- IB DP Biology 2025 SL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 1
- IB DP Biology 2025 HL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 1
- IB DP Biology 2025 SL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 2
- IB DP Biology 2025 HL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 2
B1.2.1—Generalized structure of an amino acid
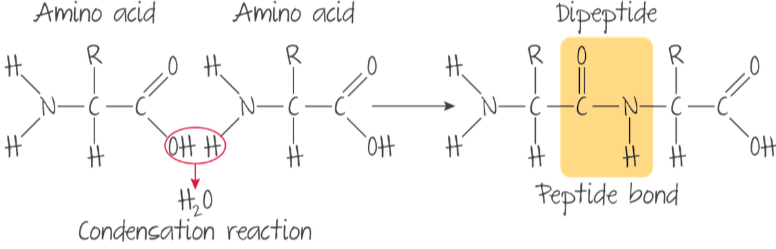
Proteins: biomolecules comprised of amino acids joined together by peptide bonds.


B1.2.2—Condensation reactions forming dipeptides and longer chains of amino acids
- Tyrosine can be synthesised from phenylalanine.
- Arginine cannot be synthesised by infants

Diet sources of essential amino acids


B1.2.4—Infinite variety of possible peptide chains
There are infinite possibilities of polypeptides because:
- 20 different amino acids are coded by the genetic code
- polypeptides can be of any length (up to thousands)
- amino acids can be in any order

If a polypeptide contains just 7 amino acids , there can be \(20^7\) = 1,280,000,000 possible polypeptides generated.

B1.2.5—Effect of pH and temperature on protein structure
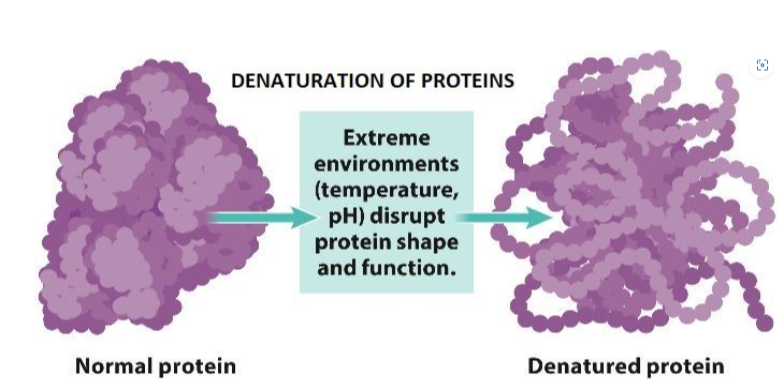

B1.2.6—Chemical diversity in the R-groups of amino acids as a basis for the immense diversity in protein form and function

Interactions between amino acid side chains determine the structure of the protein

Protein structure determines function

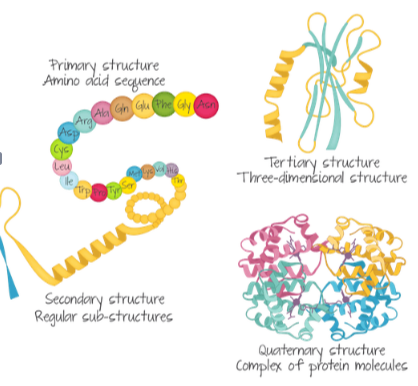
B1.2.7—Impact of primary structure on the conformation of proteins
(a) Primary structure

(b) Secondary structure

(c) Tertiary structure

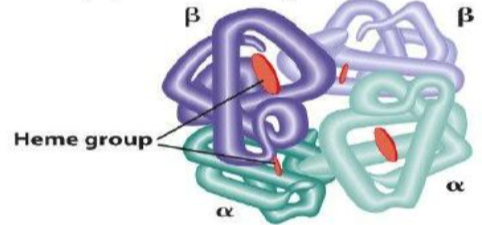
(d) Quaternary structure
Primary structure:
- Sequence of amino acids linked through covalent bonds
- Determines the subsequent conformation -> allows us to predict protein structures

B1.2.8—Pleating and coiling of secondary structure of proteins
Secondary structure is due to hydrogen bonding between the amine and carboxyl groups of non adjacent amino acids

B1.2.9—Dependence of tertiary structure on hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, disulfide covalent bonds and hydrophobic interactions

- Hydrogen bonds
- Ionic bonds: between positively or negatively charged amine and carboxyl group
- Disulfide bonds: between cysteins
- Hydrophobic interactions

B1.2.10—Effect of polar and non-polar amino acids on tertiary structure of proteins