- IB DP Biology 2025 SL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 1
- IB DP Biology 2025 HL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 1
- IB DP Biology 2025 SL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 2
- IB DP Biology 2025 HL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 2
B3.3 Muscle and motility (HL only)
Movement as a characteristic of life (HL only)
⮚ Movement = one characteristic of living organisms
- Movement inside cells
e.g. cytoplasmic streaming

- Movement within organisms
e.g. contractions of the heart

- Movement of the whole organism = locomotion
e.g. walking, running, jumping, swimming
Use of muscles in locomotion

Three basics mechanisms for locomotion for animals
1. Amoeboid movement
e.g. Amoeba, White blood cells

2. Using cilia and flagella

3. Muscular locomotion

Organisms are:
- Sessile(can move from one place to another)
- Motile(cannot move from one place to another)

Why do organisms move?
 Forging the food
Forging the food
 Escaping from danger / Foraging for food
Escaping from danger / Foraging for food
 Finding a mate
Finding a mate
 Migration
Migration
The musculo-skeletal system (HL only)
⮚ Support system of animals = skeleton
⮚ Arthropods: skeleton is outside = exoskeleton
Vertebrates: skeleton is inside = endoskeleton

⮚ Support system of animals = skeleton
⮚ Insects: skeleton is outside = exoskeleton
Vertebrates: skeleton is inside = endoskeleton
⮚ Skeleton made of many bones + tendons + ligaments + joints
Adult human body has 206 bones
⮚ In addition to skeleton itself, movement made possible by
Skeletal muscles
Nerves


Bones

⮚ Support + partially protect body parts
⮚ Articulate with other bones at joints
⮚ Anchorage for muscles through tendons
⮚ Human skeleton
– Axial skeleton = skull + vertebral column
– Appendicular skeleton = limb girdles and limbs

Girdle = set of bones that connects a limb to the axial skeleton
Ligaments

⮚ Connect bone to bone
– Restrict movement at joints
– Prevent dislocation
⮚ Form protective capsule around movable joints
⮚ Connective tissue + fibroblasts
– Made of fibres of protein collagen
– Very slightly elastic

Tendons

⮚ Attach muscles to bones
⮚ Connective tissue + fibroblasts
– Made of fibres of protein collagen
– Slightly elastic
– More elastic than ligaments

Skeletal muscles

Three types of muscles = skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscles
⮚ Skeletal muscles:
– Cause movements by contraction
– Anchored to bones by tendons at joints
– Occur in antagonistic pairs
One muscle contracts, the second is stretched
Agonist = muscle creating flexion when contracting i.e. biceps, quadriceps
Antagonist = muscle creating extension when contracting i.e. triceps, hamstrings


Antagonistic pairs of muscles

Breathing in: volume of thoracic cage increases, pressure decreases until lower than atmospheric air’s, air moves in external intercostal muscles contract, internal intercostal muscles relax
Breathing out: volume of thoracic cage decreases, pressure increases until higher than atmospheric air’s, air moves out internal intercostal muscles contract, external intercostal muscles relax
Bones, ligaments, muscles, tendons and nerves of the hand

Movement and joints (HL only)
Joints
Joints are movable (articulation between bones) or not movable (bones fused)

All movable joints are synovial joints
Thick viscous fluid = synovial fluid inside joint cavity
Lubrification
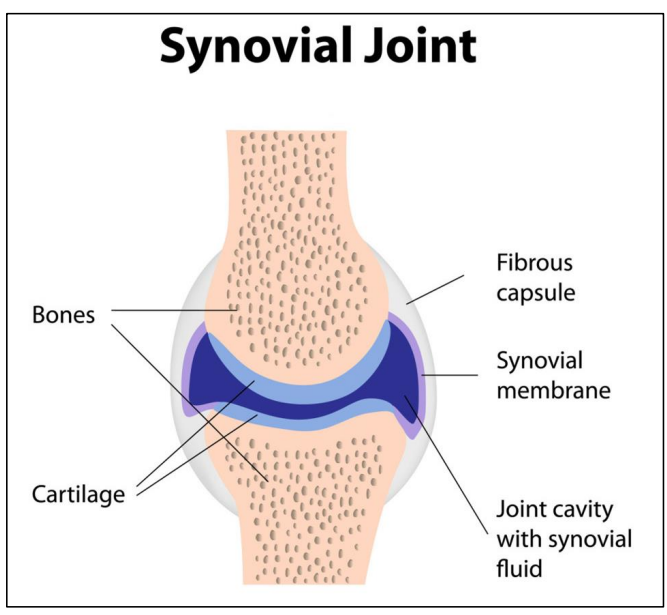
Synovial joints
Two main kinds of joints:
1. Ball-and-socket joints
2. Hinge joints
1. Ball-and-socket joints
Shoulder and hip
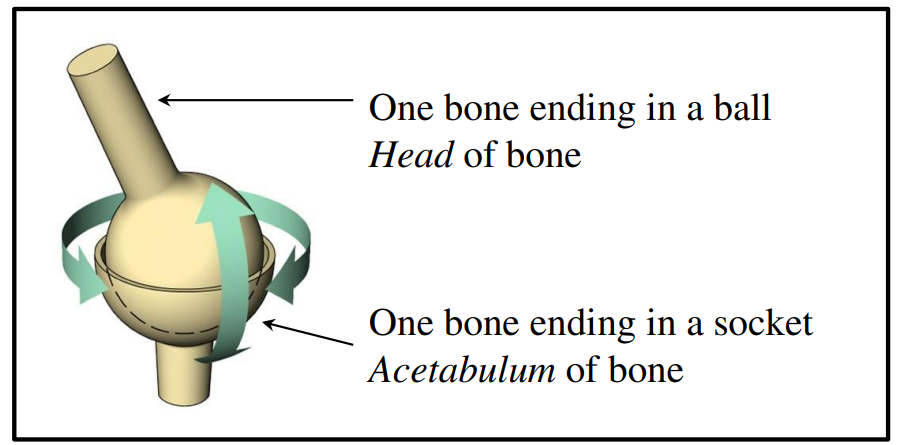


Allows movement in 3 planes
- Protraction / Retraction – forwards and backwards
- Abduction / Adduction – sideways
- Rotation – circular

2. Hinge joints
Knee and elbow

Movement in one plane only
Extension – Flexion


Ligaments hold bones together
– Movement in one plane only
Extension – Flexion
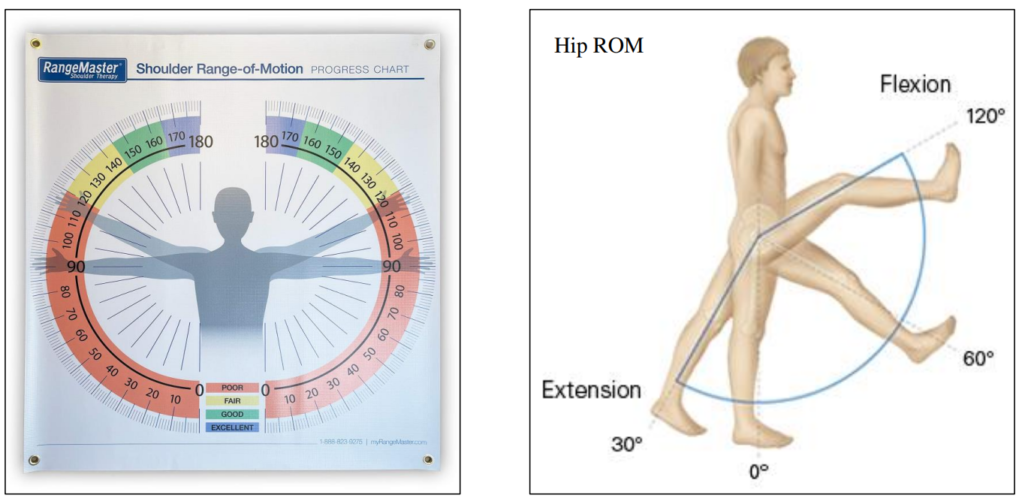
Comparing synovial joints

Comparing range of motion synovial joints
ROM = how much you can move or stretch a particular joint
Measured in degrees of the angles
Equipment = Goniometer gonia = Greek for angle
Motor units and skeletal muscle structure (HL only)
Nerves
Nerve = bundle of nerve fibers (axones) of nerve cells (neurons)
Connect central nervous system (brain + spinal cord) to other parts of body
i.e. skeletal muscles

Motor unit
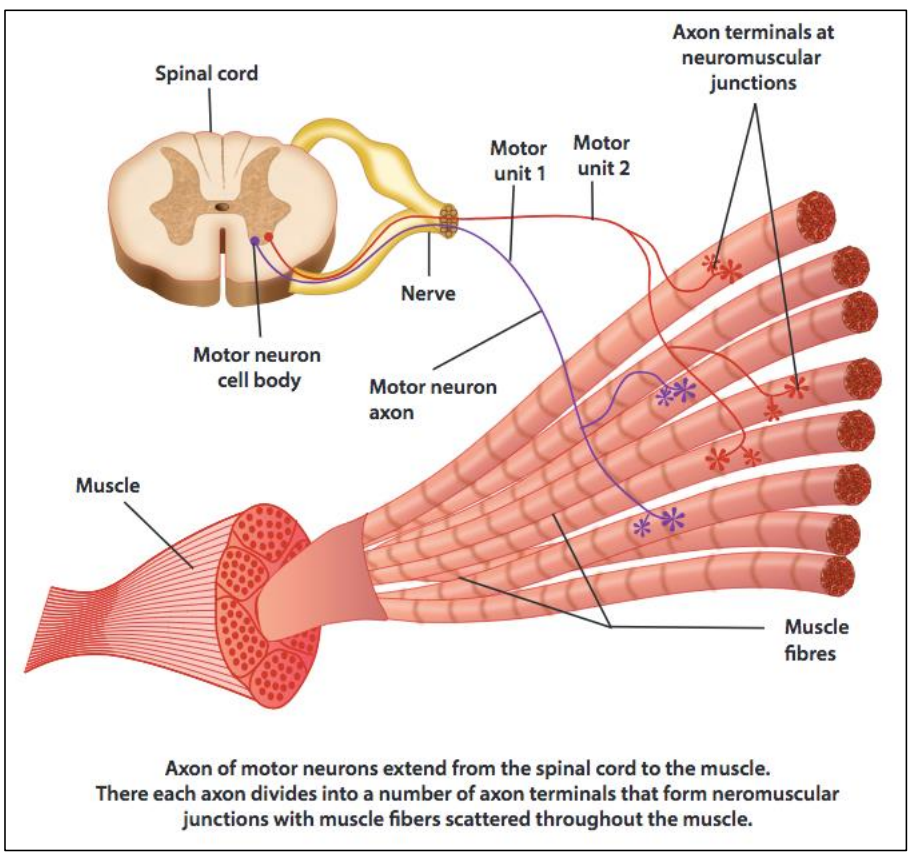
Motor unit in skeletal muscle
=
Motor neuron
+
Neuromuscular junction
+
Muscle fibres
1. Motor neuron sends impulse
2. Neuromuscular junction conveys this impulse to the muscle fibres
3. Muscle fibres contract
Skeletal muscle ultrastructure
⮚ Skeletal muscles can shorten to half to a third of its length when contracted
⮚ Skeletal muscles = bundles of muscle fibres
Muscle fibres = myocytes = “muscle cells”
Muscle fibres are multinucleated (syncytium)
⮚ Muscle fibres appear striated/striped in light microscopy
Light and dark bands
⮚ Each muscle fibre contains many myofibrils
⮚ Each myofibril = succession of sarcomeres




⮚ Sarcolemma – the plasma membrane of a muscle fibre
⮚ Sarcoplasm – the cytoplasm of a muscle fibre
⮚ Sarcoplasmic Reticulum connected to T-tubules infolding of sarcolemma into tubular E.R.
Controls the storage and release of Calcium ions (\(Ca^{2+}\))
⮚ Majority of cell volume = long protein filaments = myofibrils


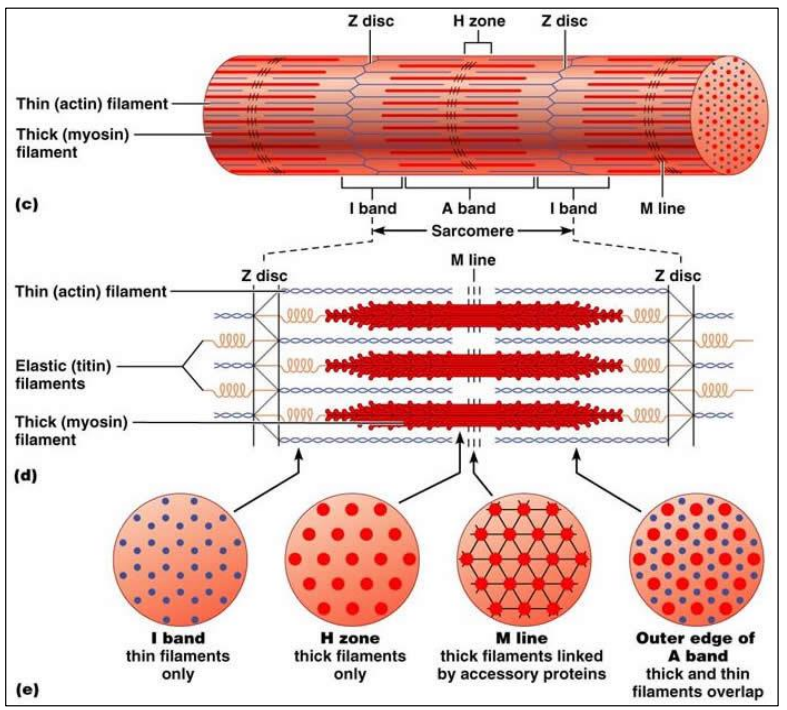
⮚The H zone is the area only occupied by the thick filaments only (myosin)
⮚ The I bands (light) are the regions occupied by thin filaments only (actin)
⮚ The A bands (dark) are the regions occupied by both filaments (overlap)
⮚ The Z lines represent the extremities of a single sarcomere

Sarcomere = functional unit of a muscle Thousands of sarcomeres contract together
1 sarcomere = Z line to Z line Z lines are so-named because they zig-zag
Actin filaments are attached to the Z lines
Z lines may have hundreds of actin myofilaments attached to them
Myosin filaments are attached to each other at the M line
Skeletal muscles contraction (HL only)




1. Action potential from motor neurone reaches muscle
2. Sarcoplasmic reticulum releases \(Ca^{2+}\) into sarcoplasm
3. \(Ca^{2+}\) binds and activates troponin
4. Troponin dislodges tropomyosin from binding site of myosin on actin
5. Myosin + ADP bind actin by forming cross-bridges, Pi away
6. Myosin releases ADP, Power stroke, making actin filament slide
7. ATP binds myosin
8. Myosin + ATP detaches from actin
Tropomyosin binds myosin binding site on actin
9. Myosin breaks down ATP into ADP + Pi
Myosin has ATPase activity
Still attached to mysosin
If \(Ca^{2+}\) still/again present, 1 – 9 happen again
On a further site on actin filament

How do skeletal muscle relax after contraction?
- Role of the protein Titin

When contraction is not needed any longer,
Titin acts as a spring to recover the sarcomere initial length
- Role of the “opposite” muscle

Pair of antagonistic muscles:
Contraction of one muscle helps the relaxation of the second muscle
Adaptations for swimming in marine animals (HL only)
How are marine animals adapted for swimming?
Consider the adaptations that have allowed dolphins to be successful inhabitants of ocean water, They are:
- have streamlined body , allowing the animal to move throughout the viscous water with relative ease and at great spreads.
- have lost almost all body hair, to reduce drag through the water.
- have tail adapted to form a fluke , which allows an up and down motion for propulsion.
- have lost their rear legs, because movement is provided by the fluke
- have front limbs adapted to become flippers primarily used for steering
- have an airway called a “blowhole” located on the dorsal (top) surface of the head , to exchange air at periodic intervals with a minimum of the body leaving the water.
- can seal the blowhole tightly between breaths so that water does not enter the airway
- can stay underwater for several minutes without breathing , so that they can make deep dives
- have retained mammalian characteristics, such as being endothermic, producing milk for their young , having an advanced two-sided circulatory system, and long-term parental care of their young.