- IB DP Biology 2025 SL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 1
- IB DP Biology 2025 HL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 1
- IB DP Biology 2025 SL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 2
- IB DP Biology 2025 HL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 2
A1.2.1—DNA as the genetic material of all living organisms

two types of nucleic acids used in cells.
- DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid
- RNA: ribonucleic acid
two primary functions of nucleic acids.
- Pass genetic information between generations.
- Code for protein production
meaning and implication of DNA being the genetic material of all living organisms.
Meaning:
All living organisms use DNA as the genetic material.
Implication:
The use of the genetic code across all forms of life is evidence of universal common ancestry of life. The sequences of DNA in cells can be analyzed and compared to determine evolutionary relationships between organisms. The more similar the sequence, the more closely related the organisms.
RNA viruses do not falsify the claim that all living things use DNA as the genetic material.
Some viruses use RNA as their genetic material. However, because viruses are not made of cells, they are not considered to be living.

A1.2.2—Components of a nucleotide
three components of a nucleotide.
A nucleotide is the monomer subunit of the nucleic acids. A nucleotide has three component parts:
- A nitrogenous base
- A 5-carbon “pentose: sugar (ribose or deoxyribose)
- A phosphate group

label the carbons of a pentose sugar.
The carbons of the sugar component of the nucleotide are numbers clockwise, starting from the oxygen in the ring at the top and the phosphate group to the left.

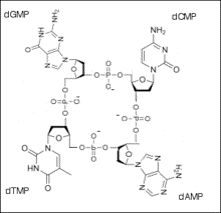
A1.2.3—Sugar–phosphate bonding and the sugar–phosphate “backbone” of DNA and RNA
Define “backbone” as related to nucleic acid structure.
The “backbone” is the alternating phosphate-sugar- phosphate-sugar-phosphate… found in a polymer of nucleic acids. The relative strength of the backbone maintains the nucleotides in their specific sequence.
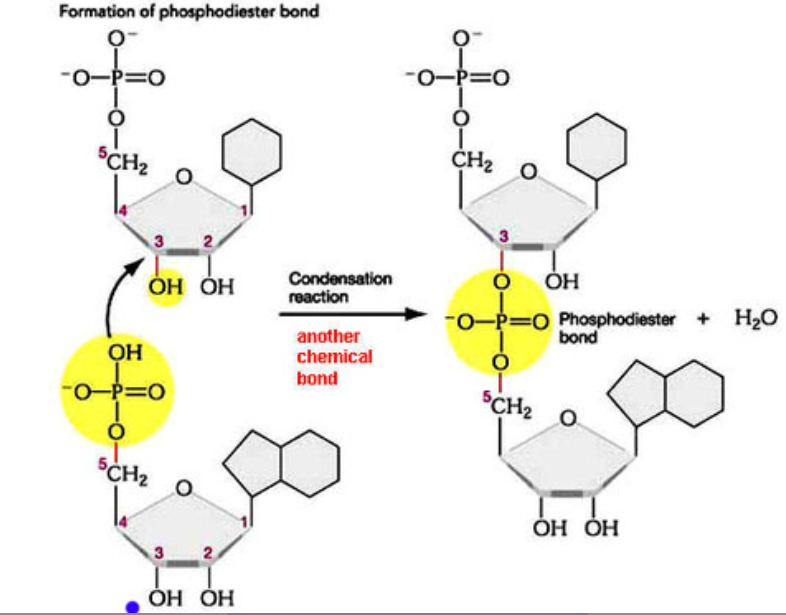
nucleotides can connect to form a nucleic acid polymer.
Nucleotides connect by creating covalent bonds between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate group of another nucleotide in a condensation reaction.
The 5’ phosphate group on one nucleotide forms a new covalent bond with the 3′ carbon on the pentose of the next nucleotide. Water is created as a biproduct
A1.2.4—Bases in each nucleic acid that form the basis of a code
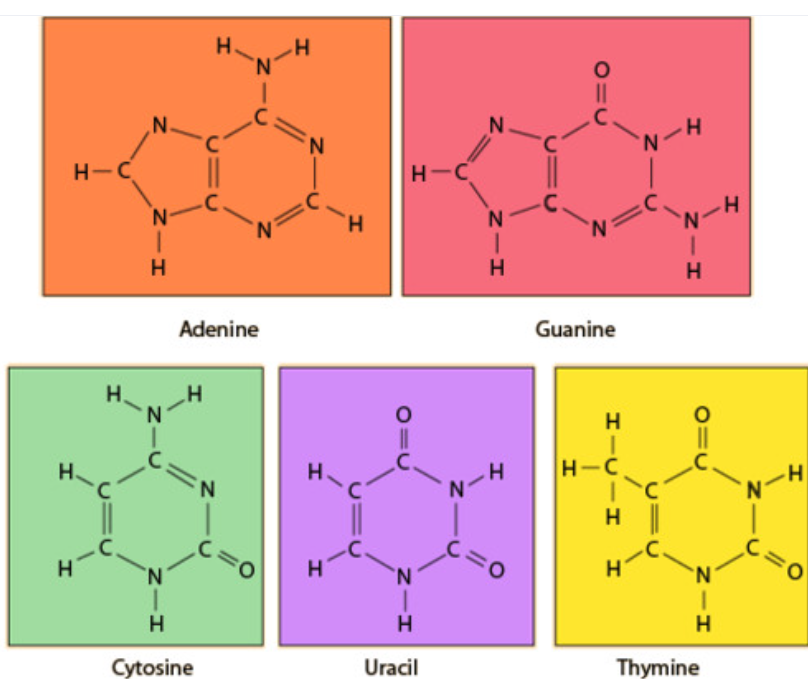
nitrogenous bases found in DNA and RNA
- Cytosine (DNA and RNA)
- Thymine (DNA only)
- Guanine (DNA and RNA)
- Adenine (DNA and RNA)
- Uracil (RNA only)
sequence of bases in a nucleic acid serves as a ‘code.’
A code is a system in which one symbol signifies the meaning of another symbol. In the genetic code, a group of three nucleic acid bases signifies for an amino acid.A gene is a specific sequence of DNA nucleotides that codes for the making of a specific protein.
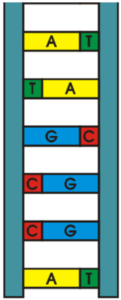
Gene
A gene is a specific sequence of nitrogenous bases in DNA nucleotides that codes for the making of a protein.
A1.2.5—RNA as a polymer formed by condensation of nucleotide monomers
condensation reaction that forms a polymer of RNA from RNA nucleotides.
RNA nucleotides connect by creating covalent bonds between the ribose sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate group of another nucleotide in a condensation reaction.
The 5’ phosphate group on one RNA nucleotide forms a new covalent bond with the 3′ carbon on the ribose of the next nucleotide. Water is created as a biproduct.

a short section of an RNA polymer (using circle, pentagon and rectangle)
Include at least three RNA nucleotides, drawn as circle (phosphate), hexagon (ribose) and rectangle (base).
Be sure the phosphate of one nucleotide is connected to the 2’C of the adjacent nucleotide.

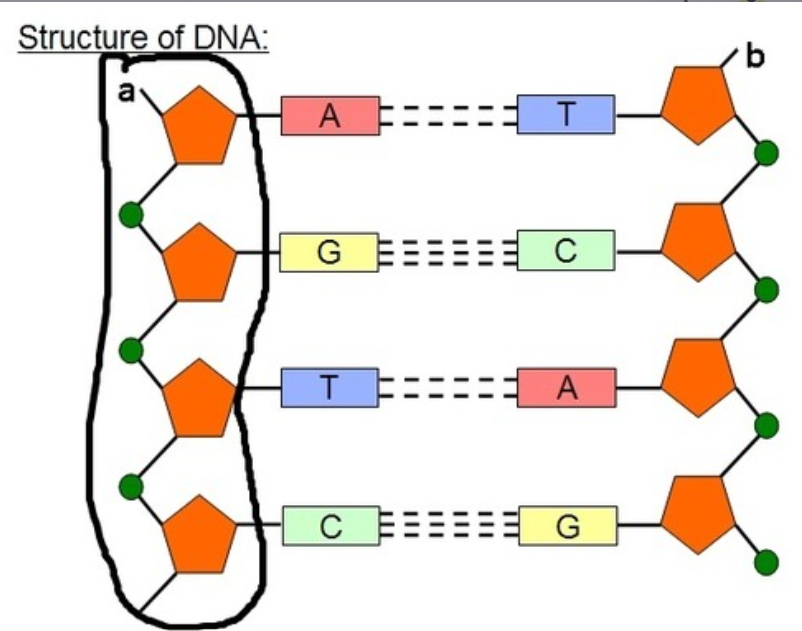
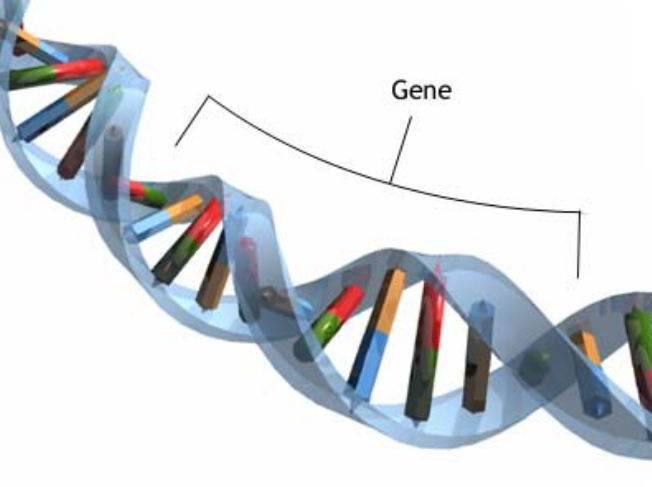
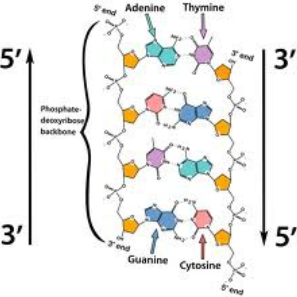
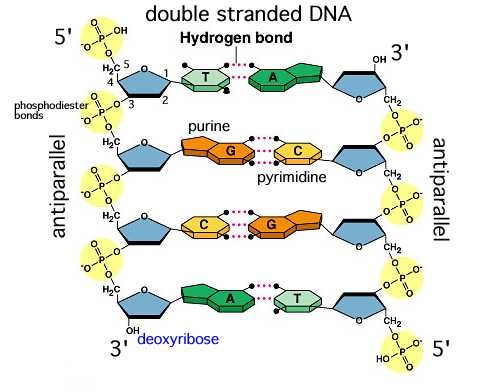
A1.2.6—DNA as a double helix made of two antiparallel strands of nucleotides with two strands linked by hydrogen bonding between complementary base pairs
Two polymers of DNA nucleotides, each with a sugar-phosphate backbone, run in antiparallel directions. Complementary DNA nitrogenous bases (A-T, C-G) form hydrogen bonds between them, binding the two polymer stands (“double”) so that they wind around each other (“helix”)
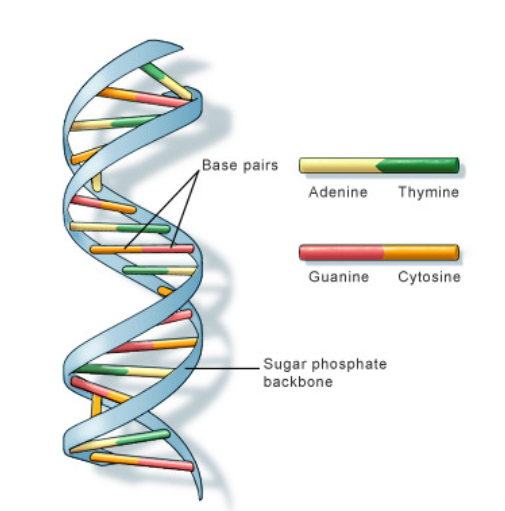
Outline the complementary base pairing rule, including the type and number of bonds between bases.
In DNA, the nitrogenous bases of two antiparallel strands form hydrogen bonds with each other. The complementary base pairing rule is that adenine only binds with thymine (with 2 H-bonds) and that guanine only binds with cytosine (with 3 H-bonds).
Define antiparallel in relation to DNA structure.
Adjacent molecules are oriented parallel to each other but oriented in opposite directions.
In DNA, one strand runs 5′ to 3′ and the complementary strand runs 3′ to 5′
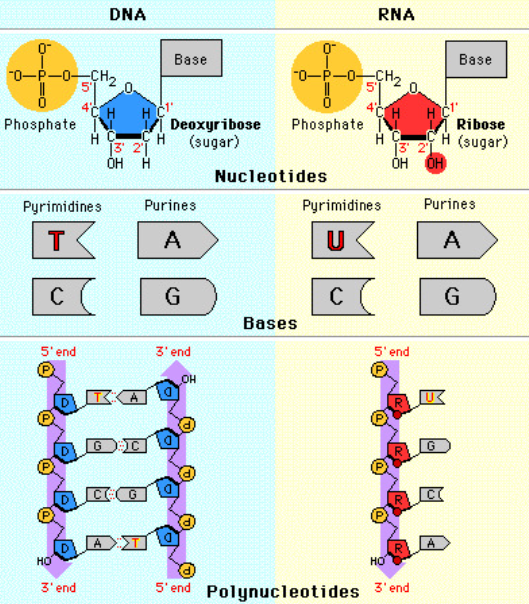
A1.2.7—Differences between DNA and RNA
Both are nucleic acids formed through condensation of nucleotides. Both DNA and RNA have a sugar-phosphate backbone.
RNA
ribose
single stranded
nitrogenous bases A, G, C, U
Complementary paring A-U, C-G
DNA
deoxyribose
double stranded
nitrogenous bases A, G, C, T
Complementary pairing A-T, C-G
Compare and contrast the functions of DNA and RNA
DNA:
Passes heredity information between generations of cells
Codes for making RNA during transcription
RNA:
Codes for making proteins during translation

Compare and contrast the location of DNA and RNA in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Eukaryotic Cells
Both DNA and RNA are found in the nucleus.
DNA also in mitochondria and chloroplasts.
RNA also in cytoplasm and as part of ribosomes (free or bound to rough ER)
Prokaryotic Cells
Both DNA and RNA are in the cytoplasm.
DNA is clumped in a region called the nucleoid.

A1.2.8—Role of complementary base pairing in allowing genetic information to be replicated and expressed
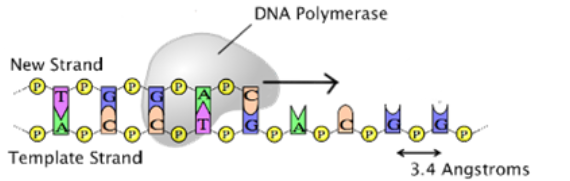
Explain the role of complementary base pairing in maintaining the DNA sequence during DNA replication.
During DNA replication, the two strands of a “parent” DNA molecule are broken apart. Each of these strands serves as a template for the creation of a new “daughter” strand. Because of the base pairing rule, the parent template strand will always code for the complementary sequence of nucleotides in the daughter strand (A to T, C to G). The complementary base paring will maintain the sequence of the DNA from generation to generation.
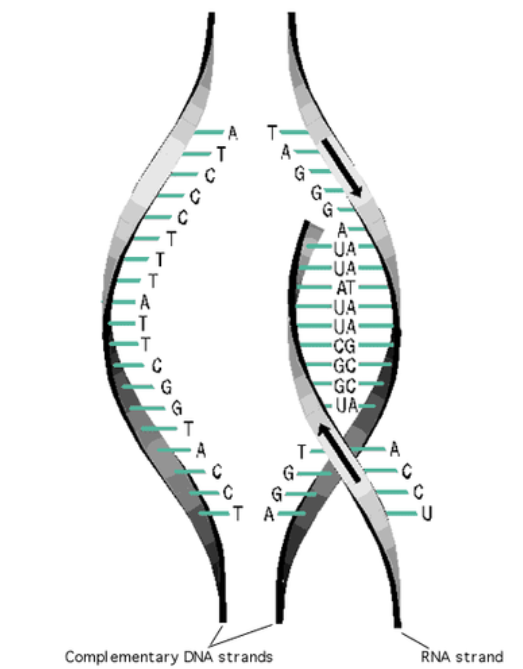
Outline the role of complementary base pairing in transmitting the genetic code in transcription.
During transcription, one of the the two strands of a DNA molecule is used as a template for the creation of an RNA strand. Because of the base pairing rule, the DNA template strand will always code for the complementary sequence of RNA nucleotides in the (A to U, C to G). The complementary base paring will maintain the sequence of the gene as mRNA is translated into protein.
Outline the role of complementary base pairing in transmitting the genetic code in translation.
During translation, an RNA strand is used as a template for the creation of a polypeptide. Because of the base pairing rule, the mRNA codon will only bind with the complementary tRNA anticodon (A to U, C to G). The complementary base paring ensures the correct amino acid are brought in the correct sequence to the ribosome.
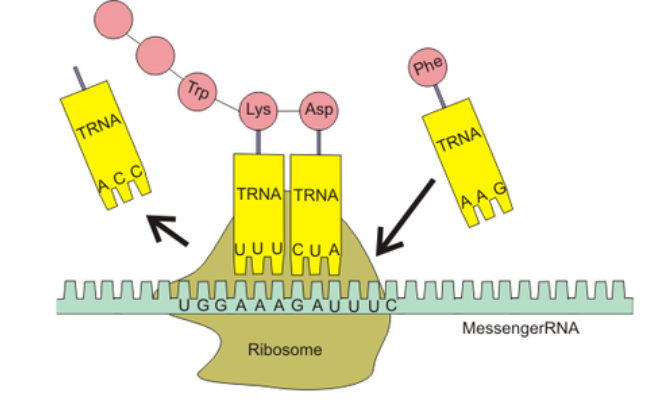
A1.2.9— Diversity of possible DNA base sequences and the limitless capacity of DNA for storing Information.
Outline why there is a limitless diversity of DNA base sequences.
There are four nitrogenous bases in DNA (A, T, C and G). These 4 bases are components of nucleotides that can form a DNA molecule in any order and of any length.
Universal means that the characteristic is shared by all life. A universal generic code means that all life uses essentially the same code when translating information stored in genes into a polypeptide.
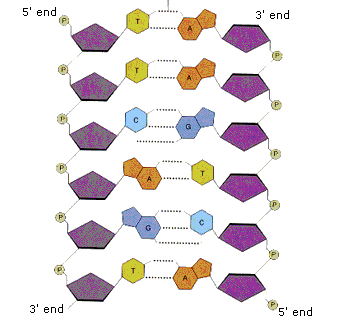
A1.2.10— Conservation of the genetic code across all life forms as evidence of universal common ancestry.
Define universal in relation to the genetic code.
Universal means that the characteristic is shared by all life. A universal generic code means that all life uses essentially the same code when translating information stored in genes into a polypeptide.
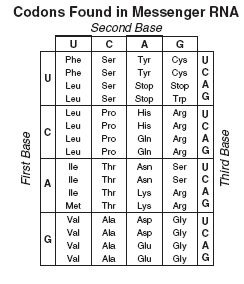
Outline why conservation of the genetic code across all forms of life is evidence of common ancestry.
Using inductive reasoning, it can be concluded that the use of the same genetic code across all forms of life indicates that all organisms inherited the use of the code from a common ancestor. The alternative, that all forms of life independently developed use of the same genetic code, is an illogical hypothesis.
AHL A1.2.11—Directionality of RNA and DNA.
Identify and label the \(5^{\prime}\) and \(3^{\prime}\) ends on a DNA or RNA diagram.
Each end of DNA nucleotide has a number. One end is referred to as \(5^{\prime}\) (five prime) and the other end is referred to as \(3^{\prime}\) (three prime). The \(5^{\prime}\) and \(3^{\prime}\) designations refer to the number of the carbon atom in a deoxyribose sugar molecule. The \(5^{\prime}\) end is identified by the presence of the phosphate group and the \(3 ‘\) end is identified as ending in the pentose sugar (ribose or deoxyribose).
In DNA, one strand will run from \(5^{\prime}\) to \(3^{\prime}\) and the complementary strand will run anti-parallel, from \(3^{\prime}\) to \(5^{\prime}\).
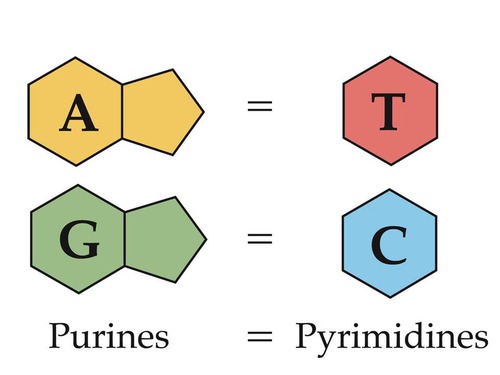
AHL A1.2.12—Purine-topyrimidine bonding as a component of DNA helix stability.
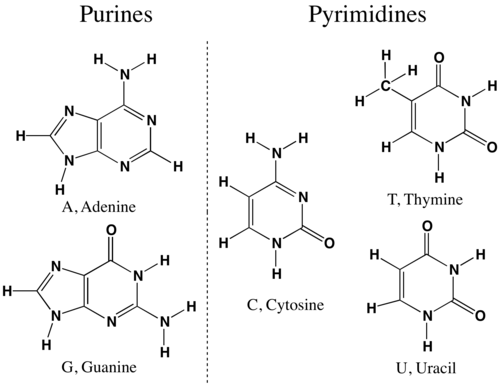
Compare and contrast the structures of purines and pyrimidines.
Both purines and pyrimidines are nitrogenous bases of DNA and RNA.
Pyrimidine: single ring nitrogenous bases Cytosine Thymine Uracil
Purine: double ring nitrogenous bases Guanine Adenine
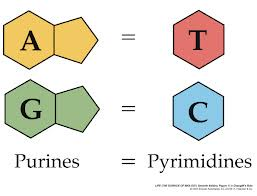
State that in DNA, a purine forms hydrogen bonds with a pyrimidine.
In DNA, a purine complementary base pairs to a pyrimidine using hydrogen bonds
In DNA and RNA, guanine bonds with cytosine with three hydrogen bonds.
In DNA, adenine bonds with thymine with two hydrogen bonds.
In RNA, adenine bonds with uracil with two hydrogen bonds
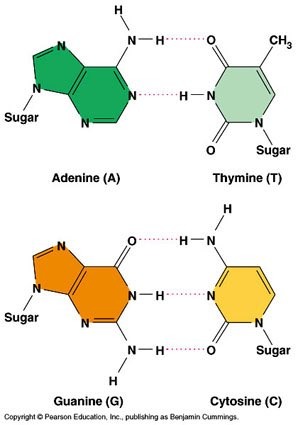
Given a diagram of DNA, identify the four bases of DNA based on purine or pyrimidine and the number of hydrogen bonds.
Purines have two rings. If it can form \(2 \mathrm{H}\)-bonds it is adenine and if it can form 3 \(\mathrm{H}\)-bonds it is guanine.
Pyrimidines have one ring. If it can form \(2 \mathrm{H}\)-bonds it is thymine and if it can form 3 \(\mathrm{H}\)-bonds it is cytosine.
AHL A1.2.13—Structure of a nucleosome.
Describe the structure of eukaryotic DNA and associated histone proteins during interphase (chromatin).
To compact DNA while regulating gene accessibility for transcription, eukaryotic organisms organize their genomes:
1. DNA double helix.
2. DNA wraps around histone proteins, forming nucleosomes and the “beads on a string” structure.
3. Multiple nucleosomes wrap into a fibre (chromatin).
4. Supercoiling of the chromatin produces the chromosome (during mitosis and meiosis). Supercoiling refers to the repeated twisting and winding of the DNA strand. Supercoiling functions to reduce the space required for DNA packaging, allowing for more compact storage of DNA.
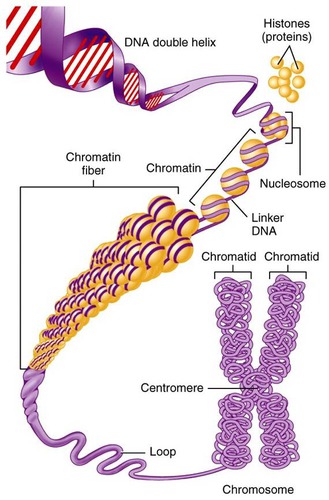
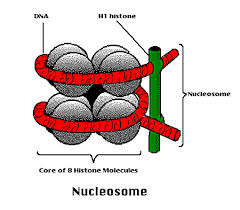
Draw and label the structure of a nucleosome, including the \(\mathrm{Hl}\) protein, the octamer core proteins, linker DNA and two wraps of DNA.
The nucleosome is the basic unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes. Each nucleosome is composed of two turns of DNA wrapped around a group of eight histone proteins (called an octamer core). Each nucleosome connects to the adjacent nucleosomes through another type of histone protein (called the \(\mathrm{H1}\) ) and a region of “linker” DNA.
AHL Al.2.14— Evidence from the Hershey-Chase experiment for DNA as the genetic material.
State the experimental question being tested in the Hershey and Chase experiment.
Both protein and nucleic acids are part of the eukaryotic cell nucleus, and prior to 1952 it was unknown which molecule type was responsible for passing genetic information between generations. Hershey and Chase designed an experiment to test whether proteins or DNA is the hereditary material.

Outline the procedure of the Hershey and Chase experiment.
Hershey and Chase (H\&C) performed their experiments on viruses that infect bacteria called bacteriophages. They incorporated radioactive isotopes of phosphorus and sulfur into phages. DNA contains phosphorus, but not sulfur, whereas protein contains sulfur, but not phosphorus. Therefore, when \(\mathrm{H} \& \mathrm{C}\) marked phages with radioactive isotopes of those elements, they placed separate, distinguishable tags on the protein and DNA parts of the phages.
They allowed the phages to replicate by infecting bacteria. By tracking the location of the radioactive tags, H$\&$C showed that phages only injected their DNA into host bacteria, and that the DNA served as the replicating genetic element of phages. The phages did not inject their protein coats into the bacteria; the protein coats remained outside the bacteria adhered to the bacterial membranes.
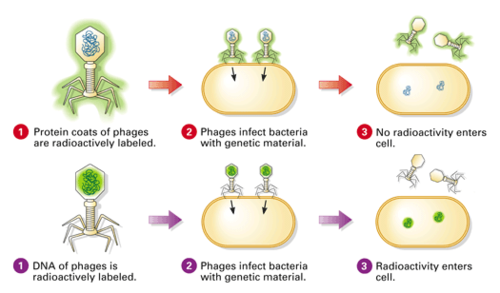
Explain how the results of the Hershey and Chase experiment supported the notion of nucleic acids as the genetic material.
The molecule of heredity must be pasted from generation to generation. When Hershey and Chase demonstrated that radioactively tagged DNA is present across generations of bacteriophages and that radioactively tagged protein is not, they demonstrated that nucleic acids must be the genetic material.

Outline the use of radioisotopes as research tools.
Hershey and Chase relied on radioactive isotopes of phosphorus and sulfur in their experiment to determine that DNA is the genetic material. Although they had been used on a small scale prior, after World War II the U.S. Atomic Energy Commission began massproducing radioisotopes, sending shipments of radioactive materials to scientists.
Because they give off energy as they convert to a more stable form, the isotopes allow biologists to track molecules as they move through biological systems.
AHL A1.2.15—Chargaff’s data on the relative amounts of pyrimidine and purine bases across diverse life forms.
Describe the implications of Chargaff’s data that showed a 1:1 ratio of purine to pyrimidine in a sample of DNA.
Chargaff’s research revealed the percentage of each base (A, T, C, G) found in different species DNA. He determined that there are equal numbers of \(A\) and \(T\) bases and \(G\) and \(C\) bases in a DNA sample, resulting in a 1:1 ratio of purines to pyrimidines in DNA.
Chargaff did not use inductive reasoning to then infer the pattern that A binds to \(T\) and \(C\) binds to \(G\). The complementary base pairing rule was inferred by Watson and Crick.
Explain the role of falsiflability in determining the structure and function of DNA.
To falsify means that a statement, theory or hypothesis is proven to be wrong.
Because he found that the amount of one base wasn’t equal to the amount of the three other bases, Chargaff’s data falsified the earlier hypothesis that DNA had a tetranucleotide structure. In this proposed model of DNA, the four bases occur in equal amounts in four strands arranged with the bases facing outward.