Question
The diagram below shows triangle PQR. The length of [PQ] is 7 cm , the length of [PR] is 10 cm , and \({\rm{P}}\widehat {\rm{Q}}{\rm{R}}\) is \(75^\circ \) .
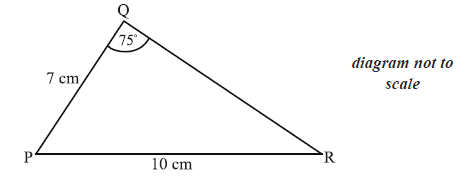
Find \({\rm{P}}\widehat {\rm{R}}{\rm{Q}}\) .
Find the area of triangle PQR.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
choosing sine rule (M1)
correct substitution \(\frac{{\sin R}}{7} = \frac{{\sin 75^\circ }}{{10}}\) A1
\(\sin R = 0.676148 \ldots \)
\({\rm{P}}\widehat {\rm{R}}{\rm{Q = 42}}{\rm{.5}}^\circ \) A1 N2
[3 marks]
\(P = 180 – 75 – R\)
\(P = 62.5\) (A1)
substitution into any correct formula A1
e.g. \({\text{area }}\Delta {\text{PQR}} = \frac{1}{2} \times 7 \times 10 \times \sin ({\text{their }}P)\)
\(= 31.0\) (cm2) A1 N2
[3 marks]
Question
A ship leaves port A on a bearing of \(030^\circ \) . It sails a distance of \(25{\text{ km}}\) to point B. At B, the ship changes direction to a bearing of \(100^\circ \) . It sails a distance of \(40{\text{ km}}\) to reach point C. This information is shown in the diagram below.
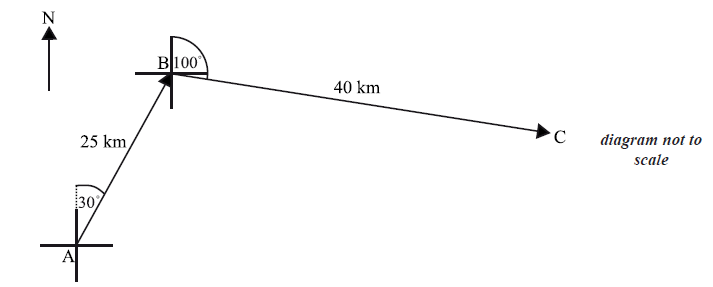
A second ship leaves port A and sails directly to C.
Find the distance the second ship will travel.
Find the bearing of the course taken by the second ship.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
finding \({\text{A}}\widehat {\rm{B}}{\rm{C}} = 110^\circ \) (\( = 1.92\) radians) (A1)
evidence of choosing cosine rule (M1)
e.g. \({\rm{A}}{{\rm{C}}^2} = {\rm{A}}{{\rm{B}}^2} + {\rm{B}}{{\rm{C}}^2} – 2({\rm{AB}})({\rm{BC}})\cos {\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{B}}{\rm{C}}\)
correct substitution A1
e.g. \({\rm{A}}{{\rm{C}}^2} = {25^2} + {40^2} – 2(25)(40)\cos 110^\circ \)
\({\rm{A}}{{\rm{C}}^{}} = 53.9\) (km) A1
METHOD 1
correct substitution into the sine rule A1
e.g. \(\frac{{\sin {\rm{B}}\widehat {\rm{A}}{\rm{C}}}}{{40}} = \frac{{\sin 110^\circ }}{{53.9}}\) A1
\({\rm{B}}\widehat {\rm{A}}{\rm{C}} = 44.2^\circ \)
bearing \( = 074^\circ \) A1 N1
METHOD 2
correct substitution into the cosine rule A1
e.g. \(\cos {\rm{B}}\widehat {\rm{A}}{\rm{C}} = \frac{{{{40}^2} – {{25}^2} – {{53.9}^2}}}{{ – 2(25)(53.9)}}\) A1
\({\rm{B}}\widehat {\rm{A}}{\rm{C}} = 44.3^\circ \)
bearing \( = 074^\circ \) A1 N1
[3 marks]
Question
The circle shown has centre O and radius 3.9 cm.
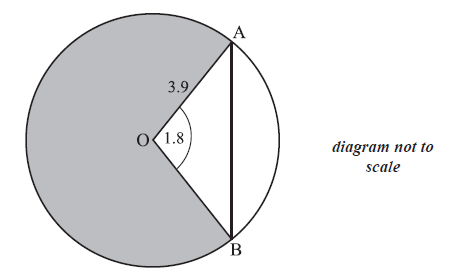
Points A and B lie on the circle and angle AOB is 1.8 radians.
Find AB.
Find the area of the shaded region.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
METHOD 1
choosing cosine rule (M1)
substituting correctly A1
e.g. \({\rm{AB}} = \sqrt {{{3.9}^2} + {{3.9}^2} – 2(3.9)(3.9)\cos 1.8} \)
\({\rm{AB}} = 6.11\) (cm) A1 N2
METHOD 2
evidence of approach involving right-angled triangles (M1)
substituting correctly A1
e.g. \(\sin 0.9 = \frac{x}{{3.9}}\) , \(\frac{1}{2}{\rm{AB}} = 3.9\sin 0.9\)
\({\rm{AB}} = 6.11\) (cm) A1 N2
METHOD 3
choosing the sine rule (M1)
substituting correctly A1
e.g. \(\frac{{\sin 0.670 \ldots }}{{3.9}} = \frac{{\sin 1.8}}{{{\rm{AB}}}}\)
\({\rm{AB}} = 6.11\) (cm) A1 N2
[3 marks]
METHOD 1
reflex \({\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{O}}{\rm{B}} = 2\pi – 1.8\) \(( = 4.4832)\) (A2)
correct substitution \(A = \frac{1}{2}{(3.9)^2}(4.4832 \ldots )\) A1
area =34.1 (cm2) A1 N2
METHOD 2
finding area of circle \(A = \pi {(3.9)^2}\) \(( = 47.78 \ldots )\) (A1)
finding area of (minor) sector \(A = \frac{1}{2}{(3.9)^2}(1.8)\) \(( = 13.68 \ldots )\) (A1)
subtracting M1
e.g. \(\pi {(3.9)^2} – 0.5{(3.9)^2}(1.8)\) , \(47.8 – 13.7\)
area = 34.1 (cm2) A1 N2
METHOD 3
finding reflex \({\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{O}}{\rm{B}} = 2\pi – 1.8\) \(( = 4.4832)\) (A2)
finding proportion of total area of circle A1
e.g. \(\frac{{2\pi – 1.8}}{{2\pi }} \times \pi {(3.9)^2}\) , \(\frac{\theta }{{2\pi }} \times \pi {r^2}\)
area = 34.1 (cm2) A1 N2
[4 marks]
Question
The diagram below shows a triangle ABD with AB =13 cm and AD = 6.5 cm.
Let C be a point on the line BD such that BC = AC = 7 cm.
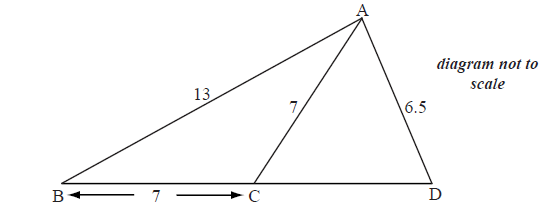
Find the size of angle ACB.
Find the size of angle CAD.
Answer/Explanation
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
METHOD 1
evidence of choosing the cosine formula (M1)
correct substitution A1
e.g. \(\cos {\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{C}}{\rm{B}} = \frac{{{7^2} + {7^2} – {{13}^2}}}{{2 \times 7 \times 7}}\)
\({\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{C}}{\rm{B}} = 2.38\) radians \(( = 136^\circ )\) A1 N2
METHOD 2
evidence of appropriate approach involving right-angled triangles (M1)
correct substitution A1
e.g. \(\sin \left( {\frac{1}{2}{\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{C}}{\rm{B}}} \right) = \frac{{6.5}}{7}\)
\({\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{C}}{\rm{B}} = 2.38\) radians \(( = 136^\circ )\) A1 N2
[3 marks]
METHOD 1
\({\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{C}} {\rm{D}} = \pi – 2.381\) \((180 – 136.4)\) (A1)
evidence of choosing the sine rule in triangle ACD (M1)
correct substitution A1
e.g. \(\frac{{6.5}}{{\sin 0.760 \ldots }} = \frac{7}{{\sin {\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{D}} {\rm{C}}}}\)
\({\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{D}}{\rm{C}} = 0.836 \ldots \) \(( = 47.9 \ldots ^\circ )\) A1
\({\rm{C}}\widehat {\rm{A}}{\rm{D}} = \pi – (0.760 \ldots + 0.836 \ldots )\) \((180 – (43.5 \ldots + 47.9 \ldots ))\)
\( = 1.54\) \(( = 88.5^\circ )\) A1 N3
METHOD 2
\({\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{B}}{\rm{C}} = \frac{1}{2}(\pi – 2.381)\) \(\left( {\frac{1}{2}(180 – 136.4)} \right)\) (A1)
evidence of choosing the sine rule in triangle ABD (M1)
correct substitution A1
e.g. \(\frac{{6.5}}{{\sin 0.380 \ldots }} = \frac{{13}}{{\sin {\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{D}}{\rm{C}}}}\)
\({\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{D}}{\rm{C}} = 0.836 \ldots \) \(( = 47.9 \ldots ^\circ )\) A1
\({\rm{C}}\widehat {\rm{A}}{\rm{D}} = \pi – 0.836 \ldots – (\pi – 2.381 \ldots )\) \(( = 180 – 47.9 \ldots – (180 – 136.4))\)
\( = 1.54\) \(( = 88.5^\circ )\) A1 N3
Note: Two triangles are possible with the given information. If candidate finds \({\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{D}}{\rm{C}} = 2.31\) \((132^\circ )\) leading to \({\rm{C}}\widehat {\rm{A}}{\rm{D}} = 0.076\) \((4.35^\circ )\) , award marks as per markscheme.
[5 marks]
Question
The following diagram shows a circle with centre O and radius 4 cm.
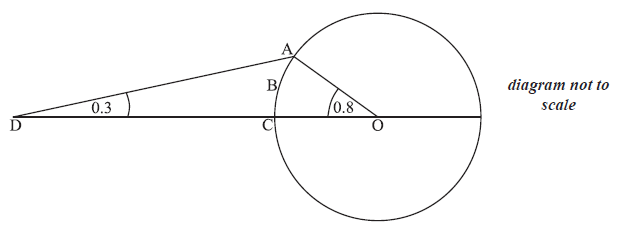
The points A, B and C lie on the circle. The point D is outside the circle, on (OC).
Angle ADC = 0.3 radians and angle AOC = 0.8 radians.
Find AD.
Find OD.
Find the area of sector OABC.
Find the area of region ABCD.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
choosing sine rule (M1)
correct substitution A1
e.g. \(\frac{{{\rm{AD}}}}{{\sin 0.8}} = \frac{4}{{\sin 0.3}}\)
\({\text{AD}} = 9.71{\text{ (cm)}}\) A1 N2
[3 marks]
METHOD 1
finding angle \({\rm{OAD}} = \pi – 1.1 = (2.04)\) (seen anywhere) (A1)
choosing cosine rule (M1)
correct substitution A1
e.g. \({\rm{O}}{{\rm{D}}^2} = {9.71^2} + {4^2} – 2 \times 9.71 \times 4 \times \cos (\pi – 1.1)\)
\({\text{OD}} = 12.1{\text{ (cm)}}\) A1 N3
METHOD 2
finding angle \({\rm{OAD}} = \pi – 1.1 = (2.04)\) (seen anywhere) (A1)
choosing sine rule (M1)
correct substitution A1
e.g. \(\frac{{{\rm{OD}}}}{{\sin (\pi – 1.1)}} = \frac{{9.71}}{{\sin 0.8}} = \frac{4}{{\sin 0.3}}\)
\({\text{OD}} = 12.1{\text{ (cm)}}\) A1 N3
[4 marks]
correct substitution into area of a sector formula (A1)
e.g. \({\rm{area}} = 0.5 \times {4^2} \times 0.8\)
\({\text{area}} = 6.4{\text{ (c}}{{\text{m}}^2}{\text{)}}\) A1 N2
[2 marks]
substitution into area of triangle formula OAD (M1)
correct substitution A1
e.g. \(A{\rm{ = }}\frac{1}{2} \times 4 \times 12.1 \times \sin 0.8\) , \(A{\rm{ = }}\frac{1}{2} \times 4 \times 9.71 \times \sin 2.04\) , \(A{\rm{ = }}\frac{1}{2} \times 12.1 \times 9.71 \times \sin 0.3\)
subtracting area of sector OABC from area of triangle OAD (M1)
e.g. \({\text{area ABCD}} = 17.3067 – 6.4\)
\({\text{area ABCD}} = 10.9{\text{ (c}}{{\text{m}}^2}{\text{)}}\) A1 N2
[4 marks]
Question
The following diagram shows \(\Delta {\rm{PQR}}\) , where RQ = 9 cm, \({\rm{P\hat RQ}} = {70^ \circ }\) and \({\rm{P\hat QR}} = {45^ \circ }\) .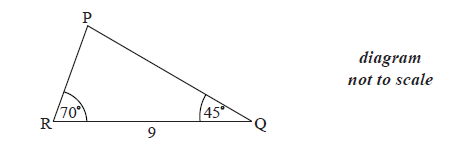
Find \({\rm{R\hat PQ}}\) .
Find PR .
Find the area of \(\Delta {\rm{PQR}}\) .
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\({\rm{R\hat PQ = }}{65^ \circ }\) A1 N1
[1 mark]
evidence of choosing sine rule (M1)
correct substitution A1
e.g. \(\frac{{{\rm{PR}}}}{{\sin {{45}^ \circ }}} = \frac{9}{{\sin {{65}^ \circ }}}\)
7.021854078
\({\rm{PR}} = 7.02\) A1 N2
[3 marks]
correct substitution (A1)
e.g. \({\rm{area}} = \frac{1}{2} \times 9 \times 7.02 \ldots \times \sin {70^ \circ }\)
\(29.69273008\)
\({\rm{area}} = 29.7\) A1 N2
[2 marks]
Question
The diagram shows a circle of radius \(8\) metres. The points ABCD lie on the circumference of the circle.
BC = \(14\) m, CD = \(11.5\) m, AD = \(8\) m, \(A\hat DC = {104^ \circ }\) , and \(B\hat CD = {73^ \circ }\) .
Find AC.
(i) Find \(A\hat CD\) .
(ii) Hence, find \(A\hat CB\) .
Find the area of triangle ADC.
(c) Find the area of triangle ADC.
(d) Hence or otherwise, find the total area of the shaded regions.
Hence or otherwise, find the total area of the shaded regions.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
evidence of choosing cosine rule (M1)
eg \({c^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} – 2ab\cos C\) , \({\rm{C}}{{\rm{D}}^2} + {\rm{A}}{{\rm{D}}^2} – 2 \times {\rm{CD}} \times {\rm{AD}}\cos D\)
correct substitution A1
eg \({11.5^2} + {8^2} – 2 \times 11.5 \times 8\cos 104\) , \(196.25 – 184\cos 104\)
AC \( = 15.5\) (m) A1 N2
[3 marks]
(i) METHOD 1
evidence of choosing sine rule (M1)
eg \(\frac{{\sin A}}{a} = \frac{{\sin B}}{b}\) , \(\frac{{\sin {\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{C}}{\rm{D}}}}{{{\rm{AD}}}} = \frac{{\sin D}}{{{\rm{AC}}}}\)
correct substitution A1
eg \(\frac{{\sin {\rm{A}}\hat {\rm{C}}{\rm{D}}}}{8} = \frac{{\sin 104}}{{15.516 \ldots }}\)
\({\rm{A}}\hat {\rm{C}}{\rm{D}} = {30.0^ \circ }\) A1 N2
METHOD 2
evidence of choosing cosine rule (M1)
eg \({c^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} – 2ab\cos C\)
correct substitution A1
e.g. \({8^2} = {11.5^2} + 15.516{ \ldots ^2} – 2(11.5)(15.516 \ldots )\cos C\)
\({\rm{A}}\hat {\rm{C}}{\rm{D}} = {30.0^ \circ }\) A1 N2
(ii) subtracting their \({\rm{A}}\hat {\rm{C}}{\rm{D}}\) from \(73\) (M1)
eg \({\rm{7}}3 – {\rm{A}}\hat {\rm{C}}{\rm{D}}\) , \(70 – 30.017 \ldots \)
\({\rm{A}}\hat {\rm{C}}{\rm{B}} = {43.0^ \circ }\) A1 N2
[5 marks]
correct substitution (A1)
eg area \(\Delta {\rm{ADC}} = \frac{1}{2}(8)(11.5)\sin 104\)
area \( = 44.6\) (m2) A1 N2
[2 marks]
(c) correct substitution (A1)
eg area \(\Delta {\rm{ADC}} = \frac{1}{2}(8)(11.5)\sin 104\)
area \( = 44.6\) (m2) A1 N2
[2 marks]
(d) attempt to subtract (M1)
eg \({\rm{circle}} – {\rm{ABCD}}\) , \(\pi {r^2} – \Delta {\rm{ADC}} – \Delta {\rm{ACB}}\)
area \(\Delta {\rm{ACB = }}\frac{1}{2}(15.516 \ldots )(14)\sin 42.98\) (A1)
correct working A1
eg \(\pi {(8)^2} – 44.6336 \ldots – \frac{1}{2}(15.516 \ldots )(14)\sin 42.98\) , \(64\pi – 44.6 – 74.1\)
shaded area is \(82.4\) (m2) A1 N3
[4 marks]
Total [6 marks]
attempt to subtract (M1)
eg \({\rm{circle}} – {\rm{ABCD}}\) , \(\pi {r^2} – \Delta {\rm{ADC}} – \Delta {\rm{ACB}}\)
area \(\Delta {\rm{ACB = }}\frac{1}{2}(15.516 \ldots )(14)\sin 42.98\) (A1)
correct working A1
eg \(\pi {(8)^2} – 44.6336 \ldots – \frac{1}{2}(15.516 \ldots )(14)\sin 42.98\) , \(64\pi – 44.6 – 74.1\)
shaded area is \(82.4\) (m2) A1 N3
[4 marks]
Total [6 marks]
Question
The following diagram shows a triangle ABC.
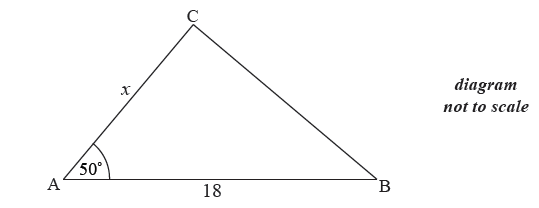
The area of triangle ABC is \(80\) cm2 , AB \( = 18\) cm , AC \( = x\) cm and \({\rm{B}}\hat {\rm{A}}{\rm{C}} = {50^ \circ }\) .
Find \(x\) .
Find BC.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
correct substitution into area formula (A1)
eg \(\frac{1}{2}(18x)\sin 50\)
setting their area expression equal to \(80\) (M1)
eg \(9x\sin 50 = 80\)
\(x = 11.6\) A1 N2
[3 marks]
evidence of choosing cosine rule (M1)
eg \({c^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab\sin C\)
correct substitution into right hand side (may be in terms of \(x\)) (A1)
eg \({11.6^2} + {18^2} – 2(11.6)(18)\cos 50\)
BC \( = 13.8\) A1 N2
[3 marks]
Question
Consider a circle with centre \(\rm{O}\) and radius \(7\) cm. Triangle \(\rm{ABC}\) is drawn such that its vertices are on the circumference of the circle.
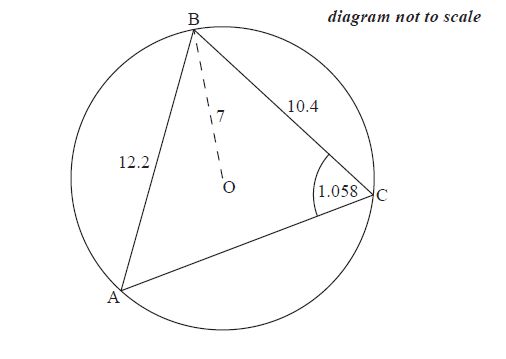
\(\rm{AB}=12.2\) cm, \(\rm{BC}=10.4\) cm and \(\rm{A}\hat{\rm{C}}\rm{B}=1.058\) radians.
Find \({\rm{B\hat AC}}\).
Find \({\text{AC}}\).
Hence or otherwise, find the length of arc \({\text{ABC}}\).
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Notes: In this question, there may be slight differences in answers, depending on which values candidates carry through in subsequent parts. Accept answers that are consistent with their working.
Candidates may have their GDCs in degree mode, leading to incorrect answers. If working shown, award marks in line with the markscheme, with FT as appropriate.
Ignore missing or incorrect units.
evidence of choosing sine rule (M1)
eg \(\frac{{\sin \hat A}}{a} = \frac{{\sin \hat B}}{b}\)
correct substitution (A1)
eg \(\frac{{\sin \hat A}}{{10.4}} = \frac{{\sin 1.058}}{{12.2}}\)
\({\rm{B\hat AC}} = 0.837\) A1 N2
[3 marks]
Notes: In this question, there may be slight differences in answers, depending on which values candidates carry through in subsequent parts. Accept answers that are consistent with their working.
Candidates may have their GDCs in degree mode, leading to incorrect answers. If working shown, award marks in line with the markscheme, with FT as appropriate.
Ignore missing or incorrect units.
METHOD 1
evidence of subtracting angles from \(\pi \) (M1)
eg \({\rm{A\hat BC}} = \pi – A – C\)
correct angle (seen anywhere) A1
\({\rm{A\hat BC}} = \pi – 1.058 – 0.837,{\text{ }}1.246,{\text{ }}71.4^\circ \)
attempt to substitute into cosine or sine rule (M1)
correct substitution (A1)
eg \({12.2^2} + {10.4^2} – 2 \times 12.2 \times 10.4\cos 71.4,{\text{ }}\frac{{{\text{AC}}}}{{\sin 1.246}} = \frac{{12.2}}{{\sin 1.058}}\)
\({\text{AC}} = 13.3{\text{ (cm)}}\) A1 N3
METHOD 2
evidence of choosing cosine rule M1
eg \({a^2} = {b^2} + {c^2} – 2bc\cos A\)
correct substitution (A2)
eg \({12.2^2} = {10.4^2} + {b^2} – 2 \times 10.4b\cos 1.058\)
\({\text{AC}} = 13.3{\text{ (cm)}}\) A2 N3
[5 marks]
Notes: In this question, there may be slight differences in answers, depending on which values candidates carry through in subsequent parts. Accept answers that are consistent with their working.
Candidates may have their GDCs in degree mode, leading to incorrect answers. If working shown, award marks in line with the markscheme, with FT as appropriate.
Ignore missing or incorrect units.
METHOD 1
valid approach (M1)
eg \(\cos {\rm{A\hat OC}} = \frac{{{\text{O}}{{\text{A}}^2} + {\text{O}}{{\text{C}}^2} – {\text{A}}{{\text{C}}^2}}}{{2 \times {\text{OA}} \times {\text{OC}}}}\), \({\rm{A\hat OC}} = 2 \times {\rm{A\hat BC}}\)
correct working (A1)
eg \({\text{13.}}{{\text{3}}^2} = {7^2} + {7^2} – 2 \times 7 \times 7\cos {\rm{A\hat OC}},{\text{ }}O = 2 \times 1.246\)
\({\rm{A\hat OC}} = 2.492{\text{ }}(142.8^\circ )\) (A1)
EITHER
correct substitution for arc length (seen anywhere) A1
eg \(2.492 = \frac{l}{7},{\text{ }}l = 17.4,{\text{ }}14\pi \times \frac{{142.8}}{{360}}\)
subtracting arc from circumference (M1)
eg \(2\pi r – l,{\text{ }}14\pi = 17.4\)
OR
attempt to find \({\rm{A\hat OC}}\) reflex (M1)
eg \(2\pi – 2.492,{\text{ }}3.79,{\text{ }}360 – 142.8\)
correct substitution for arc length (seen anywhere) A1
eg \(l = 7 \times 3.79,{\text{ }}14\pi \times \frac{{217.2}}{{360}}\)
THEN
\({\text{arc ABC}} = 26.5\) A1 N4
METHOD 2
valid approach to find \({\rm{A\hat OB}}\) or \({\rm{B\hat OC}}\) (M1)
eg choosing cos rule, twice angle at circumference
correct working for finding one value, \({\rm{A\hat OB}}\) or \({\rm{B\hat OC}}\) (A1)
eg \(\cos {\rm{A\hat OB}} = \frac{{{7^2} + {7^2} – {{12.2}^2}}}{{2 \times 7 \times 7}}\), \({\rm{A\hat OB}} = 2.116,{\rm{B\hat OC}} = 1.6745\)
two correct calculations for arc lengths
eg \({\text{AB}} = 7 \times 2 \times 1.058{\text{ }}( = 14.8135),{\text{ }}7 \times 1.6745{\text{ }}( = 11.7216)\) (A1)(A1)
adding their arc lengths (seen anywhere)
eg \(r{\rm{A\hat OB}} + r{\rm{B\hat OC}},{\text{ }}14.8135 + 11.7216,{\text{ }}7(2.116 + 1.6745)\) M1
\({\text{arc ABC}} = 26.5{\text{ (cm)}}\) A1 N4
Note: Candidates may work with other interior triangles using a similar method. Check calculations carefully and award marks in line with markscheme.
[6 marks]
Question
The following diagram shows triangle ABC.
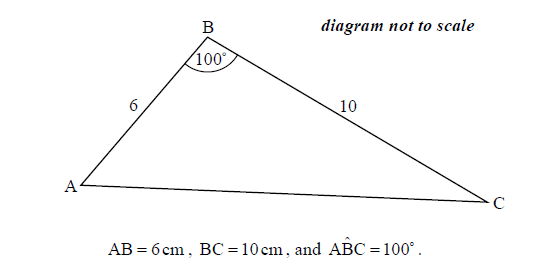
Find AC.
Find \({\rm{B\hat CA}}\).
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
evidence of choosing cosine rule (M1)
eg \({\text{A}}{{\text{C}}^2} = {\text{A}}{{\text{B}}^2} + {\text{B}}{{\text{C}}^2} – 2({\text{AB}})({\text{BC}})\cos ({\rm{A\hat BC}})\)
correct substitution into the right-hand side (A1)
eg \({6^2} + {10^2} – 2(6)(10)\cos {100^ \circ }\)
\({\text{AC}} = 12.5234\)
\({\text{AC}} = 12.5{\text{ (cm)}}\) A1 N2
[3 marks]
evidence of choosing a valid approach (M1)
eg sine rule, cosine rule
correct substitution (A1)
eg \(\frac{{\sin ({\rm{B\hat CA)}}}}{6} = \frac{{\sin 100^\circ }}{{12.5}},{\text{ }}\cos ({\rm{B\hat CA)}} = \frac{{{{({\text{AC}})}^2} + {{10}^2} – {6^2}}}{{2({\text{AC}})(10)}}\)
\({\rm{B\hat CA}} = 28.1525\)
\({\rm{B\hat CA}} = 28.2^\circ\) A1 N2
[3 marks]
Question
In triangle \(\rm{ABC}\), \(\rm{AB} = 6\,\rm{cm}\) and \(\rm{AC} = 8\,\rm{cm}\). The area of the triangle is \(16\,\rm{cm}^2\).
Find the two possible values for \(\hat A\).
Given that \(\hat A\) is obtuse, find \({\text{BC}}\).
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
correct substitution into area formula (A1)
eg \(\frac{1}{2}(6)(8)\sin A = 16,{\text{ }}\sin A = \frac{{16}}{{24}}\)
correct working (A1)
eg \(A = \arcsin \left( {\frac{2}{3}} \right)\)
\(A = 0.729727656…, 2.41186499…\); \((41.8103149^\circ, 138.1896851^\circ)\)
\(A = 0.730\); \(2.41\) A1A1 N3
(accept degrees ie \(41.8^\circ\); \(138^\circ\))
[4 marks]
evidence of choosing cosine rule (M1)
eg \({\text{B}}{{\text{C}}^2} = {\text{A}}{{\text{B}}^2} + {\text{A}}{{\text{C}}^2} – 2({\text{AB)(AC)}}\cos A,{\text{ }}{a^2} + {b^2} – 2ab\cos C\)
correct substitution into RHS (angle must be obtuse) (A1)
eg \({\text{B}}{{\text{C}}^2} = {6^2} + {8^2} – 2(6)(8)\cos 2.41,{\text{ }}{6^2} + {8^2} – 2(6)(8)\cos 138^\circ \),
\({\text{BC}} = \sqrt {171.55} \)
\({\text{BC}} = 13.09786\)
\({\text{BC}} = 13.1{\text{ cm}}\) A1 N2
[3 marks]
Question
The following diagram shows a circle with centre \(O\) and radius \(8\) cm.
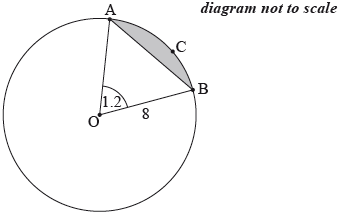
The points \(A\), \(B\) and \(C\) are on the circumference of the circle, and \({\rm{A\hat OB}}\) radians.
Find the length of arc \(ACB\).
Find \(AB\).
Hence, find the perimeter of the shaded segment \(ABC\).
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
correct substitution into formula (A1)
eg\(\;\;\;\)\(l = 1.2 \times 8\)
\(9.6{\text{ (cm)}}\) A1 N2
[2 marks]
METHOD 1
evidence of choosing cosine rule (M1)
eg\(\;\;\;\)\(2{r^2} – 2 \times {r^2} \times \cos ({\rm{A\hat OB)}}\)
correct substitution into right hand side (A1)
eg\(\;\;\;\)\({8^2} + {8^2} – 2 \times 8 \times 8 \times \cos (1.2)\)
\(9.0342795\)
\({\text{AB}} = 9.03{\text{ }}[9.03,{\text{ }}9.04]{\text{ (cm)}}\) A1 N2
METHOD 2
evidence of choosing sine rule (M1)
eg\(\;\;\;\)\(\frac{{{\text{AB}}}}{{\sin ({\rm{A\hat OB)}}}} = \frac{{{\text{OB}}}}{{\sin ({\rm{O\hat AB)}}}}\)
finding angle \(OAB\) or \(OBA\) (may be seen in substitution) (A1)
eg\(\;\;\;\)\(\frac{{\pi – 1.2}}{2},{\text{ }}0.970796\)
\({\text{AB}} = 9.03{\text{ }}[9.03,{\text{ }}9.04]{\text{ (cm)}}\) A1 N2
[3 marks]
correct working (A1)
eg\(\;\;\;\)\(P = 9.6 + 9.03\)
\(18.6342\)
\(18.6{\text{ }}[18.6,{\text{ }}18.7]{\text{ (cm)}}\) A1 N2
[2 marks]
Total [7 marks]
Question
The following diagram shows the quadrilateral \(ABCD\).
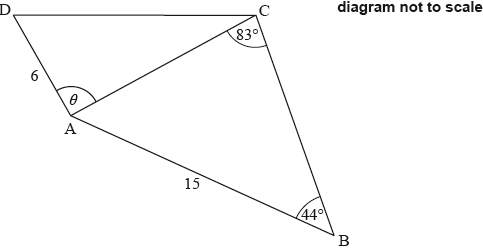
\[{\text{AD}} = 6{\text{ cm}},{\text{ AB}} = 15{\text{ cm}},{\rm{ A\hat BC}} = 44^\circ ,{\rm{ A\hat CB}} = 83^\circ {\rm{ and D\hat AC}} = \theta \]
Find \(AC\).
Find the area of triangle \(ABC\).
The area of triangle \(ACD\) is half the area of triangle \(ABC\).
Find the possible values of \(\theta \).
Given that \(\theta \) is obtuse, find \(CD\).
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
evidence of choosing sine rule (M1)
eg\(\;\;\;\frac{{{\text{AC}}}}{{\sin {\rm{C\hat BA}}}} = \frac{{{\text{AB}}}}{{\sin {\rm{A\hat CB}}}}\)
correct substitution (A1)
eg\(\;\;\;\frac{{{\text{AC}}}}{{\sin 44^\circ }} = \frac{{15}}{{\sin 83^\circ }}\)
\(10.4981\)
\({\text{AC}} = 10.5{\text{ }}{\text{ (cm)}}\) A1 N2
[3 marks]
finding \({\rm{C\hat AB}}\) (seen anywhere) (A1)
eg\(\;\;\;180^\circ – 44^\circ – 83^\circ ,{\rm{ C\hat AB}} = 53^\circ \)
correct substitution for area of triangle \(ABC\) A1
eg\(\;\;\;\frac{1}{2} \times 15 \times 10.4981 \times \sin 53^\circ \)
62.8813
\({\text{area}} = 62.9{\text{ }}{\text{ (c}}{{\text{m}}^2}{\text{)}}\) A1 N2
[3 marks]
correct substitution for area of triangle \(DAC\) (A1)
eg\(\;\;\;\frac{1}{2} \times 6 \times 10.4981 \times \sin \theta \)
attempt to equate area of triangle \(ACD\) to half the area of triangle \(ABC\) (M1)
eg\(\;\;\;{\text{area ACD}} = \frac{1}{2} \times {\text{ area ABC; 2ACD}} = {\text{ABC}}\)
correct equation A1
eg\(\;\;\;\frac{1}{2} \times 6 \times 10.4981 \times \sin \theta = \frac{1}{2}(62.9),{\text{ }}62.9887\sin \theta = 62.8813,{\text{ }}\sin \theta = 0.998294\)
\(86.6531\), \(93.3468\)
\(\theta = 86.7^\circ {\text{ }},{\text{ }}\theta = 93.3^\circ {\text{ }}\) A1A1 N2
[5 marks]
Note: Note: If candidates use an acute angle from part (c) in the cosine rule, award M1A0A0 in part (d).
evidence of choosing cosine rule (M1)
eg\(\;\;\;{\text{C}}{{\text{D}}^2} = {\text{A}}{{\text{D}}^2} + {\text{A}}{{\text{C}}^2} – 2 \times {\text{AD}} \times {\text{AC}} \times \cos \theta \)
correct substitution into rhs (A1)
eg\(\;\;\;{\text{C}}{{\text{D}}^2} = {6^2} + {10.498^2} – 2(6)(10.498)\cos 93.336^\circ \)
\(12.3921\)
\(12.4{\text{ }}{\text{ (cm)}}\) A1 N2
[3 marks]
Total [14 marks]
Question
The following diagram shows a pole BT 1.6 m tall on the roof of a vertical building.
The angle of depression from T to a point A on the horizontal ground is \({35^ \circ }\) .
The angle of elevation of the top of the building from A is \({30^ \circ }\) .
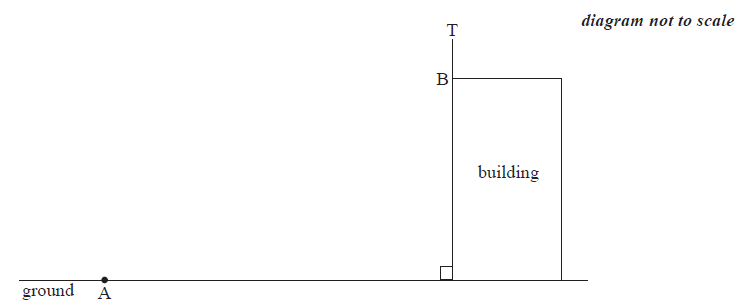
Find the height of the building.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
METHOD 1
appropriate approach M1
e.g. completed diagram
attempt at set up A1
e.g. correct placement of one angle
\(\tan 30 = \frac{h}{x}\) , \(\tan 35 = \frac{{h + 1.6}}{x}\) A1A1
attempt to set up equation M1
e.g. isolate x
correct equation A1
e.g. \(\frac{h}{{\tan 30}} = \frac{{h + 1.6}}{{\tan 35}}\)
\(h = 7.52\) A1 N3
METHOD 2
\(\sin 30 = \frac{h}{l}\) A1
in triangle ATB, \(\widehat A = {5^ \circ }\) , \(\widehat T = {55^ \circ }\) A1A1
choosing sine rule M1
correct substitution
e.g. \(\frac{{h/\sin 30}}{{\sin 55}} = \frac{{1.6}}{{\sin 5}}\) A1
\(h = \frac{{1.6 \times \sin 30 \times \sin 55}}{{\sin 5}}\) A1
\(h = 7.52\) A1 N3
[7 marks]

