Question
A small object is placed at a distance of $2.0 \mathrm{~cm}$ from the objective lens of an optical compound microscope in normal adjustment.
The following data are available.
Magnification of the microscope $=70$
Focal length of the eyepiece $\quad=3.0 \mathrm{~cm}$
Near point distance $\quad=24 \mathrm{~cm}$
a. State what is meant by normal adjustment when applied to a compound microscope.[1]
b. Calculate, in $\mathrm{cm}$, the distance between the eyepiece and the image formed by the objective lens.[2]
c. Determine, in $\mathrm{cm}$, the focal length of the objective lens.[3]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
a. «the final» image is formed at the near point of the eye
b. «image is virtual so» $v=-24$ «cm»
$« \frac{1}{u}=\frac{1}{3.0}+\frac{1}{24} »$ so $u=27$ «m»
c. $M_{\mathrm{e}}=\frac{v}{u}=\frac{24}{2.66}=9.0$ AND $M_{\mathrm{o}}=\frac{7.0}{9.0}=7.8$
$v_0=2.0 \times 7.8=15.6 \ll \mathrm{cm} »$
$« \frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{2}+\frac{1}{16} »$ so $f_0=1.8 \ll \mathrm{cm} »$
NOTE: $M P 1$ allow $M_e=\frac{D}{f}+1=9$
Question
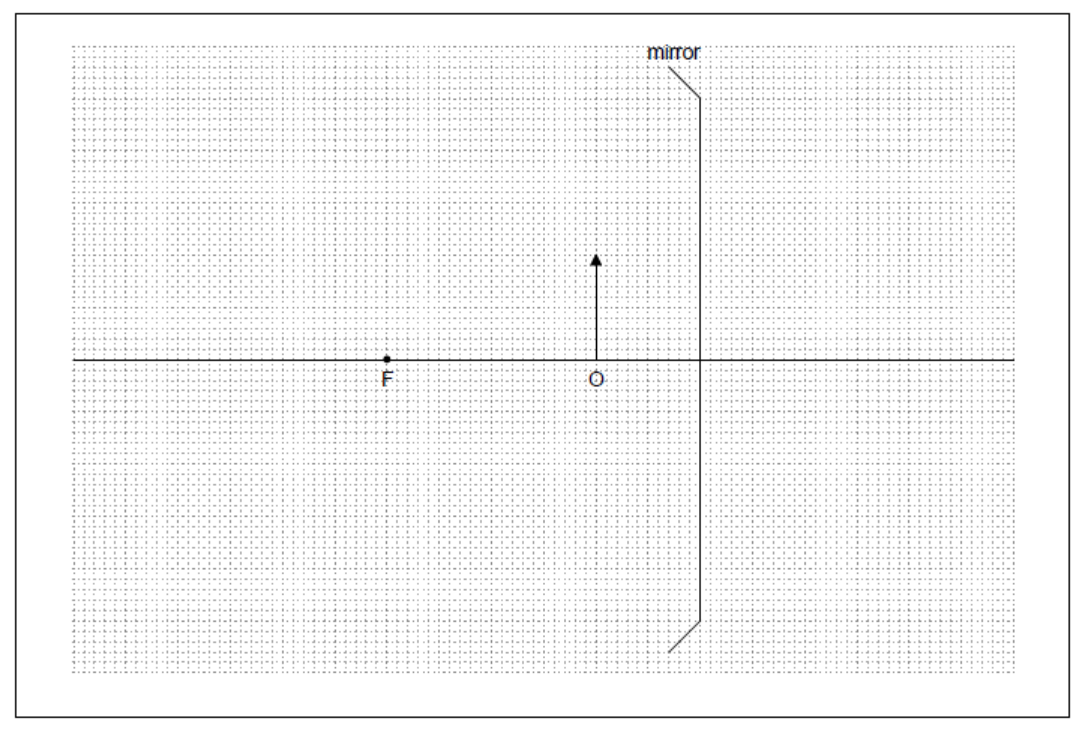
The diagram, drawn to scale, shows an object O placed in front of a converging mirror. The focal point of the mirror is labelled F.
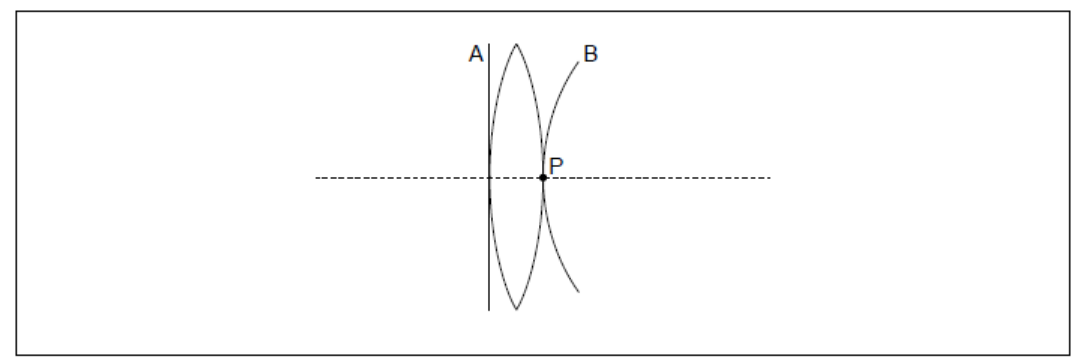
A planar wavefront of white light, labelled A, is incident on a converging lens. Point P is on the surface of the lens and the principal axis. The blue component of the transmitted wavefront, labelled B, is passing through point P.
a(i)Construct a ray diagram in order to locate the position of the image formed by the mirror. Label the image I.[2]
a(iiEstimate the linear magnification of the image.[1]
a(iiiDescribe two features of the image.[1]
$b(i)$ Sketch, on the diagram, the wavefront of red light passing through point $P$. Label this wavefront $R$.[1]
b(iiExplain chromatic aberration, with reference to your diagram in (b)(i).[2]
b(iiiAn achromatic doublet reduces the effect of chromatic aberration. Describe an achromatic doublet.[2]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
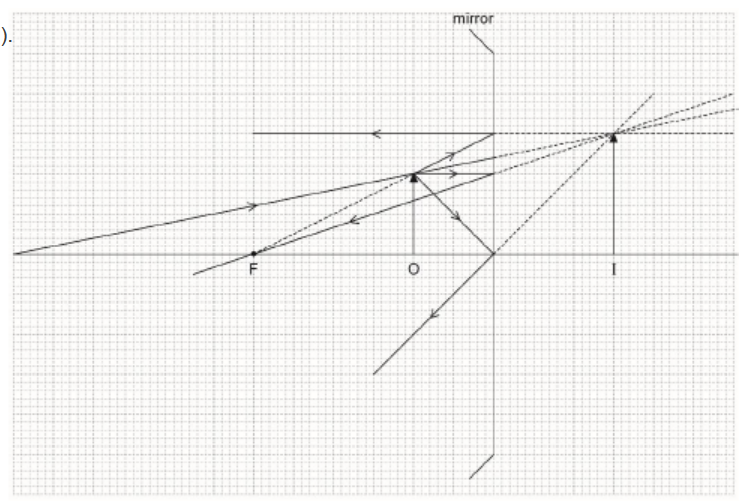
a(i) correctly draws any 2 of the 4 conventional rays from the object tip ✔
correctly extends reflections to form virtual upright image I
in approximate position shown ✔
NOTE: No ECF for incorrect rays in MP1.
Award [0] for rays of converging lens or diverging mirror.
a(ii) $1.5 \vee$
NOTE: For “correct” image position in (a)(i) allow 1.3 to 1.7
a(iiiAlny two of:
virtual $O R$ upright $O R$ larger than the object
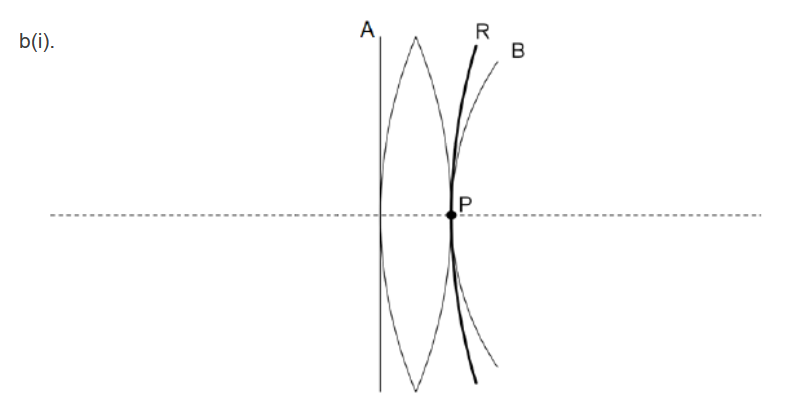
“circular” wave front through P: symmetric about the principal axis AND of greater radius than B
b(ii)ed and blue wave fronts have different curvature/radius
OR
red and blue waves are refracted differently/have different speeds
so different colors have different foci/do not focus to one point OR
so image is multi-coloured/blurred
NOTE: MP1 is for the reason for the aberration, MP2 is for the effect.
b(iii)mention combination of converging and diverging lenses
of different refractive index/material
NOTE: Achromatic doublet is in the question, so no marks for mentioning this.