Question
Two fair 4-sided dice, one red and one green, are thrown. For each die, the faces are labelled 1, 2, 3, 4. The score for each die is the number which lands face down.
List the pairs of scores that give a sum of 6.
The probability distribution for the sum of the scores on the two dice is shown below.
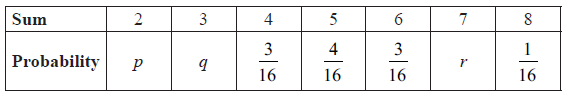
Find the value of p , of q , and of r .
Fred plays a game. He throws two fair 4-sided dice four times. He wins a prize if the sum is 5 on three or more throws.
Find the probability that Fred wins a prize.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
three correct pairs A1A1A1 N3
e.g. (2, 4), (3, 3), (4, 2) , R2G4, R3G3, R4G2
[3 marks]
\(p = \frac{1}{{16}}\) , \(q = \frac{2}{{16}}\) , \(r = \frac{2}{{16}}\) A1A1A1 N3
[3 marks]
let X be the number of times the sum of the dice is 5
evidence of valid approach (M1)
e.g. \(X \sim {\rm{B}}(n{\text{, }}p)\) , tree diagram, 5 sets of outcomes produce a win
one correct parameter (A1)
e.g. \(n = 4\) , \(p = 0.25\) , \(q = 0.75\)
Fred wins prize is \({\rm{P}}(X \ge 3)\) (A1)
appropriate approach to find probability M1
e.g. complement, summing probabilities, using a CDF function
correct substitution (A1)
e.g. \(1 – 0.949 \ldots \) , \(1 – \frac{{243}}{{256}}\) , \(0.046875 + 0.00390625\) , \(\frac{{12}}{{256}} + \frac{1}{{256}}\)
\({\text{probability of winning}} = 0.0508\) \(\left( {\frac{{13}}{{256}}} \right)\) A1 N3
[6 marks]
Question
Two events A and B are such that P(A) = 0.62 and P\(\left( {A \cap B} \right)\) = 0.18.
Find P(A ∩ B′ ).
Given that P((A ∪ B)′ ) = 0.19, find P(A | B′ ).
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
valid approach
eg Venn diagram, P(A) − P (A ∩ B), 0.62 − 0.18 (M1)
P(A ∩ B’ ) = 0.44 A1 N2
[2 marks]
valid approach to find either P(B′ ) or P(B) (M1)
eg (seen anywhere), 1 − P(A ∩ B′ ) − P((A ∪ B)′ )
correct calculation for P(B′ ) or P(B) (A1)
eg 0.44 + 0.19, 0.81 − 0.62 + 0.18
correct substitution into \(\frac{{{\text{P}}\left( {A \cap B’} \right)}}{{{\text{P}}\left( {B’} \right)}}\) (A1)
eg \(\frac{{0.44}}{{0.19 + 0.44}},\,\,\frac{{0.44}}{{1 – 0.37}}\)
0.698412
P(A | B′ ) = \(\frac{{44}}{{63}}\) (exact), 0.698 A1 N3
[4 marks]

