Question
Sock Paradise (SP)
After conducting primary market research, Pam opened Sock Paradise (SP), which sells colourful socks. SP operates a retail stall in a large department store and sells online through its own website.
Table 2 shows selected financial data for SP for 2020.
Table 2: Selected financial data for SP for 2020
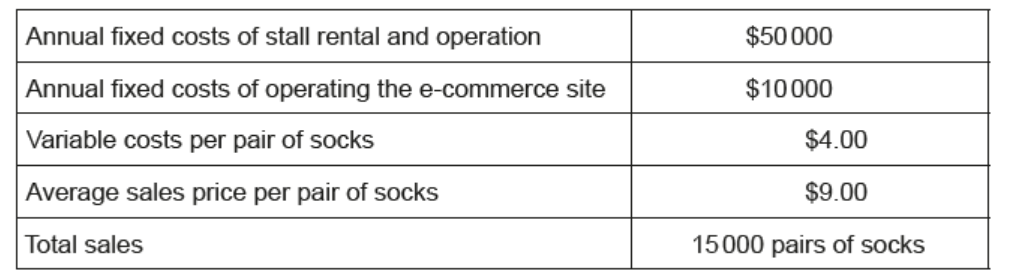
At the end of 2020 , the department store told Pam that it would increase rent by $\$ 14000$ per year starting on 1 January 2021 . Pam forecast total sales for 2021 as 18000 pairs of socks; other costs and prices were forecast to remain unchanged.
a. State two methods of primary market research.[2]
b.i. Using the selected financial data in Table 2, calculate for SP for 2020 :[2]
the break-even level of output (show all your working).
b.ii.Using the selected financial data in Table 2, calculate for SP for 2020 :[2]
the margin of safety (show all your working).
b.iiiUsing the selected financial data in Table 2, calculate for SP for 2020 :[2]
the net profit (show all your working).
c. Explain how the impact of the increase in rent and the forecast increase in sales in 2021 could affect SP’s profitability.[2]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
a.Methods of primary market research include:
Focus groups
Observations
Interviews
Surveys/questionnaires
Accept any other correct form of market research. Award [1] for each method identified up to a maximum of [2].
b.i.
$9.00 minus $4.00 = $5.00 = contribution
= 12 000 units
12 000 units is the break-even level of output. Do NOT penalize if missing word, units.
Award [1] for correct method and [1] for correct answer, for a maximum award of [2].
If a candidate uses a correct alternate method, accept. If a candidate only lists the answer but shows no workings, award [1].
If candidate calculates contribution but gives wrong break-even level of output award [1].
b.iii.
Labelling of figures is not required.
15 000 [total sales in units] − 12 000 [break-even level of output] = 3 000 units or pairs of socks.
3 000 units or pairs of socks is the margin of safety.
Award [1] for correct method and [1] for correct answer, for a maximum award of [2]. Apply OFR if candidate uses incorrect answer from b(i).
N.B. deduct one mark in b(i) and b(ii) for use of inappropriate units e.g. $
b.ii.b.iii.
Actual profit (year 2020)
$9.00 × 15 000 = $135 000 in sales revenue
$50 000 + $10 000 = $60 000 in fixed costs (FC)
$4.00 × 15 000 = $60 000 in variable costs (VC)
Net profit = $135 000 − $60 000 − $60 000 = $15 000
Alternative methods
Net profit = total contribution minus FC (15 000 × $5) − $60 000 = $15 000.
or
Net profit = MoS X contribution per unit = (18 000 − 15 000) × ($9 − $4) = 3 000 × $5 = $15 000
Award [1] for correct method and [1] for correct answer, for a maximum award of [2].
N.B. A break-even chart is not required to be drawn and will gain no marks if presented without the above calculations.
c.
SP’s profitability will probably increase. The increase in rent will add $14 000 to fixed costs. However, if the forecast sales are accurate and prices and costs do not change, then Pam can expect an additional 3000 x $5 in sales revenue ($15 000).
N.B. The actual increase in profit is not required.
Award [1] if the candidates has shown some understanding that profitability is likely to increase. Award an additional mark if in their explanation, they demonstrate some application by using figures from the case study.
N.B. Award [1] if the candidate explains increasing profitability without referring to both rent and sales forecast increases.
N.B. If candidates interpret “profitability” to mean ratios then do not penalize. The explanation would be that profitability decreases from 11.1 % to 9.88 %. For full marks some reference to the figures is necessary.
Question
ExotIce
ExotIce (EI) is a private limited company producing and selling ice cream from a centrally located shop in a large capital city. Lena, the founder and chief executive officer (CEO), owns 80 % of the shares. Her two daughters, who travel the world to find new and exotic natural ingredients for new flavours, each own 10 % of the shares. The family value their freedom in the decision-making process and the collaborative and supportive nature of EI’s culture.
EI’s unique selling point/proposition (USP) is based on:
outstanding quality and a variety of exotic flavours made from fat-free natural ingredients
excellent service provided by highly trained, committed and efficient employees
customer involvement – with the use of sophisticated technology and staff support, customers can experiment to create their own flavours of ice cream.
A strong brand name and brand loyalty has led to rapid growth in EI’s market share.
However, long queues (lines) are forming and the number of customer complaints is increasing. Lena is worried about the negative impact on EI.
Lena is considering two strategic growth options:
Option 1: Opening eight new shops locally and nationally over the next four years. To finance this internal growth, EI will sell new shares. After the sale, Lena will own 51 % of the shares.
Option 2: Franchising EI nationally. A small focus group conducted by one of Lena’s daughters and made up of local entrepreneurs revealed a strong interest in EI’s USP. Ten franchises will open each year for the next five years throughout the country.
a. Define the term unique selling point/proposition (USP).[2]
b. Explain the importance of people and processes in El’s extended marketing mix.
c. Explain one advantage and one disadvantage for $E /$ of using a focus group.$[4]$
d. Recommend which of the two strategic growth options, Option 1 or Option 2, El should implement.[10]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
a. A unique selling point is any aspect of the organization, brand or product that enables differentiation in consumers’ minds from competitors.
N.B. no application required. Do not credit examples.
Award [1] for a basic definition that conveys partial knowledge and understanding.
Award [2] for a full definition that conveys knowledge and understanding similar to the answer above. There should be some reference to differentiation from competition.
Candidates may refer to either the product or brand aspect of the organisation only.
b.
People and process are two out of the three extended marketing mix which that are highly relevant for an organisation that operates in the service sector like EI.
The stimulus refers to people, in this case the employees, who are highly motived, skills, committed and interested. They serve the customers efficiently and interact well with the customers. The characteristics of the employees enhance the lack of some tangibility of the service on top of the actual ice cream of EI. People help to create USP.
Candidates can refer to the daughter as people, who are successfully searching and finding exotics flavours to enhance customers’ satisfaction and create a USP. Do not penalize if candidates refer to employees or staff instead of ‘people’.
Processes
The employees of EI do not only serve the ice cream but constantly interact with those who wish to create their own flavours. Creative freedom and professional employees’ support enable customers to try and create their own flavour. This adds significantly to the quality of their experience and is the basis for EI’s USP. The opportunities given for creativity and testing, enhances customers experience and as stated, create a USP/ clear basis for differentiation.
Candidates can also refer to the process of serving customers efficiently. However, the long queues reported also suggest that process is not always efficient.
Mark as 2 + 2.
Award [1] for each relevant feature – P – explained and [1] for appropriate application to the organization/type of products to a maximum of [2].
[2] cannot be awarded for the importance if the response lacks either explanation and / or application.
For example:
For an identification or a description of one P with or without application [1].
For explanation of a P with no application [1].
For explanation of a P and application [2].
c.
Focus group, a primary research method, involve creating small discussion groups to gain insight into and information about opinion, attitudes and behaviour of the respondents.
The possible advantages:
Lena’s daughter can engage in meaningful discussion with the participants and ask probing questions regarding their willingness/ motivation to open an EI’s franchise, their expectations, experience, reservations and so on. Lena should be more aware of the support that might be needed to ensure that the brand is not damage. A thorough research using a focus group can reduce the risk of failure.
Asking local entrepreneurs may be a good starting point to get some initial responses about the level of interests, motivation, expectations, reservations and so on before a major strategic decision is made.
However:
The use of local entrepreneurs is unlikely to provide the right sample as EI is interested in local as well as national franchising. Moreover, local entrepreneurs are more likely to presume their own business ideas rather than using EI’s. The sampling/targeted group can be seen as inappropriate and might give Lena inappropriate information.
One may doubt Lena’s daughter ability to conduct a focus group. She has no qualification and experience as she travels the world to find exotic flavours. Lack of knowledge and experience can result in inappropriate/ leading questions and hence inappropriate information for Lena to base her decision upon.
Accept any other relevant/ applicable advantage/ disadvantage.
N.B Allow responses that may attempt to cite COVID as a disadvantage of focus groups since they rely heavily on the interaction between participants. Can ‘virtual’ focus groups e.g. Zoom, be as effective.
Mark as 2 + 2.
Award [1] for each relevant advantage/disadvantage- explained and [1] for appropriate application to the organization to a maximum of [2].
[2] cannot be awarded for the importance if the response lacks either explanation and / or application.
For example:
For an identification or a description of one advantage/disadvantage with or without application [1].
For explanation of an advantage/disadvantage with no application [1].
For explanation of an advantage/disadvantage and application [2].
d.
Refer to Paper 2 markbands for 2016 forward, available under the “Your tests” tab > supplemental materials.
The two suggested options should enable EI to take advantage of its own strengths and reduce the main weakness of queues forming which can negatively impacted on EI’s main USP.
More specifically:
Option 1: Internal growth – Issuing shares to open eight shops locally and nationally
By reducing her holding to 51 % Lena can potentially raise enough capital for EI to pursue the organic internal growth option.
Pursuing an internal growth strategy, the nature and the pace of the growth can be fully controlled by Lena/the family especially in the short run. Lena will have full control of the process and the future operation of all of the shops as Lena/the family will still have the majority shares to retain the much-desired ownership, power, control and to make a major strategic decision. The collaborative culture of EI will be maintained. These issues are of high importance for the current owner.
Still Lena will have to get some approval of other shareholders. One may judge this argument as less significant in the short run as the family will have the controlling interest in the business. In addition the only other shareholders are her daughters.
Still, if EI is to grow further, more shares will have to be issued and Lena and the family control will be eroded as it only takes 2 % for the family to lose control. Still, as shares are only sold to friends and family, one may judge this issue as less significant.
EI might also not raise all of the desired finance but this is unlikely as the targeted growth of 8 shops does not seem over ambitious.
Having more shareholders might generate useful strategic input but it appears that Lena is not after shareholders inputs/ involvement – only finance.
However, internal growth is a slower process than franchising and Lena is worried about the queues forming and its potential negative impact on the brand. N.B. do not credit candidates that wrongly assume shares can be sold publicly on a stock market – this is a Private Limited Company.
Option 2: Franchising – External growth/Non-organic growth
Some of the arguments in favour:
The issue of ownership of the business is of no significance. No ownership will be lost.
One may argue EI will be able to expand further with 50 outlets over 5 years. This growth is a much more significant growth and enables EI to build on its strong brand name and enable the brand to spread quickly throughout the country. The issue of the queues and its potential negative impact perhaps be solved quicker.
Moreover, a success might attract other franchises.
EI will receive royalty regardless if the franchise is making a profit or not. However, this is not really an important argument as the motivation is not financial.
However, this method of growth relies on the skills, motivation, the quality of management of the franchises.
Despite some damage to EI’s USP if the franchisees do not follow the exact concept, Lena can terminate the agreement after few years. Still, some of potential damage to EI’s current strong brand/USP may be difficult to correct. It is however less likely as market research revealed that there are interested franchisees.
Still EI’s USP cannot be protected and franchises can get experience and support from EI and start a similar business in the medium term. One may judge this argument as a very significant one as it is easy to open an ice cream shop, it is more difficult to come up and implement EI processes that can be copied.
EI will have to spend money on training costs and to ensure that the same ingredients are sold to each of the franchises to ensure consistency and high standards. El is currently a ‘local’ brand. If franchising is to go ‘national’ then investment in the brand name will be needed.
Control will be remained in the family but EI will have to ensure that each franchisee adheres fully to EI’s format. Poor service as well as poor quality ice cream will result in a major damage to the brand name.
Accept any relevant/ applicable argument for and against each option.
To sum up:
Candidates can recommend any option provided is well substantiated. For example:
Making more profit is not really a significant argument for EI. The issue power/ control and EI’s USP are of higher significance perhaps more than the speed.
Arguments for and against that simply mirror each other, cannot be judged as balanced/ or as two arguments.
Accept any other relevant argument for each option.
It is expected that candidates provide a conclusion with a substantiated judgment.
Accept any substantiated judgment.
Marks should be allocated according to the paper 2 markbands for May 2016 forward.
For one relevant issue that is one-sided, award up to [3]. For more than one relevant issue that is one-sided, award up to a maximum of [4].
If a candidate evaluates / addresses only one option, award a maximum of [5].
A balanced response is one that provides at least one argument for and one argument against each option. A balanced argument for Option 1 must consider both the financing as well as the growth aspect.
Candidates may contrast one option with another for a balance as long as at least two arguments are given for each option.
Award a maximum of [6] if the answer is of a standard that shows balanced analysis and understanding throughout the response with reference to the stimulus material but there is no judgment/conclusion.
Candidates cannot reach the [7–8] markband if they give judgment/conclusions that are not based on analysis/explanation already given in their response.
