Question
The graph of y = f (x) for -4 ≤ x ≤ 6 is shown in the following diagram.
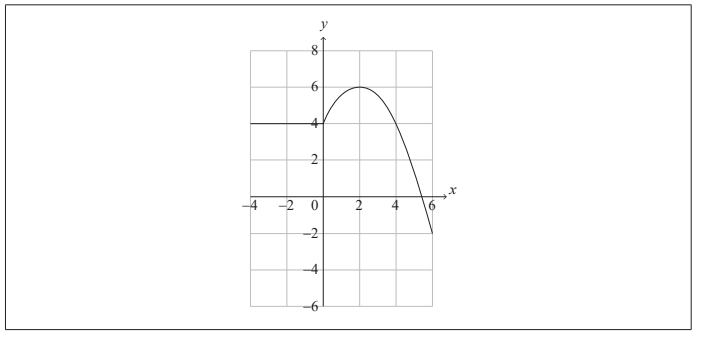
(a) Write down the value of
(i) f (2) ;
(ii) ( f o f )(2) . [2]
(b) Let g(x) = \(\frac{1}{2} f (x) +1\) for -4 ≤ x ≤ 6 . On the axes above, sketch the graph of g . [3]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) (i) f(2) = 6
(ii) (fof)2=− 2 [2 marks]
(b) 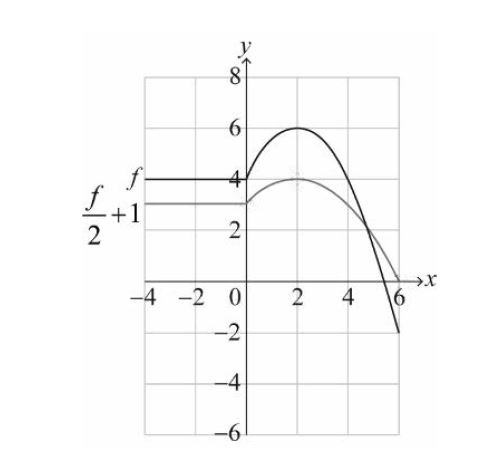
Question
Let \(f(x) = \ln (x + 5) + \ln 2\) , for \(x > – 5\) .
Find \({f^{ – 1}}(x)\) .[4]
Let \(g(x) = {{\rm{e}}^x}\) .
Find \((g \circ f)(x)\) , giving your answer in the form \(ax + b\) , where \(a,b \in \mathbb{Z}\) .[3]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
METHOD 1
\(\ln (x + 5) + \ln 2 = \ln (2(x + 5))\) \(( = \ln (2x + 10))\) (A1)
interchanging x and y (seen anywhere) (M1)
e.g. \(x = \ln (2y + 10)\)
evidence of correct manipulation (A1)
e.g. \({{\rm{e}}^x} = 2y + 10\)
\({f^{ – 1}}(x) = \frac{{{{\rm{e}}^x} – 10}}{2}\) A1 N2
METHOD 2
\(y = \ln (x + 5) + \ln 2\)
\(y – \ln 2 = ln(x + 5)\) (A1)
evidence of correct manipulation (A1)
e.g. \({{\rm{e}}^{y – \ln 2}} = x + 5\)
interchanging x and y (seen anywhere) (M1)
e.g. \({{\rm{e}}^{x – \ln 2}} = y + 5\)
\({f^{ – 1}}(x) = {{\rm{e}}^{x – \ln 2}} – 5\) A1 N2
[4 marks]
METHOD 1
evidence of composition in correct order (M1)
e.g. \((g \circ f)(x) = g(\ln (x + 5) + \ln 2)\)
\( = {{\rm{e}}^{\ln (2(x + 5))}} = 2(x + 5)\)
\((g \circ f)(x) = 2x + 10\) A1A1 N2
METHOD 2
evidence of composition in correct order (M1)
e.g. \((g \circ f)(x) = {{\rm{e}}^{\ln (x + 5) + \ln 2}}\)
\( = {{\rm{e}}^{\ln (x + 5)}} \times {{\rm{e}}^{\ln 2}} = (x + 5)2\)
\((g \circ f)(x) = 2x + 10\) A1A1 N2
[3 marks]
Question
Let \(f(x) = {x^2}\) and \(g(x) = 2x – 3\) .
Find \({g^{ – 1}}(x)\) .[2]
Find \((f \circ g)(4)\) .[3]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
for interchanging x and y (may be done later) (M1)
e.g. \(x = 2y – 3\)
\({g^{ – 1}}(x) = \frac{{x + 3}}{2}\) (accept \(y = \frac{{x + 3}}{2},\frac{{x + 3}}{2}\) ) A1 N2
[2 marks]
METHOD 1
\(g(4) = 5\) (A1)
evidence of composition of functions (M1)
\(f(5) = 25\) A1 N3
METHOD 2
\(f \circ g(x) = {(2x – 3)^2}\) (M1)
\(f \circ g(4) = {(2 \times 4 – 3)^2}\) (A1)
= 25 A1 N3
[3 marks]
Question
Let \(f(x)=6x\sqrt{(1-x^2)}, for -1\leq x\leq 1\)
and \(g(x) =cos(x), \) for \( for 0\leq x\leq \pi\)
Let \(h(x) =(fog)(x)\)
a. Write \(h(x)\) in the form \(asin(bx)\), where \(a,b \in \mathbb{Z}\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans
\(f(x)=6x\sqrt{(1-x^2)}\)
\(g(x) =cos(x)\)
hence
\(h(x) =(fog)(x)\)
\(=f(g(x))\)
\(=f(cos(x))\)
\(=6cos(x)\sqrt{(1-(cos(x))^2)}\)
Now \(cos^2(x) +sin^2(x) =1\)
Hence
\(h(x) =6cos(x)\sqrt{sin^2(x)}=6cos(x) \times sin(x)\)
now \(2cos(x) \times sin(x) =sin 2x\)
hence
\(h(x) =3sin 2x\)
\(a=3\) and \( b=2\)
Question
Let \(f(x) = 8x + 3\) and \(g(x) = 4x\), for \(x \in \mathbb{R}\).
Write down \(g(2)\).[1]
Find \((f \circ g)(x)\).[2]
Find \({f^{ – 1}}(x)\).[2]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\(g(2) = 8\) A1 N1
[1 mark]
attempt to form composite (in any order) (M1)
eg\(\,\,\,\,\,\)\(f(4x),{\text{ }}4 \times (8x + 3)\)
\((f \circ g)(x) = 32x + 3\) A1 N2
[2 marks]
interchanging \(x\) and \(y\) (may be seen at any time) (M1)
eg\(\,\,\,\,\,\)\(x = 8y + 3\)
\({f^{ – 1}}(x) = \frac{{x – 3}}{8}\,\,\,\,\,\left( {{\text{accept }}\frac{{x – 3}}{8},{\text{ }}y = \frac{{x – 3}}{8}} \right)\) A1 N2
[2 marks]
Question
[Maximum mark: 6] [without GDC]
Let \(g(x)=3x-2\), \(h(x)=\frac{5x}{x-4}\), \( x\neq 4\).
(a) Find an expression for (h ◦ g) (x). Simplify your answer.
(b) Solve the equation (h ◦ g) (x) = 0.
Answer/Explanation
(a) (h ◦ g) (x) = \(\frac{5(3x-2)}{(3x-2)-4}=\frac{15x-10}{3x-6}\)
(b) numerator = \(0\Rightarrow M1)x=\frac{2}{3} (=0.667)\)