Question
Consider \(f(x) = 2k{x^2} – 4kx + 1\) , for \(k \ne 0\) . The equation \(f(x) = 0\) has two equal roots.
Find the value of k .[5]
The line \(y = p\) intersects the graph of f . Find all possible values of p .[2]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
valid approach (M1)
e.g. \({b^2} – 4ac\) , \(\Delta = 0\) , \({( – 4k)^2} – 4(2k)(1)\)
correct equation A1
e.g. \({( – 4k)^2} – 4(2k)(1) = 0\) , \(16{k^2} = 8k\) , \(2{k^2} – k = 0\)
correct manipulation A1
e.g. \(8k(2k – 1)\) , \(\frac{{8 \pm \sqrt {64} }}{{32}}\)
\(k = \frac{1}{2}\) A2 N3
[5 marks]
recognizing vertex is on the x-axis M1
e.g. (1, 0) , sketch of parabola opening upward from the x-axis
\(p \ge 0\) A1 N1
[2 marks]
Question
Let \(f(x) = \frac{x}{{ – 2{x^2} + 5x – 2}}\) for \( – 2 \le x \le 4\) , \(x \ne \frac{1}{2}\) , \(x \ne 2\) . The graph of \(f\) is given below.
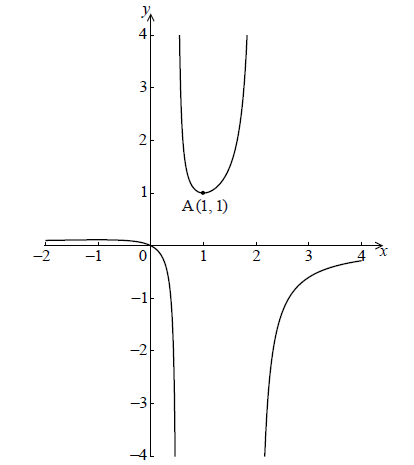
The graph of \(f\) has a local minimum at A(\(1\), \(1\)) and a local maximum at B.
Use the quotient rule to show that \(f'(x) = \frac{{2{x^2} – 2}}{{{{( – 2{x^2} + 5x – 2)}^2}}}\) .[6]
Hence find the coordinates of B.[7]
Given that the line \(y = k\) does not meet the graph of f , find the possible values of k .[3]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
correct derivatives applied in quotient rule (A1)A1A1
\(1\), \( – 4x + 5\)
Note: Award (A1) for 1, A1 for \( – 4x\) and A1 for \(5\), only if it is clear candidates are using the quotient rule.
correct substitution into quotient rule A1
e.g. \(\frac{{1 \times ( – 2{x^2} + 5x – 2) – x( – 4x + 5)}}{{{{( – 2{x^2} + 5x – 2)}^2}}}\) , \(\frac{{ – 2{x^2} + 5x – 2 – x( – 4x + 5)}}{{{{( – 2{x^2} + 5x – 2)}^2}}}\)
correct working (A1)
e.g. \(\frac{{ – 2{x^2} + 5x – 2 – ( – 4{x^2} + 5x)}}{{{{( – 2{x^2} + 5x – 2)}^2}}}\)
expression clearly leading to the answer A1
e.g. \(\frac{{ – 2{x^2} + 5x – 2 + 4{x^2} – 5x}}{{{{( – 2{x^2} + 5x – 2)}^2}}}\)
\(f'(x) = \frac{{2{x^2} – 2}}{{{{( – 2{x^2} + 5x – 2)}^2}}}\) AG N0
[6 marks]
evidence of attempting to solve \(f'(x) = 0\) (M1)
e.g. \(2{x^2} – 2 = 0\)
evidence of correct working A1
e.g. \({x^2} = 1,\frac{{ \pm \sqrt {16} }}{4}{\text{, }}2(x – 1)(x + 1)\)
correct solution to quadratic (A1)
e.g. \(x = \pm 1\)
correct x-coordinate \(x = – 1\) (may be seen in coordinate form \(\left( { – 1,\frac{1}{9}} \right)\) ) A1 N2
attempt to substitute \( – 1\) into f (do not accept any other value) (M1)
e.g. \(f( – 1) = \frac{{ – 1}}{{ – 2 \times {{( – 1)}^2} + 5 \times ( – 1) – 2}}\)
correct working
e.g. \(\frac{{ – 1}}{{ – 2 – 5 – 2}}\) A1
correct y-coordinate \(y = \frac{1}{9}\) (may be seen in coordinate form \(\left( { – 1,\frac{1}{9}} \right)\) ) A1 N2
[7 marks]
recognizing values between max and min (R1)
\(\frac{1}{9} < k < 1\) A2 N3
[3 marks]
Question
Let \(f(x) = 3x – 2\) and \(g(x) = \frac{5}{{3x}}\), for \(x \ne 0\).
Let \(h(x) = \frac{5}{{x + 2}}\), for \(x \geqslant 0\). The graph of h has a horizontal asymptote at \(y = 0\).
Find \({f^{ – 1}}(x)\).[2]
Show that \(\left( {g \circ {f^{ – 1}}} \right)(x) = \frac{5}{{x + 2}}\).[2]
Find the \(y\)-intercept of the graph of \(h\).[2]
Hence, sketch the graph of \(h\).[3]
For the graph of \({h^{ – 1}}\), write down the \(x\)-intercept;[1]
For the graph of \({h^{ – 1}}\), write down the equation of the vertical asymptote.[1]
Given that \({h^{ – 1}}(a) = 3\), find the value of \(a\).[3]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
interchanging \(x\) and \(y\) (M1)
eg \(x = 3y – 2\)
\({f^{ – 1}}(x) = \frac{{x + 2}}{3}{\text{ }}\left( {{\text{accept }}y = \frac{{x + 2}}{3},{\text{ }}\frac{{x + 2}}{3}} \right)\) A1 N2
[2 marks]
attempt to form composite (in any order) (M1)
eg \(g\left( {\frac{{x + 2}}{3}} \right),{\text{ }}\frac{{\frac{5}{{3x}} + 2}}{3}\)
correct substitution A1
eg \(\frac{5}{{3\left( {\frac{{x + 2}}{3}} \right)}}\)
\(\left( {g \circ {f^{ – 1}}} \right)(x) = \frac{5}{{x + 2}}\) AG N0
[2 marks]
valid approach (M1)
eg \(h(0),{\text{ }}\frac{5}{{0 + 2}}\)
\(y = \frac{5}{2}{\text{ }}\left( {{\text{accept (0, 2.5)}}} \right)\) A1 N2
[2 marks]
 A1A2 N3
A1A2 N3
Notes: Award A1 for approximately correct shape (reciprocal, decreasing, concave up).
Only if this A1 is awarded, award A2 for all the following approximately correct features: y-intercept at \((0, 2.5)\), asymptotic to x-axis, correct domain \(x \geqslant 0\).
If only two of these features are correct, award A1.
[3 marks]
\(x = \frac{5}{2}{\text{ }}\left( {{\text{accept (2.5, 0)}}} \right)\) A1 N1
[1 mark]
\(x = 0\) (must be an equation) A1 N1
[1 mark]
METHOD 1
attempt to substitute \(3\) into \(h\) (seen anywhere) (M1)
eg \(h(3),{\text{ }}\frac{5}{{3 + 2}}\)
correct equation (A1)
eg \(a = \frac{5}{{3 + 2}},{\text{ }}h(3) = a\)
\(a = 1\) A1 N2
[3 marks]
METHOD 2
attempt to find inverse (may be seen in (d)) (M1)
eg \(x = \frac{5}{{y + 2}},{\text{ }}{h^{ – 1}} = \frac{5}{x} – 2,{\text{ }}\frac{5}{x} + 2\)
correct equation, \(\frac{5}{x} – 2 = 3\) (A1)
\(a = 1\) A1 N2
[3 marks]
Question
The following diagram shows part of the graph of a quadratic function \(f\).
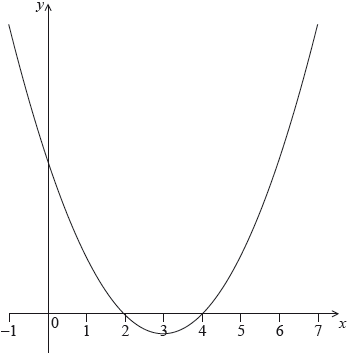
The vertex is at \((3,{\text{ }} – 1)\) and the \(x\)-intercepts at 2 and 4.
The function \(f\) can be written in the form \(f(x) = {(x – h)^2} + k\).
The function can also be written in the form \(f(x) = (x – a)(x – b)\).
Write down the value of \(h\) and of \(k\).[2]
Write down the value of \(a\) and of \(b\).[2]
Find the \(y\)-intercept.[2]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\(h = 3,{\text{ }}k = – 1\) A1A1 N2
[2 marks]
\(a = 2,{\text{ }}b = 4{\text{ }}({\text{or }}a = 4,{\text{ }}b = 2)\) A1A1 N2
[2 marks]
attempt to substitute \(x = 0\) into their \(f\) (M1)
eg\(\,\,\,\,\,\)\({(0 – 3)^2} – 1,{\text{ }}(0 – 2)(0 – 4)\)
\(y = 8\) A1 N2
[2 marks]