- IB DP Biology 2025 SL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 1
- IB DP Biology 2025 HL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 1
- IB DP Biology 2025 SL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 2
- IB DP Biology 2025 HL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 2
B2.3.1—Production of unspecialized cells following fertilization and their development into specialized cells by differentiation
Unicellular organisms: the unique cell performs all 8 functions of life.
Multicellular organisms: not all cells perform all 8 functions of life.

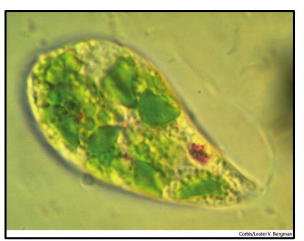
- Cells are specialized
Most cells are dedicated to a specific function of life
i.e. gametes (sex cells) – Reproduction, not Movement or Nutrition
i.e. muscles cells – Movement, not Reproduction or Nutrition
i.e. stomach cells – Nutrition, not Movement or Reproduction
- Most cells perform Respiration
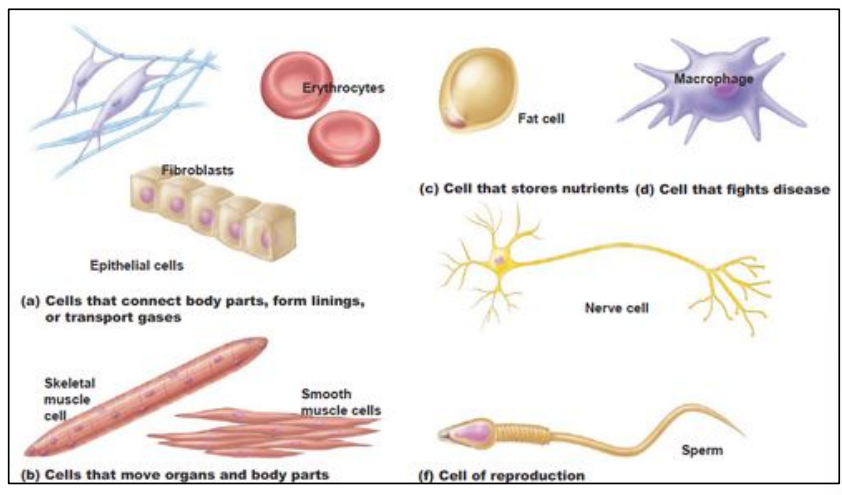
- Specialized cells in humans
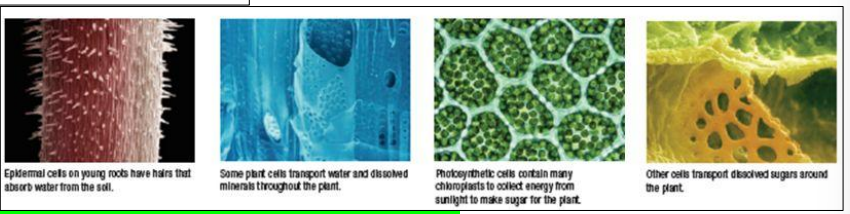
- Specialized cells in plants
What is cell differentiation?
Cell differentiation is the WAY by which cells become specialized.
All cells of an organism contain all the chromosomes, hence the same genes
But all cells are specialized
e.g. White blood cells to fight against pathogens (1)
ex. Heart’s muscle cells to pump blood out of the heart (2)
ex. Skeletal muscles’ cells for body movement (3)
ex. Neurons carry nervous impulses (4)

- A cell does not need all proteins all the time
– A stomach cell needs the proteins the stomach needs
– An iris cell needs the proteins the iris needs

BUT
– A stomach cell does not need all proteins needed by the iris
– An iris cell does not need all proteins needed by the stomach

Gene : Fragment of chromosome containing instructions to produce a specific protein

An organism has different types of specialized cells because each cell type “expresses” ONLY the genes that are necessary for this cell type
In humans: A few hundred of genes among the 20 500 available genes are expressed in cells
All other genes are not expressed.
Fertilization = fusion of nuclei of two gametes
Outcome = zygote
Divides via mitosis
Then cells start to specialize via differentiation
To give specific tissues and organs :Heart, eyes, liver, kidneys…

Gradients of gene expression impact greatly the “choice” of genes to be expressed or not

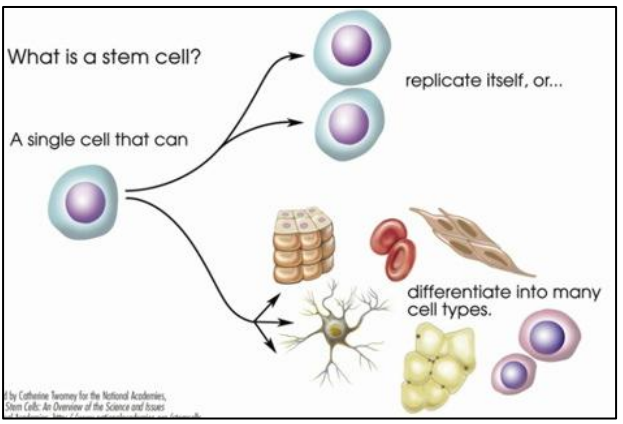
B2.3.2—Properties of stem cells
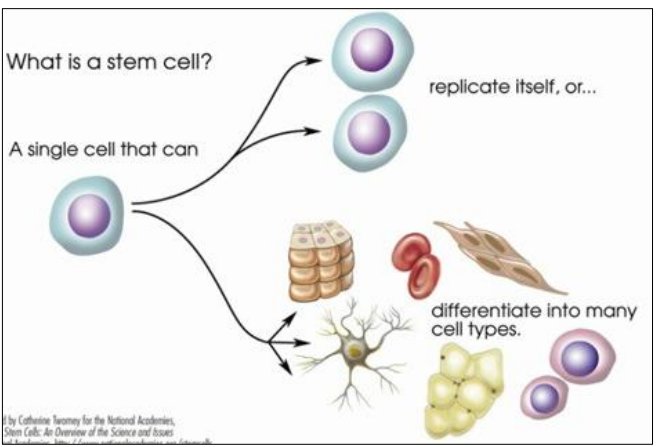

| POTENT | GIVE RISE TO | FOUND IN |
| Totipotent | Any cell type | Zygote to Morula |
Pluripotent “Embryonic | Any cell type | Inner mass cells of embryo |
| Multipotent | Several cell types | In some adult tissues |
| Unipotent | Only one cell type | In some adult tissues |
- Obtaining Embryonic stem cells 1/3
Fertility clinics: In Vitro Fertilization process for couples that cannot procreate naturally

More embryos than needed for implantation are produced \(\Rightarrow\) Extra embryos \(\Rightarrow\) Frozen for future implantation
OR
Source of embryonic stem cells
If allowed by laws
If agreed by donors
- Obtaining Embryonic stem cells 2/3

Genetic screening:
IVF produces numerous embryos
A single cell from 8-cell embryo is removed
This cell is used to check any genetic anomaly
e.g. Down syndrome, Cystic fibrosis…
The seven cells left are implanted into the mother’s uterus
Develop normally into blastocyst, fetus, and healthy baby
Could use the removed 8th cell to obtain/produce embryonic stem cells
- Obtaining Embryonic stem cells 3/3
Blood of umbilical cord at birth
Contains embryonic stem cells
Can be collected and used


- Using embryonic stem cells in therapies


B2.3.3—Location and function of stem cell niches in adult humans
Obtaining adult stem cells
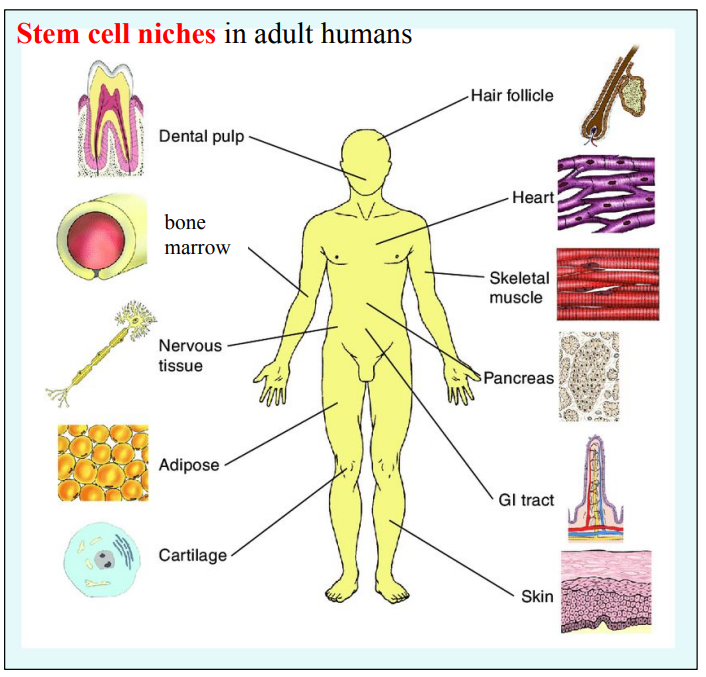
Drawbacks:
Small quantities
Hard to access from stem cell niches
In their niche, the stem cells are maintained or they differentiate
Therapeutic uses of adult stem cells
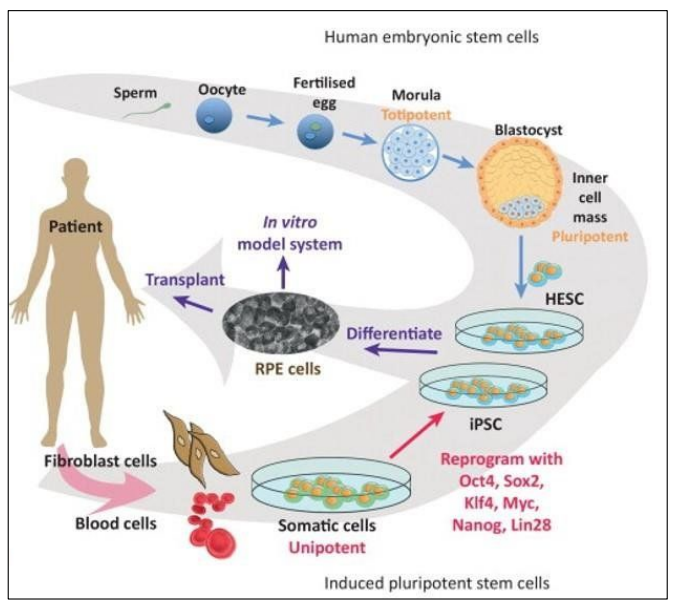
Treatment of:
Burns
Leukemia
Diabetes type I
Parkinson’s disease
Alzheimer’s disease
Glaucoma
Stargardt’s disease
Muscle atrophy
B2.3.5—Cell size as an aspect of specialization
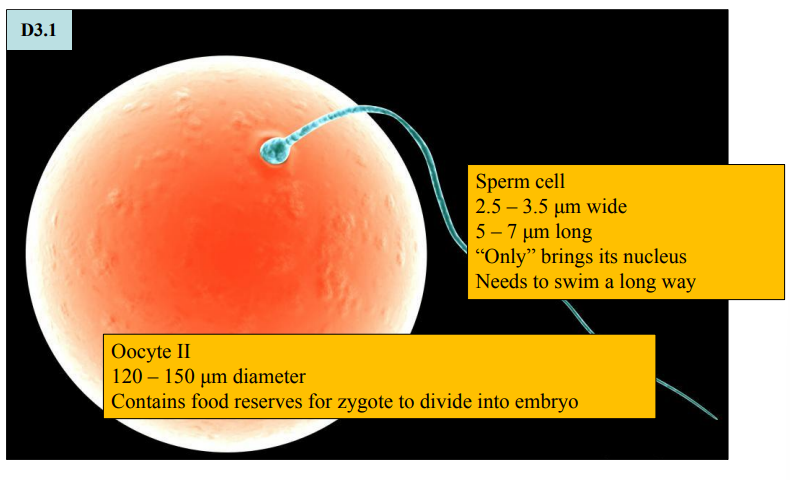
Relative sizes of sperm and secondary oocyte
Relative sizes of red and white blood cells
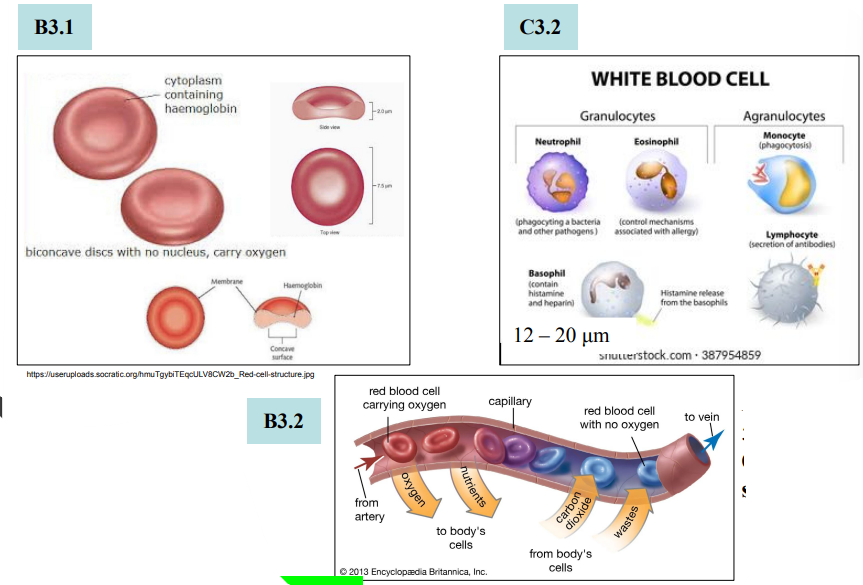
Diameter of lumen
5-10 μm
Only RBCs can
squeeze through
Structure-function of neurons
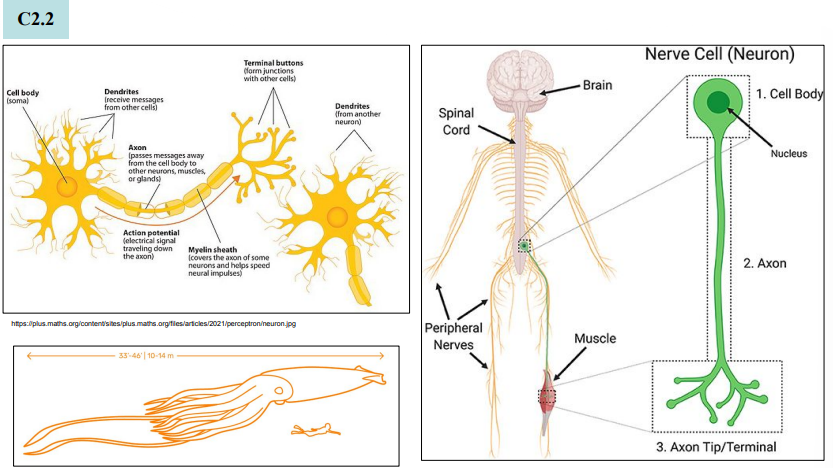
Longest neuron = 12 m
Human neurons: Length 1 nm to 1 m
Structure-function of striated muscle cells
Human 3 types of muscle cells enable movement of body parts
Skeletal aka Striated muscle cells = muscles attached to bones.
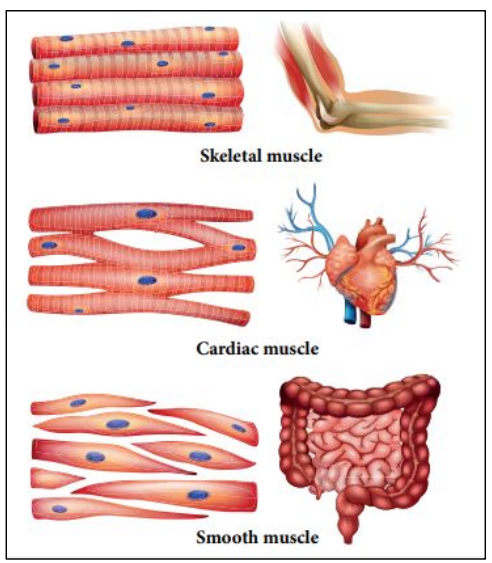

Diameter 10 – 50 μm
Length 40 mm
Surface area to volume ratio
Surface area to volume ratio is often misunderstood
It is a representation of how much surface area is available for exchange of substances per unit of volume.
As size increases, surface area increases.
However, as size increases, surface area to volume ratio decreases



One unit of volume can rely on six units of surface area to exchange with surroundings
One unit of volume can rely on three units of surface area to exchange with surroundings
One unit of volume can rely on two units of surface area to exchange with surroundings
What is best for cells exchange with surroundings? Many small cells OR A few huge cells?
Have many cells of a small size ,to facilitate exchange of materials between cells and their environment
Oxygen and nutrients in CO2 and other waste out
B2.3.7—Adaptations to increase surface area-to-volume ratios of cells
How to increase surface area to volume ratio?
Extended length, Villi and microvilli of the small intestine for better absorption
7 meters 250 \(m^2\) (a tennis court)

Round and biconcave (flattened) shape of red blood cells for better gas exchange
SA/V ratio = 1.5 5 million per microliter of blood
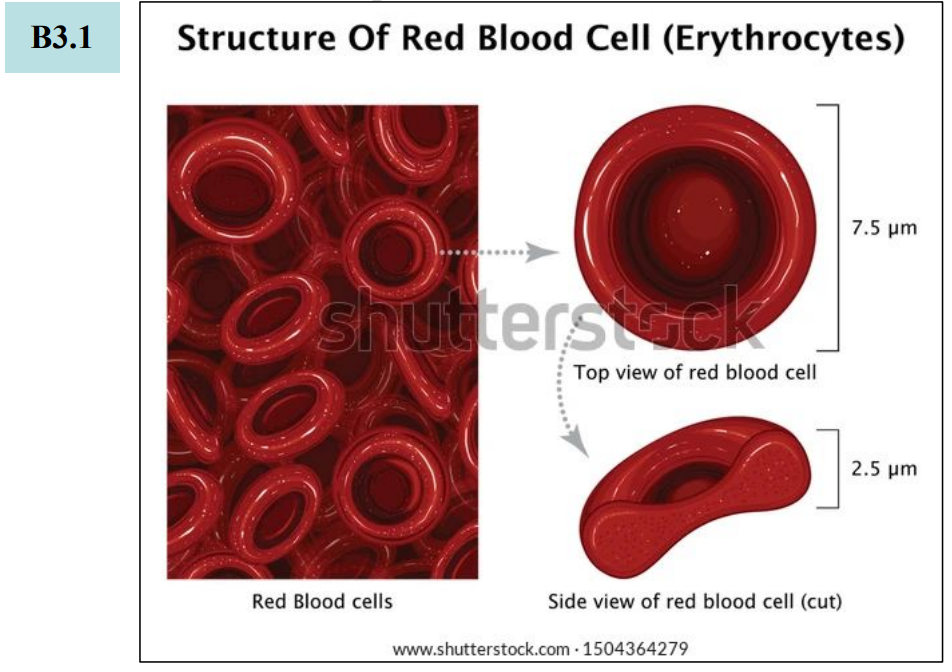
Extended length of proximal convoluted tubule of nephron for reabsorption of glucose

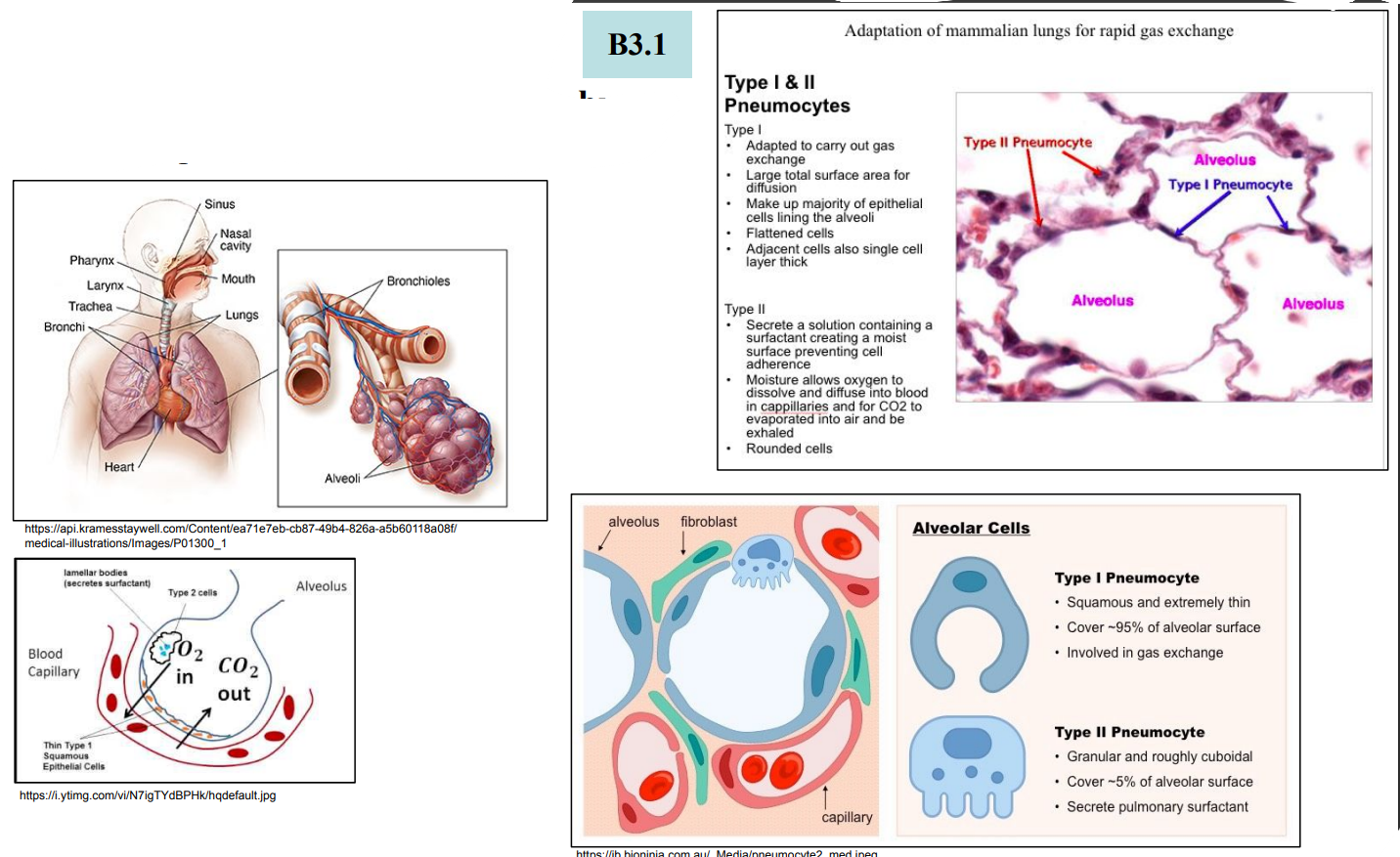
B2.3.8—Adaptations of type I and type II pneumocytes in alveoli
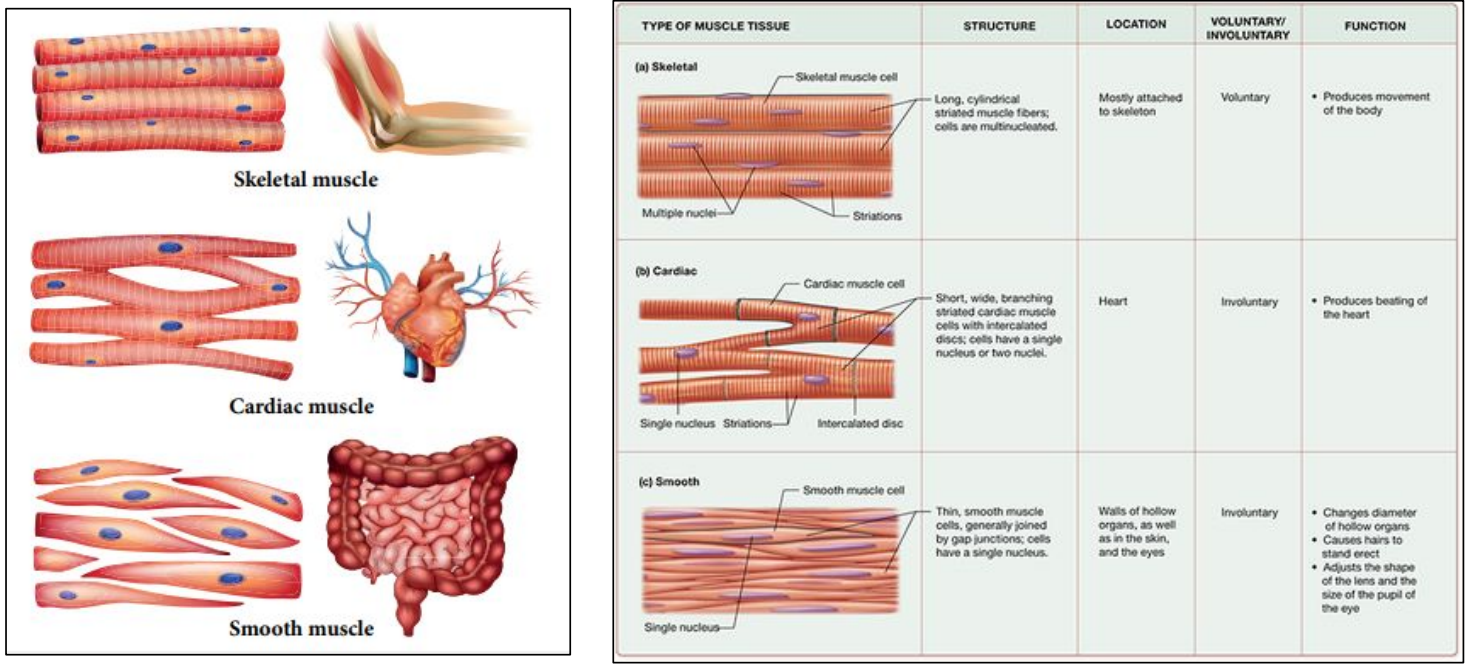
B2.3.9—Adaptations of cardiac muscle cells and striated muscle fibres
Compare and contrast cardiac and striated (skeletal) muscle cells
Human 3 types of muscle cells
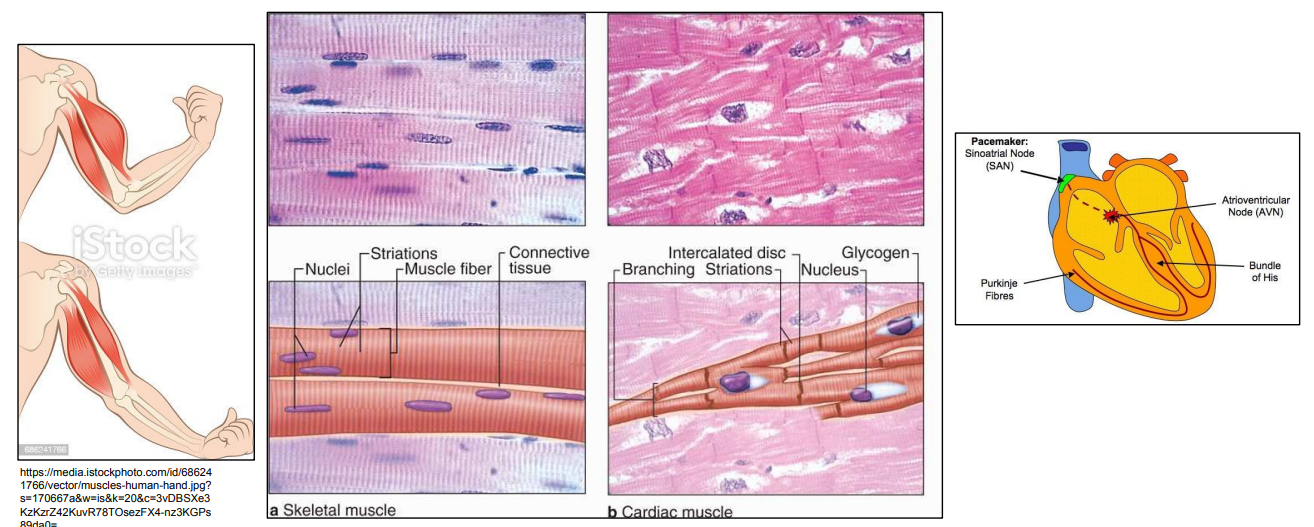
No branching (overall tubular shape) as the contraction is in one dimension = length
Branching so each cell is in contact with 3 to 4 other cardiac muscle cells. To speed up signal propagation to contract
Adaptations of sperm and egg cells (HL only)
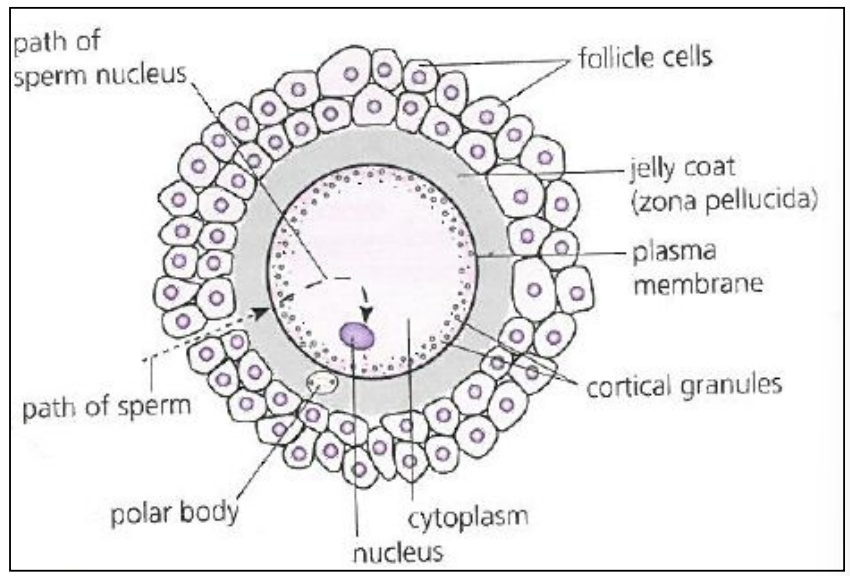
Haploid nucleus for fusion with sperm’s nucleus
Cortical granules below plasma membrane
To prevent polyspermy (more than one sperm nucleus entering)
Surrounded by:
1. Zona pellucida (jelly coat) = layer of glycoproteins
Binding for sperm + Initiation of acrosome reaction
2. Follicle cells (remains of secondary follicle)
