Question
Two boxes contain numbered cards as shown below.
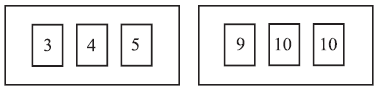
a.Two cards are drawn at random, one from each box.
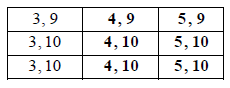
Copy and complete the table below to show all nine equally likely outcomes.
 [2]
[2]
b.Let S be the sum of the numbers on the two cards.
Find the probability of each value of S.[2]
c.Find the expected value of S.[3]
d.Anna plays a game where she wins \(\$ 50\) if S is even and loses \(\$ 30\) if S is odd.
Anna plays the game 36 times. Find the amount she expects to have at the end of the 36 games.[3]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
 A2 N2
A2 N2
[2 marks]
\({\rm{P}}(12) = \frac{1}{9}\) , \({\rm{P}}(13) = \frac{3}{9}\) , \({\rm{P}}(14) = \frac{3}{9}\) , \({\rm{P}}(15) = \frac{2}{9}\) A2 N2
[2 marks]
correct substitution into formula for \({\text{E}}(X)\) A1
e.g. \({\rm{E}}(S) = 12 \times \frac{1}{9} + 13 \times \frac{3}{9} + 14 \times \frac{3}{9} + 15 \times \frac{2}{9}\)
\({\rm{E}}(S) = \frac{{123}}{9}\) A2 N2
[3 marks]
METHOD 1
correct expression for expected gain E(A) for 1 game (A1)
e.g. \(\frac{4}{9} \times 50 – \frac{5}{9} \times 30\)
\({\rm{E}}(A) = \frac{{50}}{9}\)
amount at end = expected gain for 1 game \( \times 36\) (M1)
= 200 (dollars) A1 N2
METHOD 2
attempt to find expected number of wins and losses (M1)
e.g. \(\frac{4}{9} \times 36\) , \(\frac{5}{9} \times 36\)
attempt to find expected gain E(G) (M1)
e.g. \(16 \times 50 – 30 \times 20\)
\({\text{E}}(G) = 200\) (dollars) A1 N2
[3 marks]
Question
The probability distribution of a discrete random variable X is given by \[{\rm{P}}(X = x) = \frac{{{x^2}}}{{14}}{\text{, }}x \in \left\{ {1{\text{, }}2{\text{, }}k} \right\}{\text{, where}} k > 0\] .
a.Write down \({\rm{P}}(X = 2)\) .[1]
b.Show that \(k = 3\) .[4]
c.Find \({\rm{E}}(X)\) .[2]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\({\rm{P}}(X = 2) = \frac{4}{{14}}\) \(\left( { = \frac{2}{7}} \right)\) A1 N1
[1 mark]
\({\rm{P}}(X = 1) = \frac{1}{{14}}\) (A1)
\({\rm{P}}(X = k) = \frac{{{k^2}}}{{14}}\) (A1)
setting the sum of probabilities \( = 1\) M1
e.g. \(\frac{1}{{14}} + \frac{4}{{14}} + \frac{{{k^2}}}{{14}} = 1\) , \(5 + {k^2} = 14\)
\({k^2} = 9\) (accept \(\frac{{{k^2}}}{{14}} = \frac{9}{{14}}\) ) A1
\(k = 3\) AG N0
[4 marks]
correct substitution into \({\rm{E}}(X) = \sum {x{\rm{P}}(X = x)} \) A1
e.g. \(1\left( {\frac{1}{{14}}} \right) + 2\left( {\frac{4}{{14}}} \right) + 3\left( {\frac{9}{{14}}} \right)\)
\({\rm{E}}(X) = \frac{{36}}{{14}}\) \(\left( { = \frac{{18}}{7}} \right)\) A1 N1
[2 marks]
Question
The random variable X has the following probability distribution, with \({\rm{P}}(X > 1) = 0.5\) .
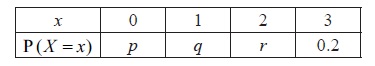
a.Find the value of r .[2]
b.Given that \({\rm{E}}(X) = 1.4\) , find the value of p and of q .[6]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
attempt to substitute \({\rm{P}}(X > 1) = 0.5\) (M1)
e.g. \(r + 0.2 = 0.5\)
\(r = 0.3\) A1 N2
[2 marks]
correct substitution into \({\rm{E}}(X)\) (seen anywhere) (A1)
e.g. \(0 \times p + 1 \times q + 2 \times r + 3 \times 0.2\)
correct equation A1
e.g. \(q + 2 \times 0.3 + 3 \times 0.2 = 1.4\) , \(q + 1.2 = 1.4\)
\(q = 0.2\) A1 N1
evidence of choosing \(\sum {{p_i} = 1} \) M1
e.g. \(p + 0.2 + 0.3 + 0.2 = 1\) , \(p + q = 0.5\)
correct working (A1)
\(p + 0.7 = 1\) , \(1 – 0.2 – 0.3 – 0.2\) , \(p + 0.2 = 0.5\)
\(p = 0.3\) A1 N2
Note: Exception to the FT rule. Award FT marks on an incorrect value of q, even if q is an inappropriate value. Do not award the final A mark for an inappropriate value of p.
[6 marks]
Question
Let \(\boldsymbol{A} = \left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
0&3 \\
{ – 2}&4
\end{array}} \right)\) and \(\boldsymbol{B} = \left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{ – 4}&0 \\
5&1
\end{array}} \right)\).
a.Find AB .[3]
b.Given that \({\boldsymbol{X}} – 2{\boldsymbol{A}} = {\boldsymbol{B}}\), find X.[3]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
evidence of multiplying (M1)
e.g. one correct element, \((0 \times – 4) + (3 \times 5)\)
\({\boldsymbol{AB}} = \left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{15}&3\\
{28}&4
\end{array}} \right)\) A2 N3
Note: Award A1 for three correct elements.
[3 marks]
finding \(2{\boldsymbol{A}} = \left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
0&6\\
{ – 4}&8
\end{array}} \right)\) (A1)
adding 2\({\boldsymbol{A}}\) to both sides (may be seen first) (M1)
e.g. \({\boldsymbol{X}} = {\boldsymbol{B}} +2{\boldsymbol{A}}\)
\({\boldsymbol{X}} = \left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{ – 4}&6\\
1&9
\end{array}} \right)\) A1 N2
[3 marks]
Question
The following table shows the probability distribution of a discrete random variable X .
a.Find the value of k .[3]
b.Find \({\text{E}}(X)\) .[3]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
evidence of summing to 1 (M1)
e.g. \(\sum\limits_{}^{} {p = 1{\text{, }}0.3 + k + 2k + 0.1 = 1} \)
correct working (A1)
e.g. \(0.4 + 3k{\text{, }}3k = 0.6\)
\(k = 0.2\) A1 N2
[3 marks]
correct substitution into formula \({\text{E}}(X)\) (A1)
e.g. \(0(0.3) + 2(k) + 5(2k) + 9(0.1){\text{, }}12k + 0.9\)
correct working
e.g. \(0(0.3) + 2(0.2) + 5(0.4) + 9(0.1){\text{, }}0.4 + 2.0 + 0.9\) (A1)
\({\text{E}}(X)\)= 3.3 A1 N2
[3 marks]