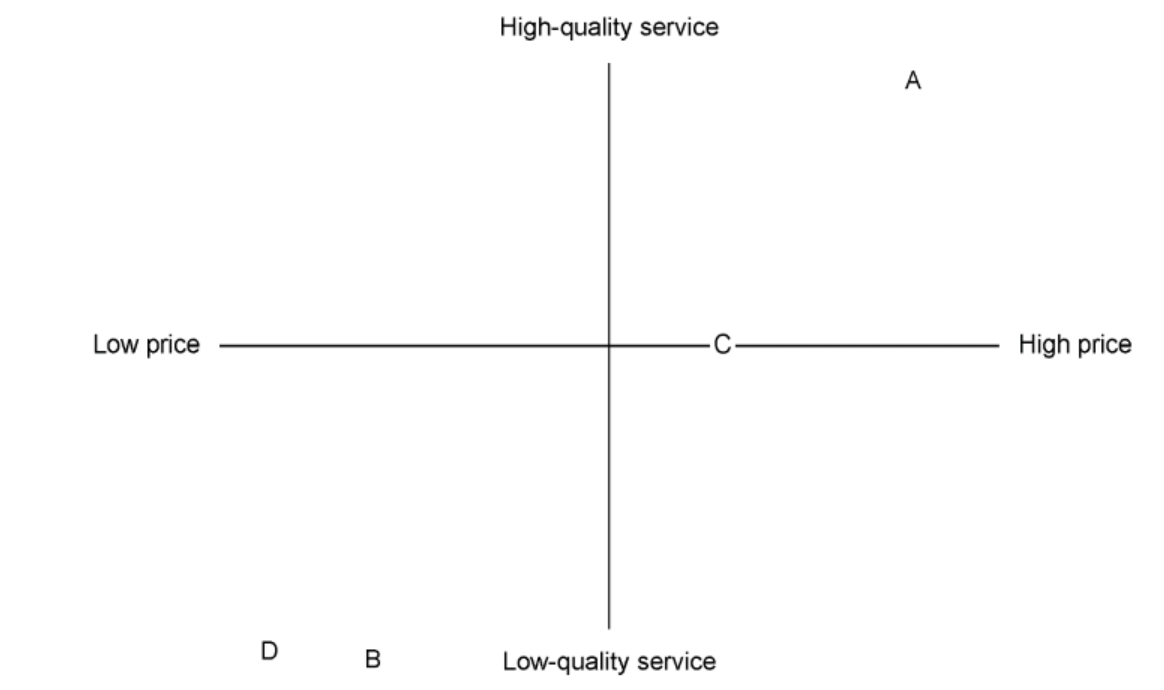
Award [1] for the overall layout of the map with both axes labelled correctly (price: high or low; service: high or low).
N.B. It does not matter which one is horizontal/vertical.
The correct positioning is as shown above. Adjust appropriately if a candidate makes the price the vertical axis and quality the horizontal axis.
Award [2] for a correctly labelled position map with two of the companies properly placed.
Award [3] for a correctly labelled position map with three of the companies properly placed.
Award [4] for a correctly labelled position map with all four companies properly placed.
The position map has been scaled from $155–$245 for the horizontal axis and 3 stars to 5 stars for the vertical axis. If candidates scale the perception map differently (1 to 5 stars, for example), mark accordingly and per the explanation for [1], [2], [3] and [4] above.
The candidates were asked to position the four hotels prior to the opening of the GR. The four hotels represent the full range of the market (at the time, before GR opened) and, therefore, the positioning should be as shown above. However, candidates may consider a 3-star hotel to be “middle quality” rather than low quality because three is the mid-point between 1 star and 5 star. Thus, some candidates may position the four hotels more toward quadrant one than they should.
Nevertheless, examiners should have some forbearance: as long as the relative position of the hotels is accurate, award marks appropriately. For example, the position map below would earn [4].

N.B. If the relative position is correct but the candidate has compressed the positions of the four hotels into one quadrant (which would typically be quadrant 1), award a maximum of [3].
c. Three ways in which $G R$ is able to have lower costs than traditional hotels include:
- more modest rooms, which include smaller room size and less elegant furniture
- lower personnel costs, as much of the traditional staff is replaced by kiosks and automated billing
- Fewer amenities, like a swimming pool and a high-quality restaurant.
Accept any other relevant example.
If a candidate refers to the airport versus city-centre location and assumes that the airport location is less expensive, award [1].
Mark as $[2+2]$.
Award [1] for identification of a way to lower costs and an additional [1] for an explanation thereof.
d. Refer to Paper 2 markbands for 2016 forward, available under the “Your tests” tab > supplemental materials.
Main differences in the marketing mix of the two hotels are:

The question of place is tricky. At one level of argument, place is different than location. However, in the case of a hotel, place and location are virtually indistinguishable, as hotels are ontologically a venue where customers rent rooms for the night. Thus, in the case of hotels, place devolves to location.
Possible changes to the IF’s marketing mix include:
Product: Cutting back on amenities and passing some of those savings on to customers via lower room rental rates. There are negatives to this tack. First, a reduction of amenities could be viewed as a deterioration of the high quality, which is currently IF’s USP.
Price: Reducing the rates that it charges for rooms. If prices are lowered and changes are not made in quality of service or amenities, IF could experience lower profits. IF would certainly experience lower profits per room. Unclear is whether the lower prices would lead to higher occupancy.
Promotion: Increasing its promotion. IF has three noteworthy features that GR does not have: elegance, five-star quality and a central city centre location. With greater promotion, IF may be able to attract customers back based upon the convenience of being in the city centre and the elegance of staying in an old palace.
Place/Location: It is not very realistic to think that IF would or could change its location. Any discussion of location will probably occur under promotion, whereby candidates will discuss ways in which IF can, through promotion, make their location in the city centre a selling point.
Remember that at standard level, the candidates are not expected to know the extended marketing mix but rather just the four Ps: price, place, promotion, product. Candidates should not be penalized if they address the extended
marketing mix.
Marks should be allocated according to the paper 2 markbands for May 2016 forward with further guidance below.
N.B. The marks listed in the far right column are maximum awards. Candidates could technically have a response that addresses two Ps in a balanced way yet still lacks the depth, precision, or application for [4] (for example).
Question
Visionary Toys (VT)
Visionary Toys (VT) produces highly innovative toys for children. VT began operation in January 2017 and its unique selling point/proposition (USP) is producing toy parts with a 3D printer. The financial director presented financial information for VT at the end of 2017. He was concerned about VT’s liquidity.
Table 1: Revenue and expense information for the year 2017 and balance sheet items at 31 December 2017

a. Define the term unique selling point/proposition (USP).[2]
b.i. Construct a fully labelled balance sheet for $V T$ for the end of 2017.[5]
b.ii.Calculate the acid test (quick) ratio for $V T$ for 2018.[1]
c. Explain one way $V T$ could improve its liquidity.[2]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
a. A unique selling point is any aspect of the organization, brand or product that enables differentiation in consumers’ minds from the competitors.
N.B. no application required. Do not credit examples.
Award [1] for a basic definition that conveys partial knowledge and understanding.
Award [2] for a full definition that conveys knowledge and understanding similar to the answer above.
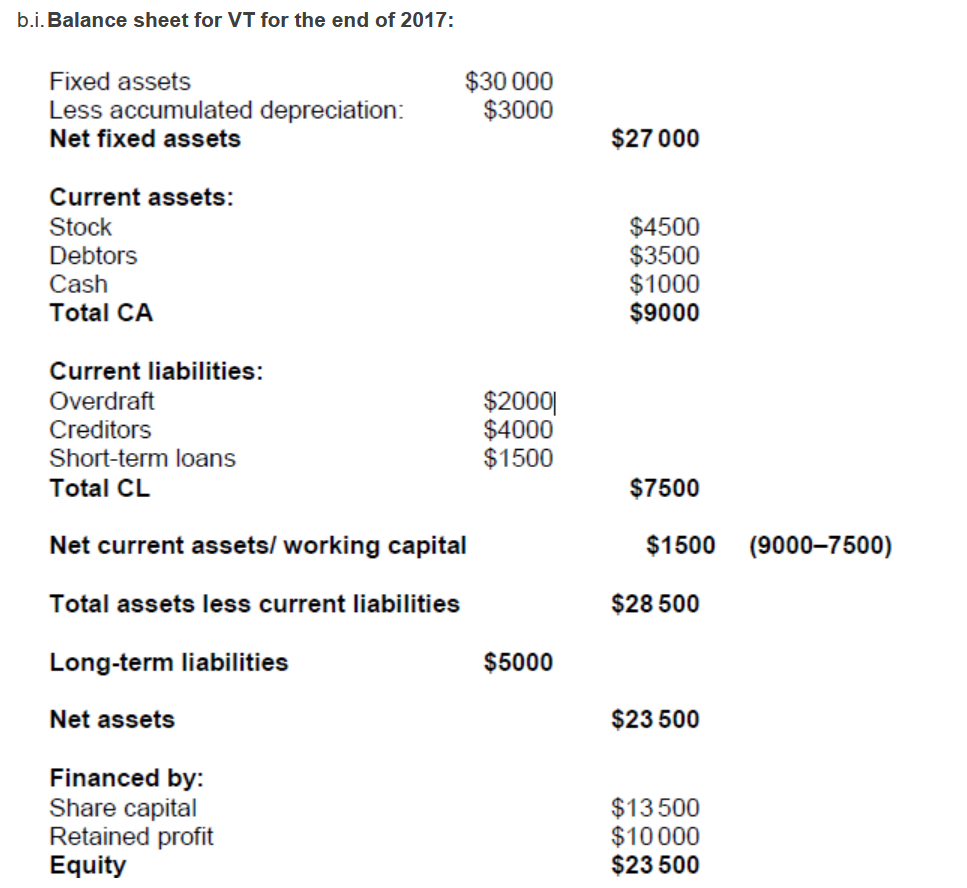
Accurate presentation refers to the correct heading, sub-heading and to the inclusion of all and only the relevant figures.
Allow OFR.[0]
The B/S does not reach a standard described below.[1–2]
The B/S is not accurately constructed, and/or the calculations within and between the various components are not presented or largely incorrect. However, there is limited evidence of a general understanding of the format[3–4]
The principal elements of the B/S are constructed, but may not be entirely accurate. The calculations under each heading/component/part are largely correct.
Allow up to two mistakes in calculations and/or presentation for [3].
Allow for either one error in calculation or one error in presentation [4].
For an accurately constructed B/S with incorrect calculations, award up to a maximum of [3].
Allow OFR.
For example, if one irrelevant figure that belongs to the P/L account is added, obviously the rest will not match.[5]
The B/S is accurately constructed in the expected IBO format. All the relevant headings of each component/ parts are used and correctly classified. Do not penalise for internal order of classification. All and only the relevant figures are presented. No extra irrelevant figures that belong to the P/L are included.
Deduct [1] for one omission including the overall heading provided the B/S is accurately balanced.
N.B. If the candidate did not follow the IBO format award up to [3] marks.
b.ii.Current assets: $\$ 9000$
Stock: $\$ 4500$
Current liabilities: $\$ 7500$
Acid test ratio: $\frac{\$ 9000-\$ 4500}{\$ 7500}=0.6$
Apply OFR where applicable. Candidates are not required to show workings.
Award [1] for a correct answer.
c. Ways VT could improve liquidity include:
- attempt to operate with a lower re-order level of stock
- sell fixed assets and lease long-term assets
- pay less in dividends
- raise capital, either more share capital or long-term debt.
Accept any other acceptable and relevant means to improve liquidity.
If a candidate proposes negotiating longer trade terms with VT’s creditors, award [1]. This response is theoretically correct if all of the funds generated by the longer payment terms are used for no other purpose than building cash. Thus, while theoretically correct (the ATR would go up), it is not a particularly useful approach to the problem.
N.B. The question provides no real opportunity for application and thus application is not expected. However, a response must be relevant to receive full marks.