Question
The position of a squirrel running through a field is given by $x(t)=0.5 t^2+t, y(t)=3-t$, where $0 \leqslant t \leqslant 10$ is the time in seconds, and the distance units are metres.
a Find the initial position of the squirrel.
b Find the velocity vector of the squirrel.
c Find the speed of the squirrel after:
i 2 seconds
ii 5 seconds.
d At what time is the squirrel running:
i parallel to $\left(\begin{array}{c}-5 \\ 1\end{array}\right)$
ii perpendicular to $\left(\begin{array}{l}3 \\ 4\end{array}\right)$ ?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Sol:
a
$x(0)=0$ and $y(0)=3$
$\therefore$ the squirrel is initially at $(0,3)$.
The velocity vector can be used
b
$\mathbf{v}=\left(\begin{array}{l}x^{\prime}(t) \\ y^{\prime}(t)\end{array}\right)=\left(\begin{array}{c}t+1 \\ -1\end{array}\right)$ to find the speed and direction of the squirrel at any time.
c i
$\begin{aligned} & \text { When } t=2, \quad \mathbf{v}=\left(\begin{array}{c}3 \\ -1\end{array}\right) \\ & \therefore \quad \text { speed }=\sqrt{3^2+(-1)^2} \\ & \approx 3.16 \mathrm{~m} \mathrm{~s}^{-1} \\ & \end{aligned}$
ii
When
$$
\begin{aligned}
t=5, \quad \mathbf{v} & =\left(\begin{array}{c}
6 \\
-1
\end{array}\right) \\
\therefore \quad \text { speed } & =\sqrt{6^2+(-1)^2} \\
& \approx 6.08 \mathrm{~m} \mathrm{~s}^{-1}
\end{aligned}
$$
d i
The squirrel is running parallel to $\left(\begin{array}{c}-5 \\ 1\end{array}\right)$ when
$$
\begin{aligned}
\left(\begin{array}{c}
t+1 \\
-1
\end{array}\right) & =k\left(\begin{array}{c}
-5 \\
1
\end{array}\right) \text { for some } k \in \mathbb{R} \\
\therefore t+1 & =-5 k \text { and }-1=k \\
\therefore t+1 & =5 \\
\therefore t & =4 \mathrm{~s}
\end{aligned}
$$
ii
The squirrel is running perpendicular to $\left(\begin{array}{l}3 \\ 4\end{array}\right)$ when $\left(\begin{array}{c}t+1 \\ -1\end{array}\right) \cdot\left(\begin{array}{l}3 \\ 4\end{array}\right)=0$
$$
\begin{aligned}
\therefore 3 t+3-4 & =0 \\
\therefore 3 t & =1 \\
\therefore \quad t & =\frac{1}{3} \mathrm{~s}
\end{aligned}
$$
Question
Consider the differential equation $\frac{d y}{d x}=e^x+1$ with $y(0)=1$.
a. Estimate $y(0.5)$ by applying Euler’s method with:
i) $h=0.25$ for two steps
ii) $h=0.1$ for five steps.
b. Find $y(0.5)$ exactly using the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Sol:
$y(0)=1$ gives us $x_0=0$ and $y_0=1$.
(a) (i)
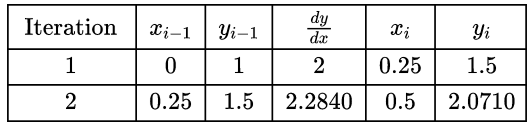
$\therefore \quad y(0.5) \approx 2.0710$
(a) (ii)
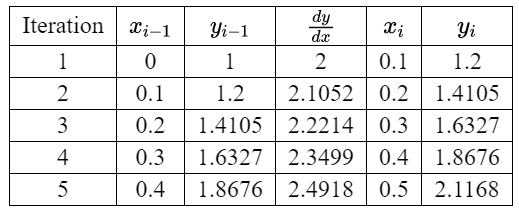
$\therefore \quad y(0.5) \approx 2.1168$
(b)
$y(0.5)=y(0)+\int_0^{0.5} \frac{d y}{d x} d x \quad$ \{Fundamental Theorem of Calculus $\}$
$$
\begin{aligned}
& =1+\int_0^{0.5}\left(e^x+1\right) d x \\
& =1+\left[e^x+x\right]_0^{0.5} \\
& =1+\left(e^{0.5}+0.5\right)-\left(e^0+0\right) \\
& =e^{0.5}+0.5 \\
& \approx 2.1487
\end{aligned}
$$
