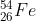Question
Magnetite, Fe3O4, is another ore of iron that contains both Fe2+ and Fe3+.
(a) Deduce the ratio of Fe2+:Fe3+ in Fe3O4. [1]
(b) Iron exists as several isotopes.
(i) State the type of spectroscopy that could be used to determine their relative abundances. [1]
(ii) State the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in each species. [2]
| Protons | Neutrons | Electrons |
| . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . | . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . | . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
| . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . | . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . | . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
(c) Iron has a relatively small specific heat capacity; the temperature of a 50 g sample rises by 44.4°C when it absorbs 1 kJ of heat energy.
Determine the specific heat capacity of iron, in J g–1 K–1. Use section 1 of the data booklet. [1]
(d) A voltaic cell is set up between the Fe2+ (aq) | Fe (s) and Fe3+ (aq) | Fe2+ (aq) half-cells.
Deduce the equation and the cell potential of the spontaneous reaction. Use section 24 of the data booklet. [2]
Equation:
Cell potential:
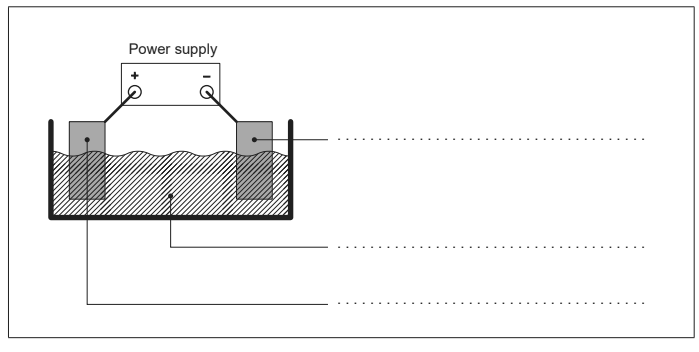
(e) The figure shows an apparatus that could be used to electroplate iron with zinc. Label the figure with the required substances. [2]
(f) Outline why, unlike typical transition metals, zinc compounds are not coloured. [1]
(g) Transition metals like iron can form complex ions. Discuss the bonding between transition metals and their ligands in terms of acid-base theory. [2]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
a 1:2 Accept 2 Fe3+: Fe2+ Do not accept 2:1 only
b i mass «spectroscopy»/MS
b ii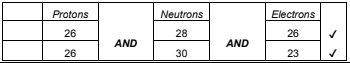
c specific heat capacity « = » = 0.45 «J g −1 K −1»
d
Equation: 2Fe3+ (aq) + Fe(s) → 3Fe2+ (aq)
Cell potential: «+0.77 V − (−0.45 V) = +»1.22 «V»
Do not accept reverse reaction or equilibrium arrow. Do not accept negative value for M2.
e
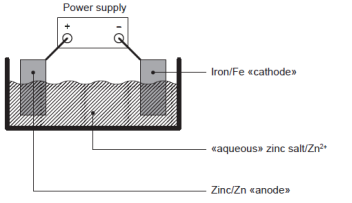
left electrode/anode labelled zinc/Zn AND right electrode/cathode labelled iron/Fe
electrolyte labelled as «aqueous» zinc salt/Zn2+
Accept an inert conductor for the anode. Accept specific zinc salts such as ZnSO4
f
« Zn2+» has a full d-shell
OR does not form « ions with» an incomplete d-shell
Do not accept “Zn is not a transition metal”. Do not accept zinc atoms for zinc ions.
g
ligands donate pairs of electrons to metal ions
OR forms coordinate covalent/dative bond ligands are Lewis bases
AND metal «ions» are Lewis acids
Question
Explain why the relative atomic mass of cobalt is greater than the relative atomic mass of nickel, even though the atomic number of nickel is greater than the atomic number of cobalt.
Deduce the numbers of protons and electrons in the ion \({\text{C}}{{\text{o}}^{2 + }}\).
Deduce the electron configuration for the ion \({\text{C}}{{\text{o}}^{2 + }}\).
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
cobalt has a greater proportion of heavier isotopes / OWTTE / cobalt has greater number of neutrons;
27 protons and 25 electrons;
\({\text{1}}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{2}}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{2}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{6}}}{\text{3}}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{3}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{6}}}{\text{3}}{{\text{d}}^{\text{7}}}/{\text{[Ar] 3}}{{\text{d}}^{\text{7}}}\);
Examiners report
Candidates did reasonably well on this question. Many candidates got (a) correct.
Most candidates got the correct number of protons and electrons in the \({\text{C}}{{\text{o}}^{2 + }}\) ion in part (b).
In (c), a small minority of candidates tried to answer this question with a 2,8,15 type electron arrangement which showed weakness at HL and many candidates did not realise that electrons come out of the 4s level first before the 3d in part (c).