- IB DP Biology 2025 SL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 1
- IB DP Biology 2025 HL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 1
- IB DP Biology 2025 SL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 2
- IB DP Biology 2025 HL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 2
B1.1.1—Chemical properties of a carbon atom allowing for the formation of diverse compounds upon which life is based
Carbon atoms can form 4 covalent bonds







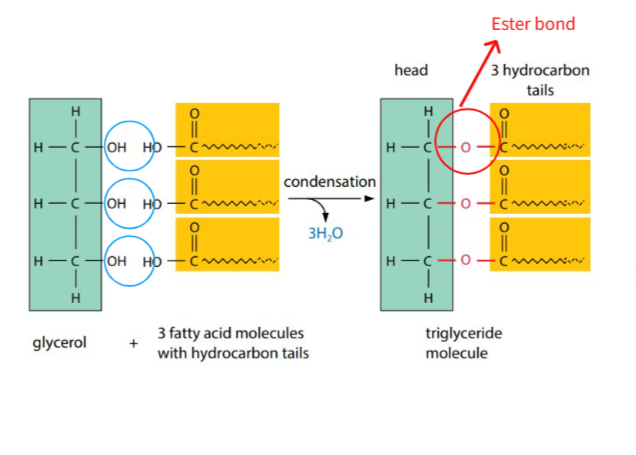
B1.1.2—Production of macromolecules by condensation reactions that link monomers to form a polymer
Macromolecules or polymers are large molecules that are made up of smaller building blocks called monomers.
Monomers are individual subunits that can be linked together to form longer chains or polymers.

- Formation of polymers by condensation reactions
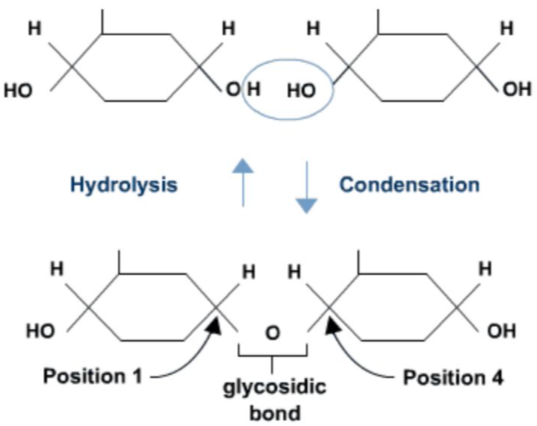
Condensation: polymerisation reaction in which two molecules join together. One molecule loses a hydroxyl group (−OH) and the other loses a hydrogen atom (−H), forming a water molecule and resulting in formation of a new covalent bond.

B1.1.3—Digestion of polymers into monomers by hydrolysis reactions
Break down of polymers by hydrolysis reactions
Hydrolysis: chemical reaction in which water molecules are used to split larger polymer down into its individual monomers (by breaking down the covalent bonds). It is the reverse reaction for the condensation.
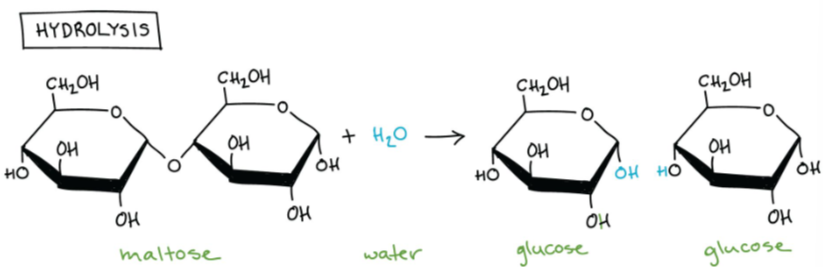
B1.1.4 – Form and function of monosaccharides
Carbohydrates are macromolecules composed of C, O and H. They are essential to life.
Monosaccharide: simplest form of a carbohydrate, consisting of a single sugar unit that cannot be broken down into smaller molecules by hydrolysis.
According to the number of C, they are classified into:
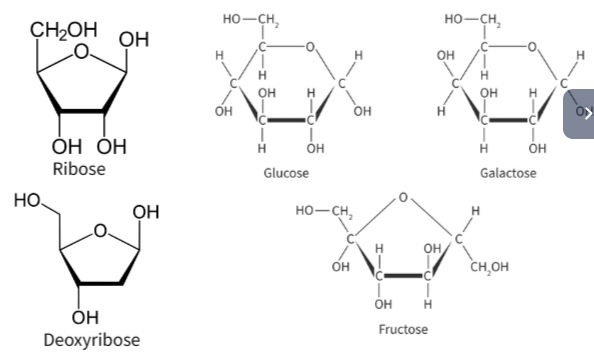
- Pentose: 5 C atoms
(a) Ribose
(b) Deoxyribose
- Hexoses : 6 C atoms
(a) Glucose
(b) Fructose
(c) Galactose
Properties and uses of glucose
- Structure
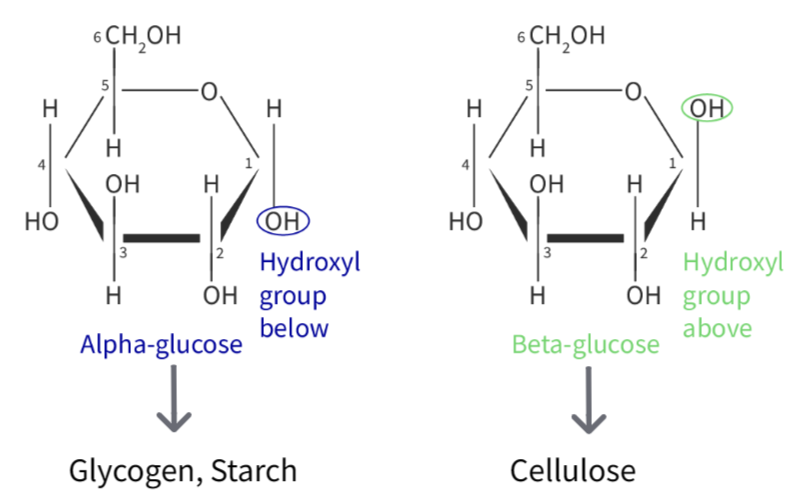
Different isomers depending on the position of the hydroxyl group of the carbon linked to the O atom.
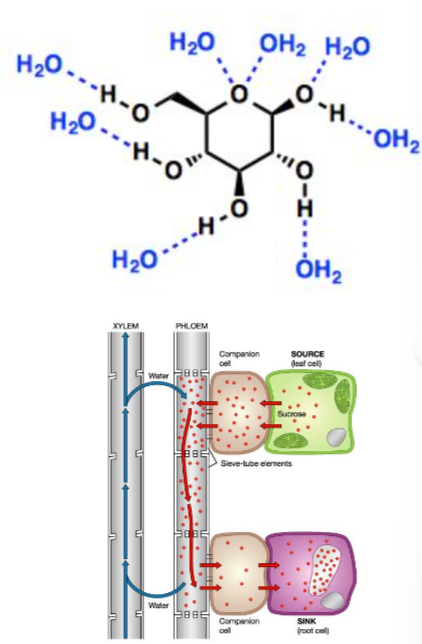
- Solubility and transport
- Chemical stability
The –OH groups situated in the axial regions of the molecule, minimise the electrostatic repulsions within it, making glucose stable.
– structural stability of cellulose
– storage in glycogen and starch

- Oxidation
Oxidation: chemical reaction that involves the loss of electrons from an atom or molecule. During cellular respiration, glucose, in the presence of O2, is oxidised, broken down into CO2 and H2O. In this process, energy is produced in the form of ATP.

B1.1.5—Polysaccharides as energy storage compounds
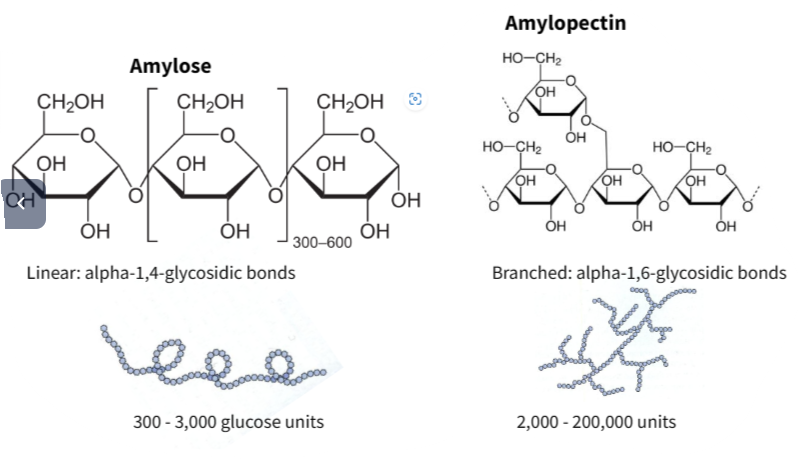
Starch: Storage of glucose in plants.
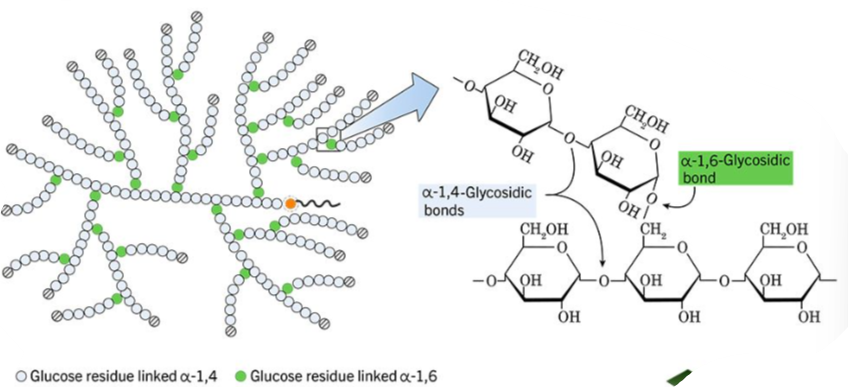
Glycogen: Storage of glucose in animals (muscle and liver)


B1.1.6—Structure of cellulose related to its function as a structural polysaccharide in plants
Cellulose
Beta-glucose molecules alternate in orientation forming a straight line, resulting in long chains that can be grouped into bundles (microfibrils).
Microfibrils are held together by hydrogen bonds between adjacent cellulose molecules.
This results in a strong an rigid structure that forms the cell wall in plant cells, providing tensile strength.
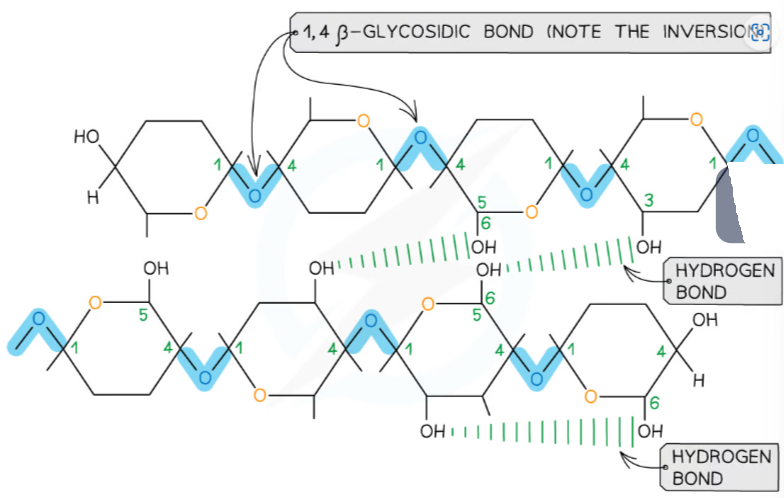
B1.1.7—Role of glycoproteins in cell–cell recognition
Glycoproteins: proteins with carbohydrates attached.
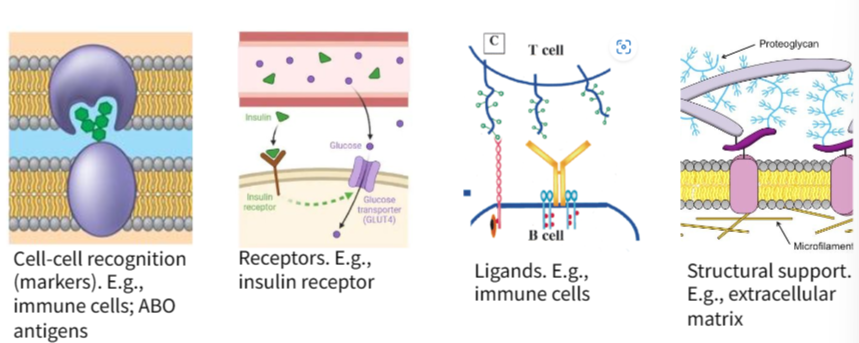
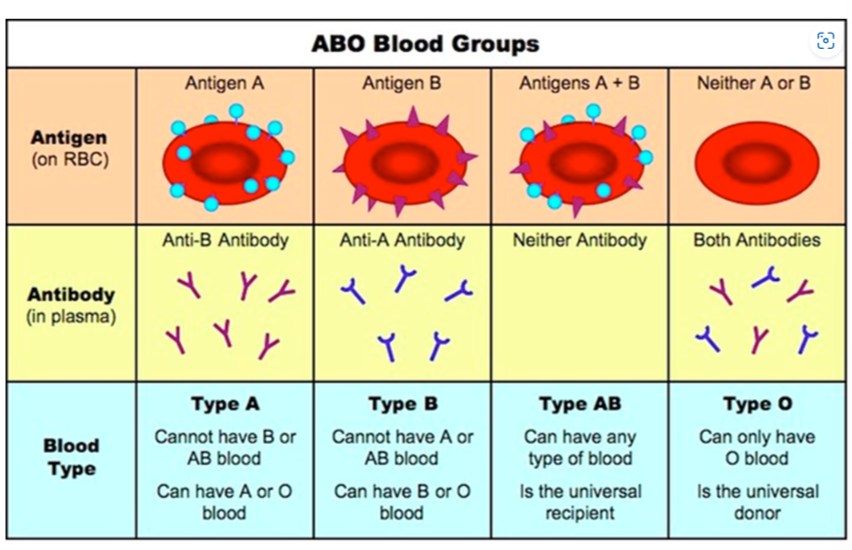
ABO antigens
B1.1.8—Hydrophobic properties of lipids
Lipids: substances that dissolve in non-polar solvents but are only sparingly soluble in aqueous solvents.
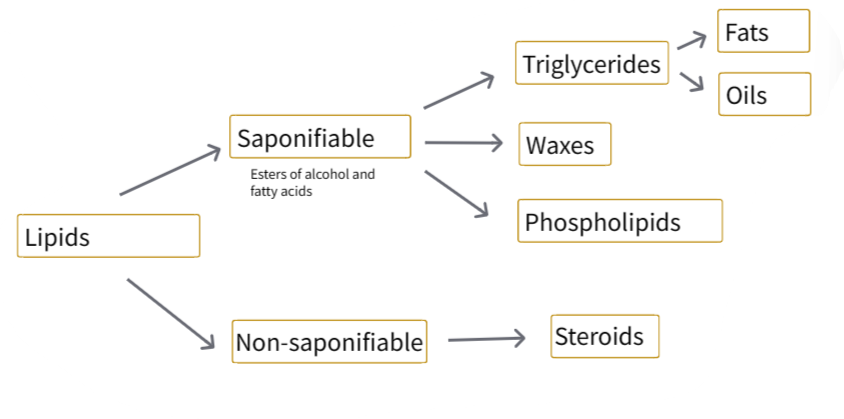
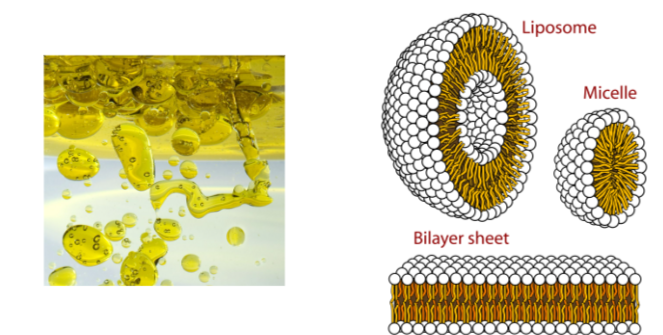
Lipids with high melting points are solid at room temperature, whereas those with low melting points are liquid.
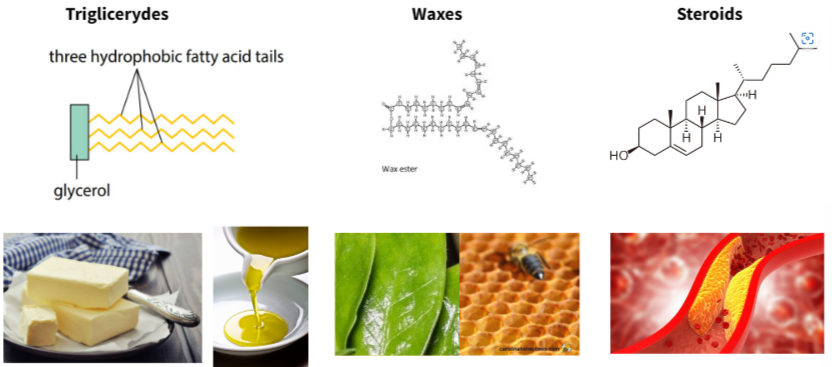
B1.1.9—Formation of triglycerides and phospholipids by condensation reactions
Triglicerydes
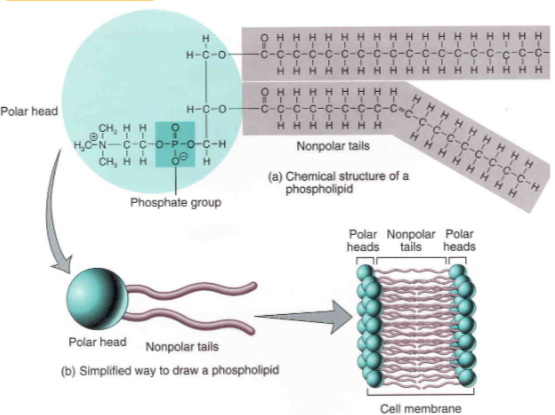
Phospholipids
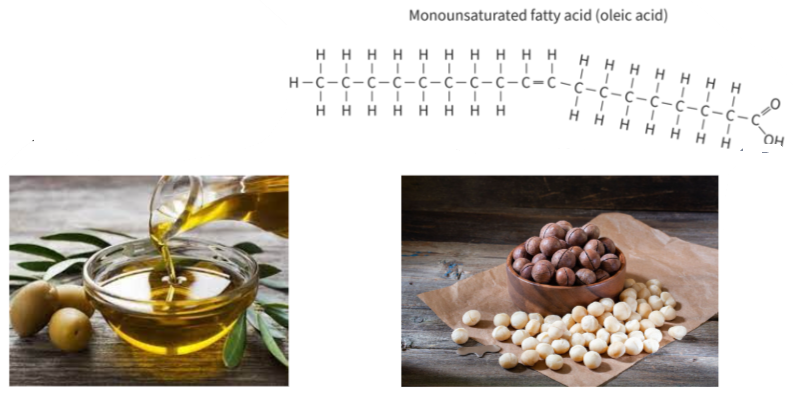
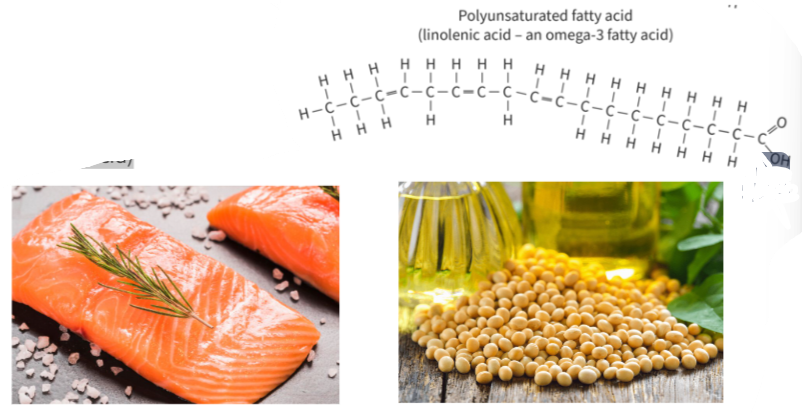
B1.1.10—Difference between saturated, monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids

- beef, pork and poultry
- whole milk, cheese, butter and cream
- coconut and palm oil
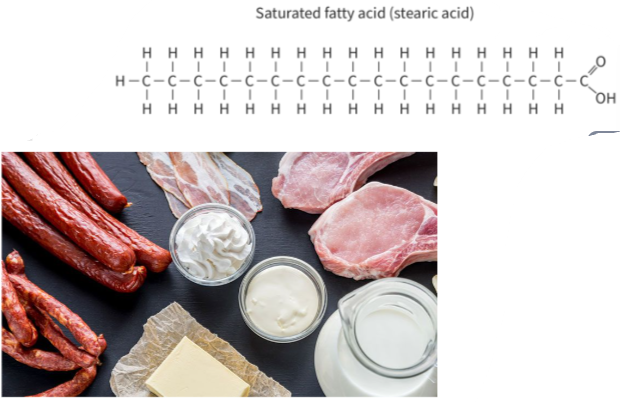
- olive oil (oleic acid)
- macadamia nuts (palmitoleic acid)
- soybean oil and other vegetable oils (linoleic acid)
- fatty fish, e.g. salmon (alpha-linolenic acid)


B1.1.11—Triglycerides in adipose tissues for energy storage and thermal insulation
Functions of lipids:
- Long term energy storage: triglicerydes in adipose tissues
- Thermal insulation: triglicerydes in animals adipose tissues
- Structural: phospholipids in cell membranes
- Hormonal signalling: steroids
- Protection against physical injury: triglicerydes in adipose tissue around organs in animals

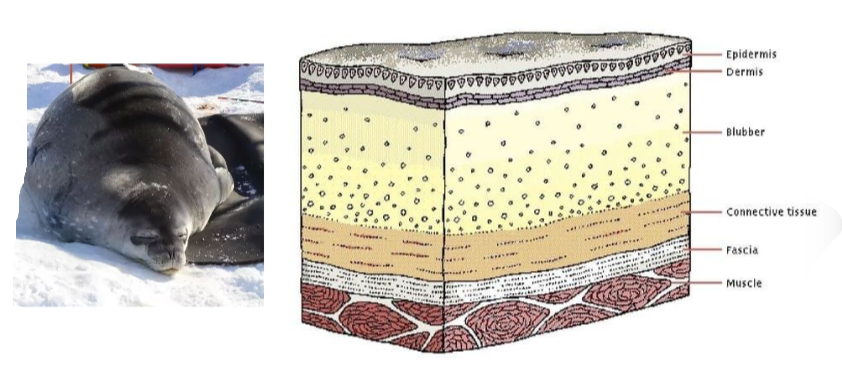
B1.1.11—Triglycerides in adipose tissues for energy storage and thermal insulation AND B1.1.10—Difference between saturated, monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids
Long term energy storage: fats provide 9 kcal/g when consumed through respiration.

B1.1.11—Triglycerides in adipose tissues for energy storage and thermal insulation AND B1.1.5—Polysaccharides as energy storage compounds
Energy storage: Fats vs Carbohydrates

B1.1.12—Formation of phospholipid bilayers as a consequence of the hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions
Phospholipids are amphipathic molecules
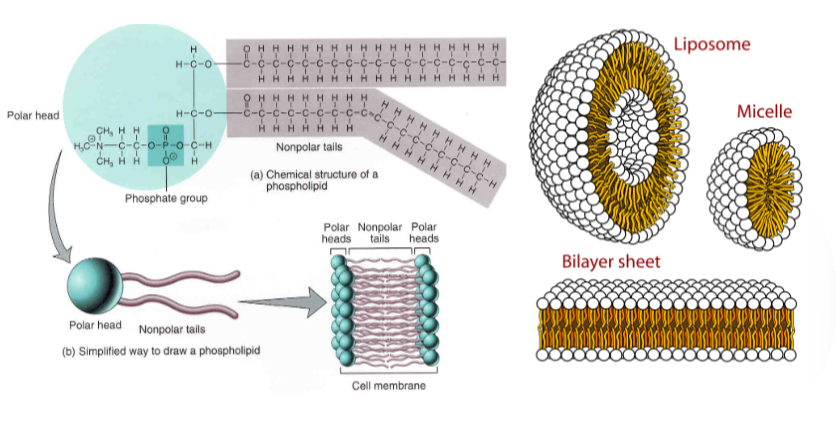
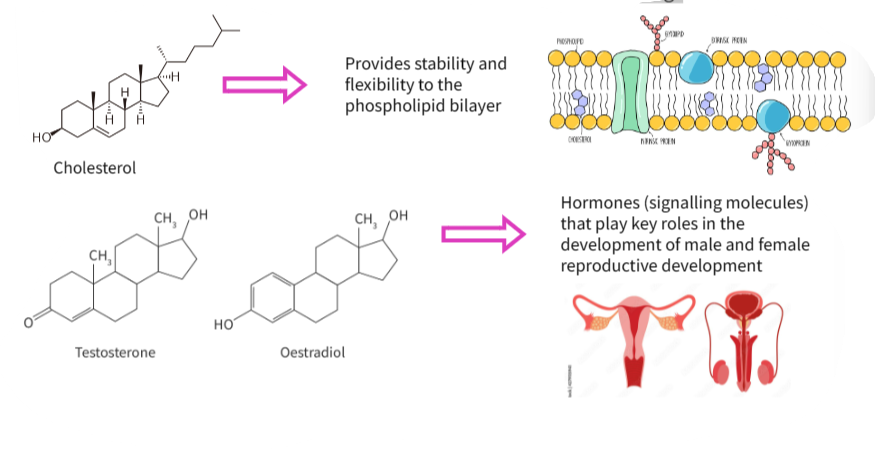
B1.1.13—Ability of non-polar steroids to pass through the phospholipid bilayer
Steroids: non-polar organic molecules with 4 different carbon-based rings
Question 1:
a) What does organic compounds mean?
b) Give examples of organic compounds/biomolecules in our body.
▶️Answer/Explanation
a) Carbon containing compounds are referred as organic compounds.
b) Examples of organic compounds/biomolecules in our body are : carbohydrate , proteins , nucleic acid , lipids
Question 2:
Name the four most common elements in living organisms.
▶️Answer/Explanation
The most common elements in living organism are : carbon , hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Question 3:
What is biomolecule?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Any molecule produced by a living organism is known as biomolecule.
Question 4:
How many covalent bonds can carbon form and why?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Carbon can form 4 covalent bonds. It is because they have 4 outer shell electrons that can be shared with other atoms
Question 5:
(a) How many compounds can carbon form and why?
(b) Name the 3 structures / chains carbon bonds can form.
▶️Answer/Explanation
(a) Carbon can form infinite compounds as it forms double and triple bonds with itself or with other elements.
(b) Carbon can form straight chains , branched chains and cyclic structures.
Question 6:
What is condensation?
▶️Answer/Explanation
A reaction where two or more monomers form together to make water polymers is known as condensation.
Question 7:
(a) What is a hydrolysis reaction?
(b) Give an example of this.
▶️Answer/Explanation
(a) A reaction where water polymers are broken down into individual monomers is known as hydrolysis reaction.
(b) \(H_2 O \rightarrow OH\) and H
Question 8:
(a) What are the two types of metabolic reactions? Give examples
▶️Answer/Explanation
(a) Two types of metabolic reactions are:
- Anabolic: Monomers put together to make polymers ( e.g condensation reaction)
- Catabolic: Polymers broken down into monomers (e.g hydrolysis reaction)
Question 9:
(a) What are ribose?
(b) What are glucose? What is it used for?
▶️Answer/Explanation
(a) 5 ring sugar or pentose found in RNA is known as ribose.
(b) 6 ring sugar or hexose is known as glucose.
Uses:
- Essential molecule for photosynthesis.
- Used for respiration , cellular structural support (cellulose) and energy storage(starch) .
- Found in animal and plant cell.
- It is the main type of sugar in the blood and is the major source of energy for the body’s cell.
Question 10:
(a) Is glucose polar or non polar? Why?
(b) Give 4 characteristics of glucose.
▶️Answer/Explanation
(a) Glucose is polar due to covalent bonding of oxygen with hydrogen.
(b) Four characteristics of glucose are:
- Highly soluble in water
- Easily transportable in blood
- Bonds don’t break easily
- Yields a lot of energy produced in oxidation reactions.
Question 11:
(a) What is starch made up of?
(b) What does starch do?
▶️Answer/Explanation
(a) Starch is made up of hundreds of Glucose monomers that are compacted together by additional bonds creating branching and coiling.
(b) Starch acts as energy storage for plants. Large molecules not easily soluble , easily stored.
Question 12:
Condensation and hydrolysis reaction in starch?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Condensation: More glucose monomers can be added to the starch polymer as it is made in photosynthesis
Hydrolysis: The starch can then be broken up so the glucose can be used as an energy source
Question 13:
Give difference between Monosaccharides and Polysaccharides
Question 14:
(a) What is glycogen made up of?
(b) What does glycogen do?
(c) Solubility of glycogen?
▶️Answer/Explanation
(a) Glycogen is made up of hundreds of glucose monomers.
(b) Glycogen is highly branched to create an energy storage molecule for animals. It can be broken down to glucose when energy is needed.
(c) It is not easily soluble in cytoplasm and other liquids.
Question 15:
Give examples of polysaccharides.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Examples are: starch , glycogen , cellulose.
Question 16:
(a) What are the two types of glucose?
(b) Give difference between the above two types.
▶️Answer/Explanation
(a) Two types of glucose are:
- Alpha glucose
- Beta glucose
(b) Alpha glucose: same order on each end of the monomer (eg. H HO both sides)
Beta glucose: reversed group order on one end (e,g H OH on left , HO H on right)

Question 17:
How do cellulose fibres link to each other?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Hydrogen bonding creates molecules of cellulose.

Question 18:
What are the different chain structures in the 3 types of polysaccharides?
▶️Answer/Explanation
- Starch : branched
- Glycogen : highly branched
- Cellulose : straight

Question 19:
Give examples of carbohydrate with protein/lipid bond.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Examples are : glycoprotein and glycolipid.
Glycoprotein is a type of carbohydrate chain on the top of membrane proteins .
Glycolipid is a type of carbohydrate chain on the top of lipid head on membrane.
Question 20:
What is the function of glycoprotein and glycolipid?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Function of them is cell adhesion and cell recognition.

Question 21:
What determines blood type?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Glycoproteins on the surface of red blood cells (RBC) determines the blood type.
Question 22:
(a) What are antigens?
(b) What are antibodies ? Give its types?
▶️Answer/Explanation
(a) Antigens are a toxin or other foreign substance (glycoprotein on RBC) that includes an immune response in the body, especially the production of antibodies.
(b) Antibodies are the proteins that protects you when an unwanted substance enters your body. It is of two types
- Anti a
- Anti b
Question 23:
(a) State the solubility of lipids?
(b) Give examples of lipids.
▶️Answer/Explanation
(a) Lipids are hydrophobic and doesn’t dissolve in water. However , they dissolve in non polar solvents like petrol because lipids are made up of non polar covalent bonds between carbon and hydrogen.
(b) Examples of lipids are: fat , oil , waxes and steroids.
Question 24:
(a) Give the structure of fatty acids.
(b) What are the three categories of fatty acid?
(c) Give melting points , state of matter at room temperature and examples of the above three categories.
▶️Answer/Explanation
(a) Fatty acids are long chains of carbon and hydrogen , with a carboxyl group at one end \(CHO_2\)
(b) Saturated : no double bonds
Monounsaturated : one double bond
Polysaturated: two or more double bond
(c) 
Question 25:
(a) What are the subunits or monomers in lipids?
(b) Give the structure of lipids.
▶️Answer/Explanation
(a) Subunits in lipids are : fatty acids and glycerol
(b) 3 fatty acids link to a single glycerol by condensation reaction to make triglyceride.

Question 26:
Give the structure of phospholipid.
▶️Answer/Explanation
2 fatty acids and a phosphate bond to a glycerol to form phospholipid.

Question 27:
What are endotherms?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Animals who maintain body temperature through metabolic heat is known as endotherms.
They require a constant supply of energy through food.
Question 28:
(a) Where is the fat stored?
(b) What are the characteristics of triglyceride?
▶️Answer/Explanation
(a) Adipose tissue as triglycerides , can be broken down into ATP used to power cellular processes.
(b) Characteristics of triglyceride are:
- good for long term storage.
- provide twice the energy of carbohydrates
- insoluble in body fluids
Question 29:
(a) What are hormones?
(b) Where are steroids made?
(c) Give the structure of steroids . Is it hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
▶️Answer/Explanation
(a) Hormones are the chemical messengers produced by glands and include a group called steroids.
(b) Steroid are made in lipid cholesterol
(c) Steroids are made by 4 carbon based rings as the basic structure but have different functional groups resulting in different functions.
It is hydrophobic and can easily pass through bilayer from within the hydrophobic region.

Question 30:
What makes metabolism?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Anabolism (condensation) and Catabolism (hydrolysis) make metabolism.
Question 31:
Give examples of anabolic reactions.
▶️Answer/Explanation
- Amino acids: proteins
- Nucleotides : DNA and RNA
Question 32:
(a) What are glycoproteins a type of? What are the two types of blood?
(b) What are their functions?
▶️Answer/Explanation
(a) Glycoproteins are a type of antigen.
Two types of blood are:
- type a
- type b
(b) Their functions are cell recognition in immune system , which is why if the wrong blood is transfused , the patient will die as the blood will start attacking and clotting.
Question 33:
What is the difference between cis and trans fatty acid?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Cis = hydrogen same side
Trans = hydrogen opposite side
It only applies to unsaturated fatty acids.
Question 34:
What creates the straight chains in cellulose?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Alternating beta glucose (eg. \(CH_2OH\) on top and bottom sides alternating , OH on left OH on right). creates straight chains in cellulose.


