Question
Consider the binomial expansion \((1+x)^7=x^7+ax^6+bx^5+35x^4+..+1 where x\neq 0 and a,b \in \mathbb{Z}^+\)
(a) Show that b = 21 . [2]
The third term in the expansion is the mean of the second term and the fourth term in the expansion.
(b) Find the possible values of x .
Answer/Explanation
Ans
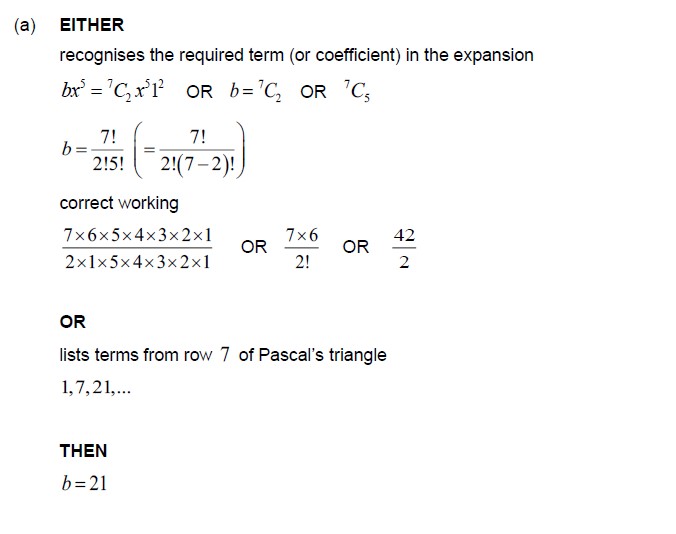
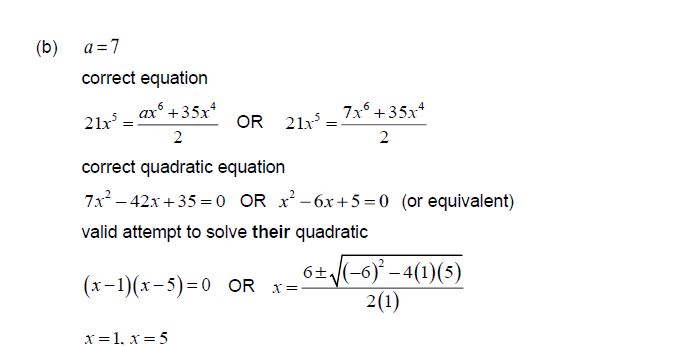
Question
The values in the fourth row of Pascal’s triangle are shown in the following table.

Write down the values in the fifth row of Pascal’s triangle.
Hence or otherwise, find the term in \({x^3}\) in the expansion of \({(2x + 3)^5}\).
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
1, 5, 10, 10, 5, 1 A2 N2
[2 marks]
evidence of binomial expansion with binomial coefficient (M1)
eg\(\,\,\,\,\,\)\(\left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} n \\ r \end{array}} \right){a^{n – r}}{b^r}\), selecting correct term, \({(2x)^5}{(3)^0} + 5{(2x)^4}{(3)^1} + 10{(2x)^3}{(3)^2} + \ldots \)
correct substitution into correct term (A1)(A1)(A1)
eg\(\,\,\,\,\,\)\(10{(2)^3}{(3)^2},{\text{ }}\left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 5 \\ 3 \end{array}} \right){(2x)^3}{(3)^2}\)
Note: Award A1 for each factor.
\(720{x^3}\) A1 N2
Notes: Do not award any marks if there is clear evidence of adding instead of multiplying.
Do not award final A1 for a final answer of 720, even if \(720{x^3}\) is seen previously.
[5 marks]
Question
[Maximum mark: 6] [with / without GDC]
Complete the following expansion.
\((2+ax)^{4}=16+32ax+…\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans.
\(…+6×2^{2}(ax)^{2}+4×2(ax)^{3}+(ax)^{4}=…+24a^{2}x^{2}+8a^{3}x^{3}+a^{4}x^{4}\)
Question
[Maximum mark: 4] [with / without GDC]
Find the coefficient of a3b4 in the expansion of \((5a+b)^{7}\).
Answer/Explanation
Ans.
\((5a+b)^{7}=…+\binom{7}{4}(5a)^{3}(b)^{4}+…=\frac{7x6x5x4}{1x2x3x4}x5^{3}x(a^{3}b^{4})=35×5^{3}xa^{3}b^{4}\)
So the coefficient is 4375
Question
[Maximum mark: 6] [without GDC]
(a) Expand \(\left ( e+\frac{1}{e} \right )^{4}\) in terms of e.
(b) Express \(\left ( e+\frac{1}{e} \right )^{4}+\left ( e-\frac{1}{e} \right )^{4}\) as the sum of three terms.
Answer/Explanation
Ans.
(a) \(\left ( e+\frac{1}{e} \right )^{4}=\binom{4}{0}e^{4}+\binom{4}{1}e^{3}\left ( \frac{1}{e} \right )+\binom{4}{2}e^{2}\left ( \frac{1}{e} \right )^{2}+\binom{4}{3}e\left ( \frac{1}{e} \right )^{3}+\binom{4}{4}\left ( \frac{1}{e} \right )^{4}\)
\(\left ( e+\frac{1}{e} \right )^{4}=e^{4}+4e^{3}\left ( \frac{1}{e} \right )+6e^{2}\left ( \frac{1}{e} \right )^{2}+4e\left ( \frac{1}{e} \right )^{3}+\left ( \frac{1}{e} \right )^{4}=e^{4}+4e^{2}+6+\frac{4}{e^{2}}+\frac{1}{e^{4}}\)
(b) \(\left ( e-\frac{1}{e} \right )^{4}=e^{4}-4e^{3}\left ( \frac{1}{e} \right )+6e^{2}\left ( \frac{1}{e} \right )^{2}-4e\left ( \frac{1}{e} \right )^{3}+\left ( \frac{1}{e} \right )^{4}=e^{4}-4e^{2}+6-\frac{4}{e^{2}}+\frac{1}{e^{4}}\)
Adding gives \(2e^{4}+12+\frac{2}{e^{4}}\)