- IB DP Biology 2025 SL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 1
- IB DP Biology 2025 HL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 1
- IB DP Biology 2025 SL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 2
- IB DP Biology 2025 HL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 2
C1.2 Cell respiration
ATP, the cell energy currency
Adenine + Ribose = Adenosine
Adenosine + 3 Phosphates = Adenosine Triphosphate = ATP
ATP is a nucleotide (the AMP part can be used in making RNA strands during transcription making DNA strands during DNA replication)
Universal energy currency
– Used as the source of energy for all chemical reactions, active transport, endo/exocytosis…

Stores energy in the bonds between its phosphate groups
The bond between the second and third phosphates is broken to give its energy
ATP→ ADP + Pi
ADP = Adenosine diphosphate
Pi = Inorganic phosphate
A phosphate which is not inside an organic molecule

Energy used by cells
Formation of ATP during cell respiration

”ATP is a small, water-soluble molecule”
– Moves easily inside organisms by facilitated diffusion
”ATP is a small, water-soluble molecule”
– Transfer small amount of energy at a time
– Sufficient for individual reactions
Glucose contains much more energy
Cell respiration produces 38 ATP per molecule of glucose
– Glucose transports much more energy than individual reactions require
– ATP was “chosen” as the universal energy currency

How the cells use energy

Cell respiration produces ATP
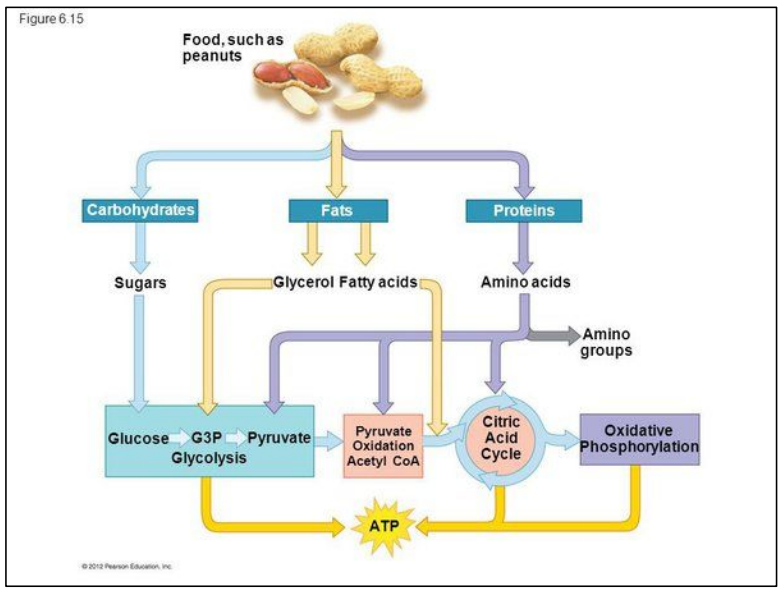
What is cell respiration?

Cell respiration is not gas exchange
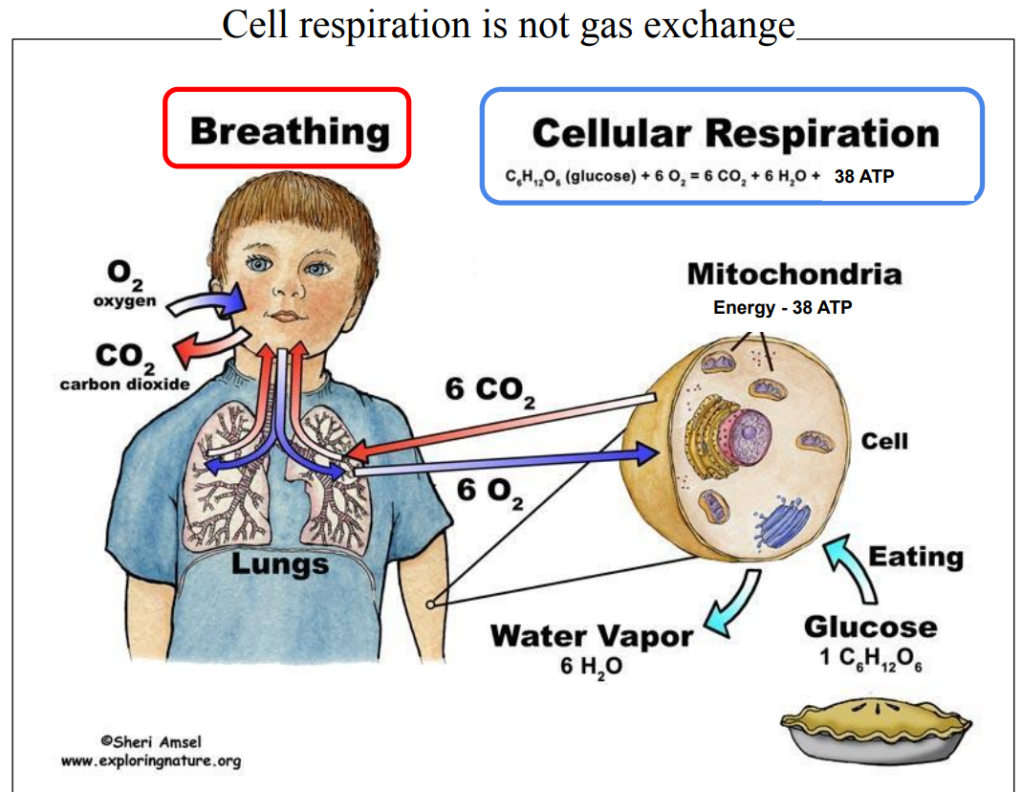
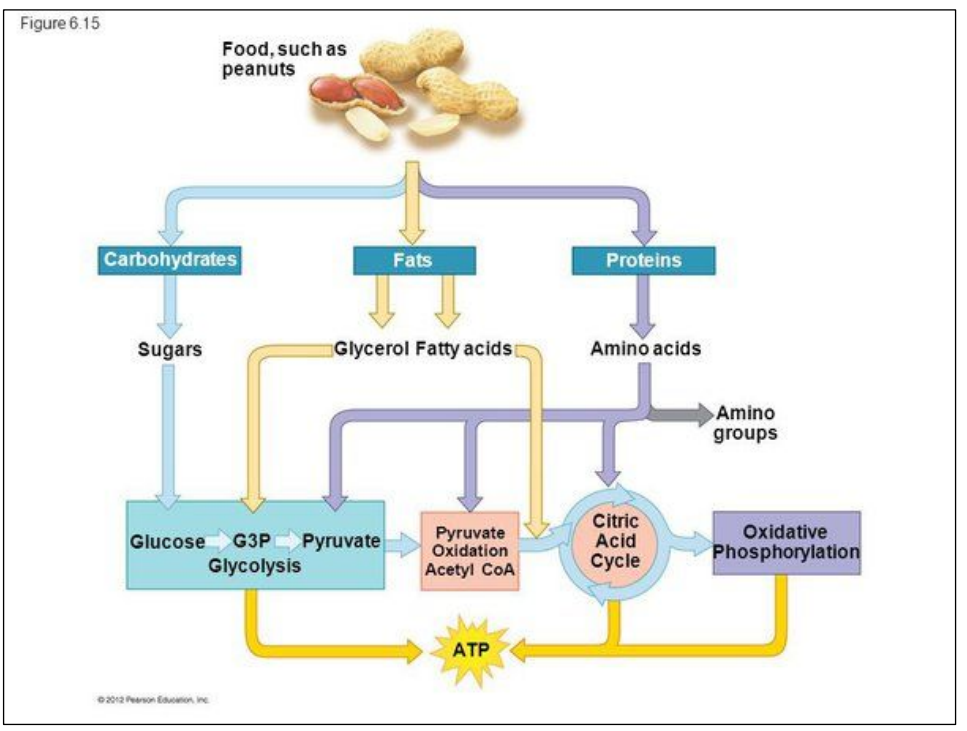
Cell respiration uses different substrates from food
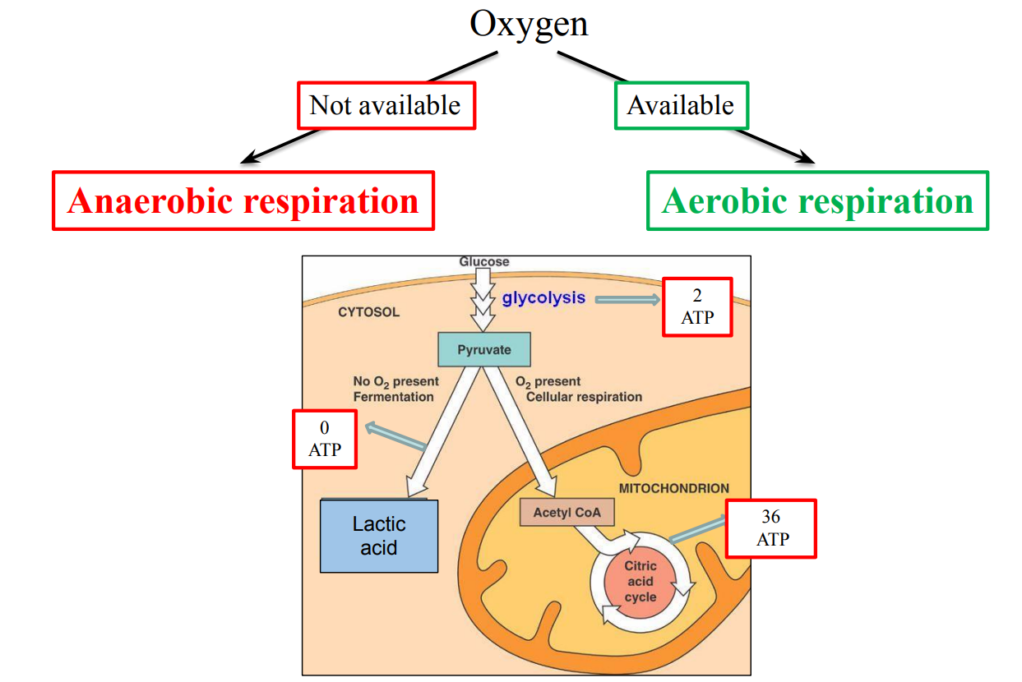
Aerobic and anaerobic respiration in humans
Common steps: (left side)
1. Glycolysis in the cytoplasm
Product = pyruvate + 2ATP
2. Continues inside the cytoplasm
Production lactic acid
Common steps: (right side)
1. Glycolysis in the cytoplasm
Product = pyruvate + 2ATP
2. Continues inside the mitochondrion
Pyruvate imported into it
3. Production of 36 more ATP

In aerobic respiration, glucose is oxidised into \(CO_2\)
\(O_2\) is reduced into water + a LOT of energy (ATP) is produced
Word Equation:
Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide + water (+ATP+ Heat)
Chemical equation (unbalanced):
\(C_6H_{12}O_6 + O_2 → CO_2 + H_2O\) (+ATP+Heat)
Chemical equation (balanced):
\(C_6H_{12}O_6 + 6O_2 →6 CO_2 + 6H_2O\) (+ATP+Heat)
In anaerobic respiration, glucose is fermented into lactic acid + a LITTLE of energy (ATP) is produced
Word Equation:
Glucose → Lactic Acid (+ATP+ Heat)
Chemical equation (unbalanced):
\(C_6H_{12}O_6 → C_3H_{6}O_3 \) (+ATP+Heat)
Chemical equation (balanced):
\(C_6H_{12}O_6 → 2C_3H_{6}O_3 \) (+ATP+Heat)
Variables affecting the rate of respiration
Two kinds of respiration
Depending on availability of Oxygen
– Oxygen available: Aerobic respiration
“Aerobic”: that requires air (oxygen)
– Oxygen not available: Anaerobic respiration
“Anaerobic”: that does not require air
Aerobic respiration : enzymatic reactions that use oxygen to break down nutrients molecules to release energy
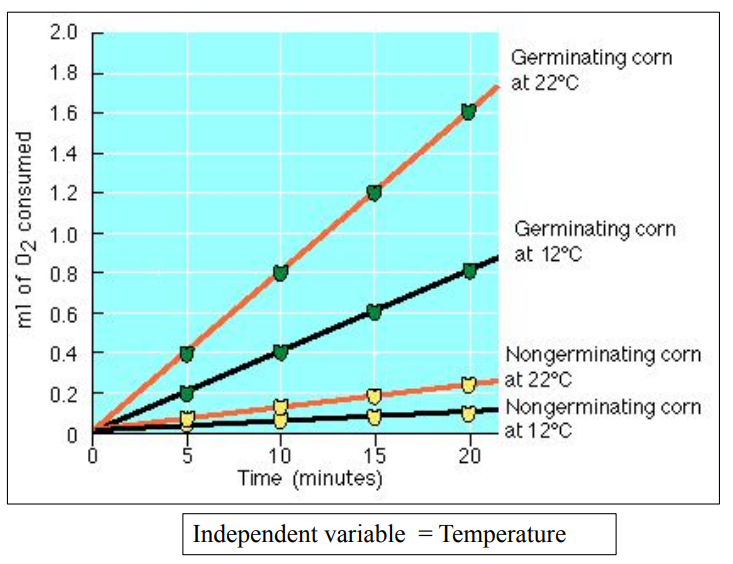
Dependent variable
– Measure the rate of oxygen uptake = measure the rate of aerobic respiration
Balanced chemical Equation:
\(C_6H_{12}O_6 + 6O_2 → 6CO_2 + 6H_2O\) (+ATP+Heat)
Setting up
Apparatus to measure rate of oxygen uptake = Respirometer / Spirometer
– Simple to use with small organisms
e.g. germinating seeds, maggots
Both are very active in respiration
– Elaborate to use with humans
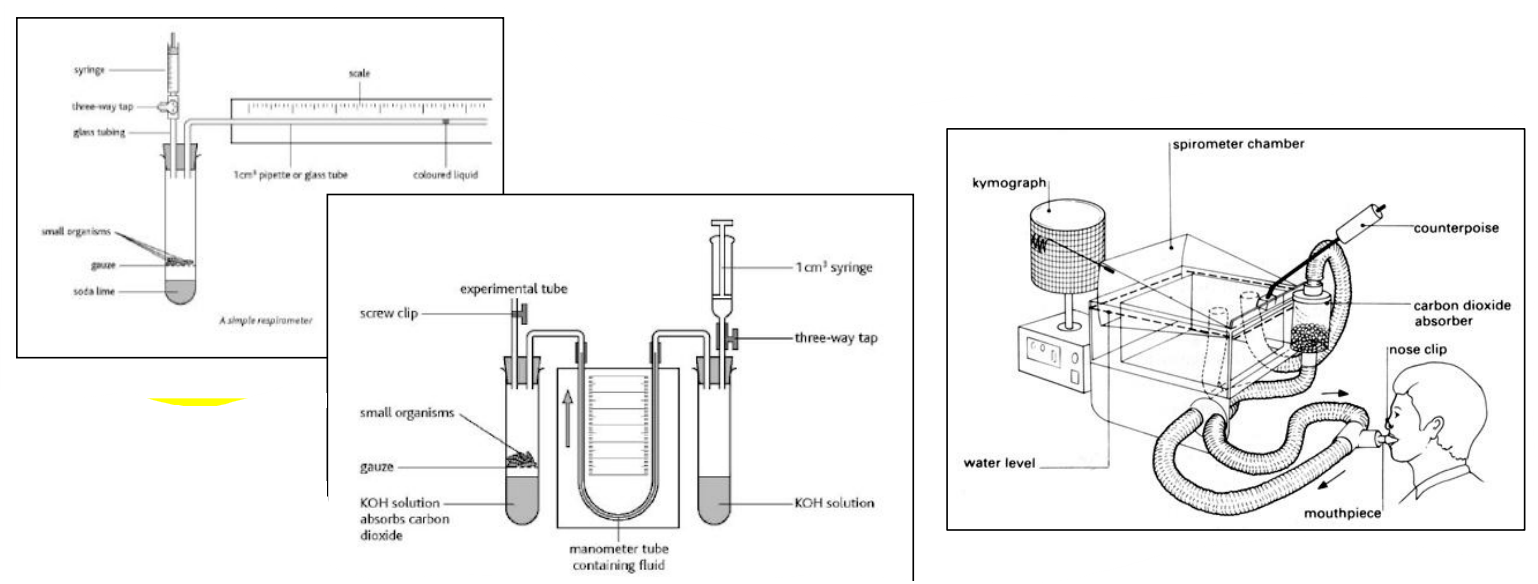
How to measure rate of oxygen uptake using small organisms





Useful tips:
To measure the rate of oxygen uptake
Measure the volume of oxygen per unit of time
Time of adaptation must be controlled
Seeds may need to “wake up” from dormancy before respiration starts
There will be a delay before oxygen starts being consumed
To control temperature (as a controlled variable, or as the independent variable)
Use a water-bath
If organisms do not have access to oxygen
They will turn to anaerobic respiration
No oxygen uptaken
Germinating seeds will release \(CO_2\) : absorbed by KOH/soda lime
Maggots will not perform any gas exchange
– No movement of fluid in manometer
Dependent variable……………………Rate of oxygen uptake
Independent variable……………………Temperature / Number of organisms / Age of organisms / Species of organisms
Controlled variables……………………Temperature: wait for water-bath to be at desired temperature before putting organisms in tube
/ Number of organisms / Age of organisms / Species of organisms / Measuring time
/ Adaptation time / Volume and concentration of KOH solution/soda lime solution
/ Respirometer has to be airtight / Manometer fluid returned to initial position before each sample
/ Volume both tubes identical: add glass beads to second tube
Control…………………………………Negative: No organism in tube
“Standard curve”……………………….Previous experiments can serve as reference
Reliability………………………………Repeats (5 to 10) for each type of sample
Anomalies, Means, SDs, Line/Bar graph, compare SDs
Validity……………………………….. Use the right apparatus the right way
Ethics…………………………………Handle maggots with care and respect
No contact with KOH/soda lime solution
Return maggots to natural environment after experiment
Safety…………………………………Basic
Soda lime/KOH solutions corrosive
High temperature

ENZYMES: Inactive at 0oC
Kinetic energy helps enzymatic reactions (0 to 40oC)
40 degree C = optimum temperature
Above 40 degree C, enzymes denature
Glycolysis (HL only)
The four steps of aerobic respiration:
1. Glycolysis
2. Link reaction
3. Krebs cycle
4. Electron transport chain + Chemiosmosis


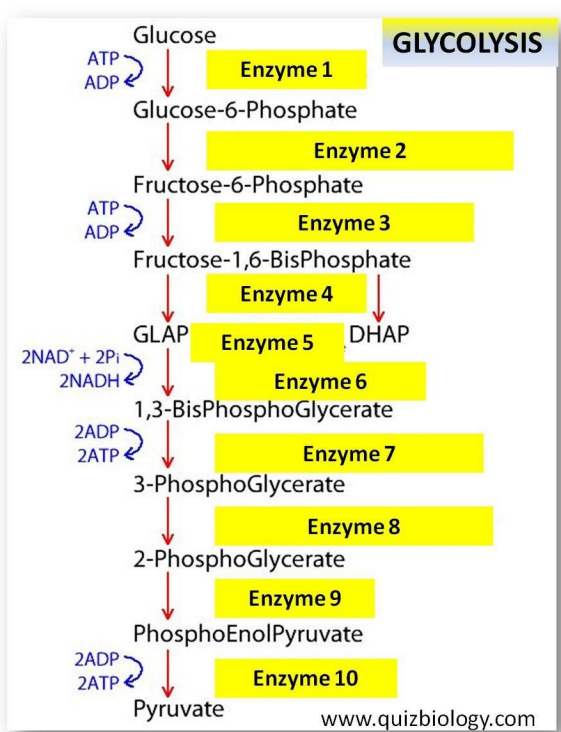
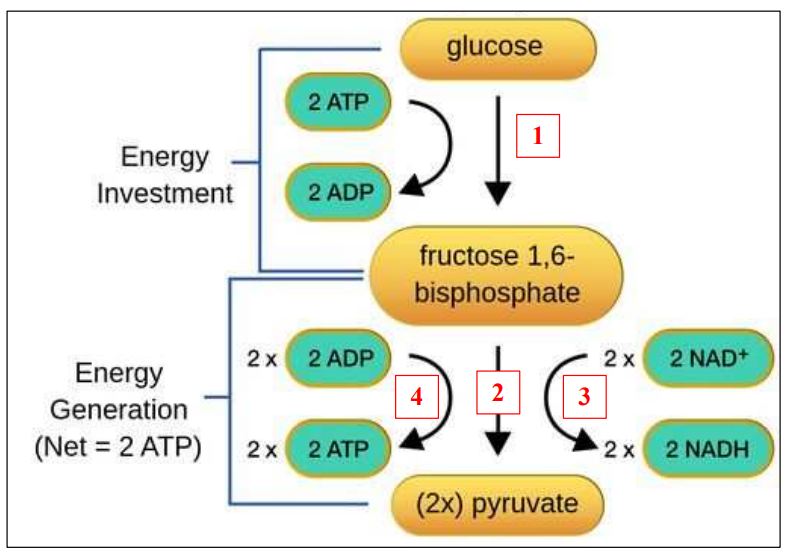
Glycolysis
“Glycolysis” = glucose breakdown

In the cytoplasm
Four steps in glycolysis
1. Phosphorylation
2. Lysis
3. Redox reaction
4. ATP formation
In the figure above:
1. Phosphorylation:
Transfer 2 phosphates from ATP to Glucose
– Use of 2 ATP
2. Lysis:
6- carbon split into 2X 3-carbon
3. Redox reaction:
2X NAD+ reduced into 2X NADH
4. ATP formation:
4X ADP phosphorylated into 4X ATP
“OIL RIG”
Oxidation is loss of electrons and hydrogen
Reduction is gain of electrons and hydrogen
When a chemical is oxidised, another one is reduced
– Redox reaction = exchange of electrons and hydrogen


Anaerobic respiration

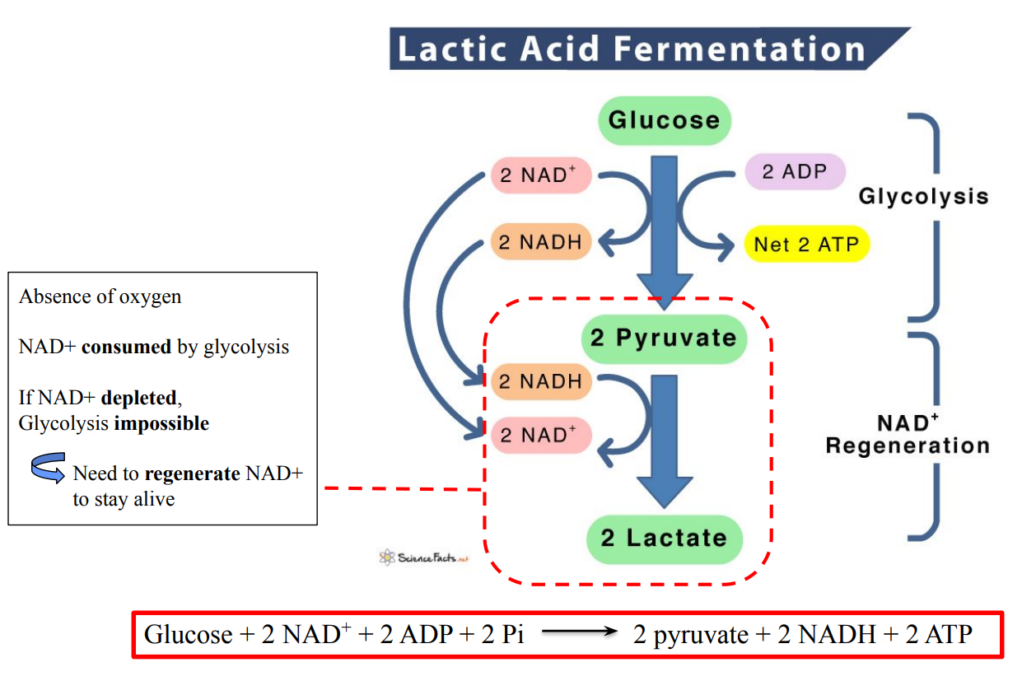
Net yield of anaerobic respiration = glycolysis
2 ATP per molecule of glucose
The link reaction (HL only)
The four steps of aerobic respiration
1. Glycolysis
2. Link reaction
3. Krebs cycle
4. Electron transport chain + Chemiosmosis

“Link” reaction = links glycolysis to Krebs cycle
In the matrix of the mitochondrion
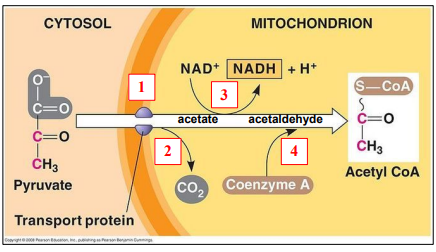
Four steps in link reaction
1. Import Pyruvate into matrix
2. Decarboxylation pyruvate
3. Redox reaction
4. Join Coenzyme A and acetyl
1. Import Pyruvate into matrix
Facilitated diffusion of pyruvate
Glycolysis produces pyruvate in cytoplasm
+
Pyruvate used quickly in matrix
– Concentration gradient favorable
2. Decarboxylation pyruvate
“Decarboxylation” = take out CO2
Here, from pyruvate to produce acetate
First time CO2 is produced
3. Redox reaction
NAD is reduced into NADH
Acetate is oxidised into acetaldehyde
4. Join Coenzyme A and acetyl
Acetaldehyde and Coenzyme A are joined together
To produce Acetyl Coenzyme A
Lipids feed the link reaction too

Fatty acids from lipids from diet contain long carbon chains
– provide many 2-carbon acetyl groups to link reaction
The Krebs cycle (HL only)
The four steps of aerobic respiration
1. Glycolysis
2. Link reaction
3. Krebs cycle
4. Electron transport chain + Chemiosmosis



Three points in Krebs cycle
A. Synthesis of citrate
B. Two decarboxylations
C. Four redox reactions

A. Synthesis of citrate

4C + 2C = 6C
Acetyl coA and oxaloacetate joined to form citric acid
coA recycled towards link reaction
B. Two decarboxylations

From citrate back to oxaloacetate
Oxaloacetate is regenerated
– Krebs cycle sustained
Second and third times CO2 is produced
C. Four redox reactions

TWO Krebs cycles per molecule of glucose
3 \(NAD^{+}\) reduced into NADH
1 \(FAD^{+}\) reduced into FADH2
Electron transport chain and chemiosmosis (HL only)
The four steps of aerobic respiration
1. Glycolysis
2. Link reaction
3. Krebs cycle
4. Electron transport chain + Chemiosmosis


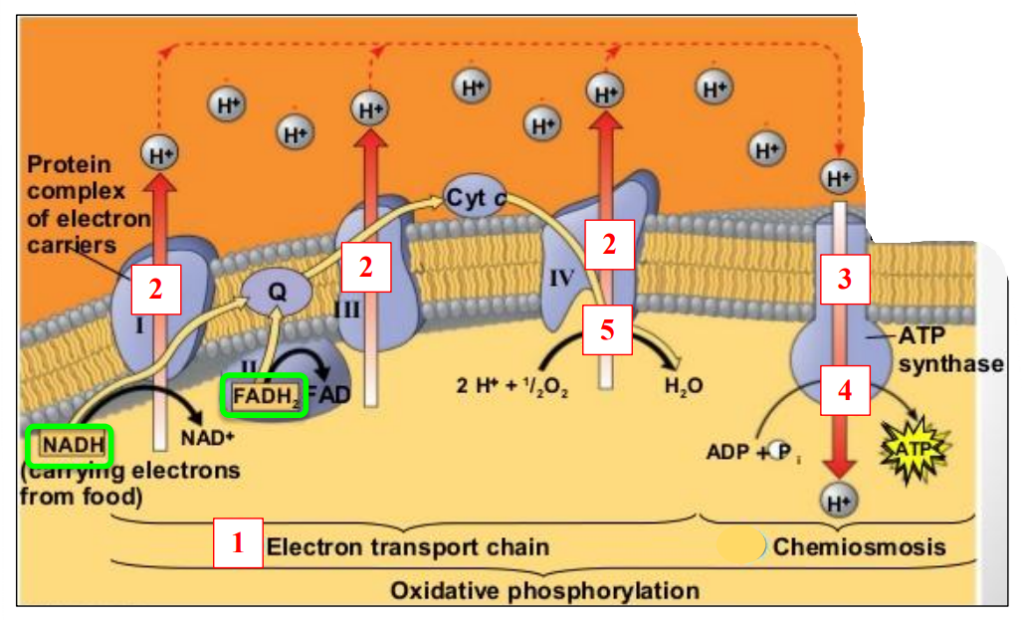
Five important steps
1. Transport of electrons
2. Transport of protons
3. Diffusion of protons
4. Synthesis of ATP
5. Synthesis of water
5 enzymes involved
1. Transport of electrons
NADH and FADH2 are oxidised: lose electrons and protons
Their electrons are transferred to inner membrane proteins
5 proteins transport the electrons = “Electron transport chain”
2. Transport of protons
NADH and FADH2 are oxidised: lose electrons( energy is released) and protons
Their protons are pumped (energy is used) to intermembrane space by inner membrane proteins
– Accumulation of protons in intermembrane space
– Gradient of protons (intermembrane space > matrix)
3. Diffusion of protons
Gradient of protons (intermembrane space > matrix)
– Protons diffuse from intermembrane space to matrix
– By facilitated diffusion using proton channels: “Chemiosmosis”
4. Synthesis of ATP
Protons diffuse from intermembrane space to matrix
– Energy released
– Energy used to phosphorylate ADP into ATP
5. Synthesis of water
Protons in matrix + Electrons in matrix combine with oxygen
– Water produce
Oxygen is the final acceptor of electrons and protons
Review of aerobic respiration
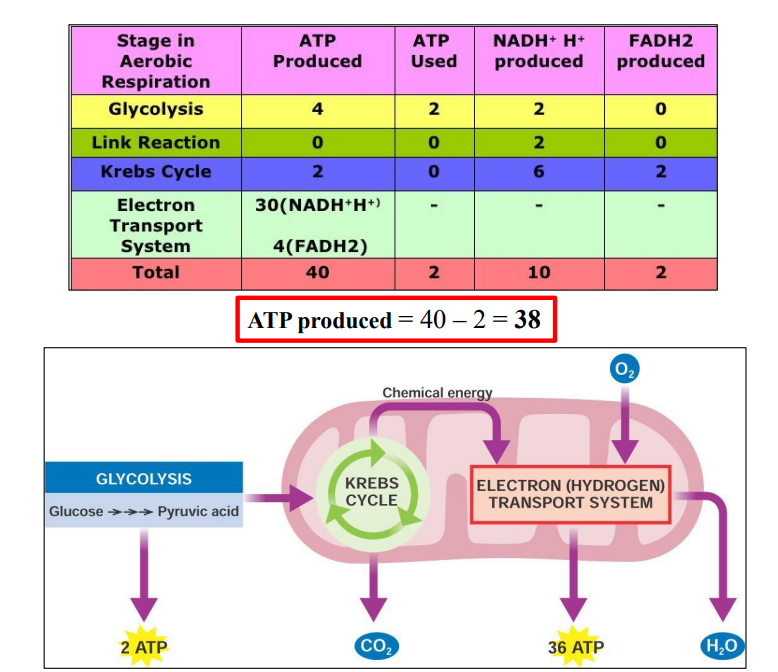
Lipids and carbohydrates as respiratory substrates (HL only)
Compare and contrast carbohydrates, lipids and proteins as sources of energy
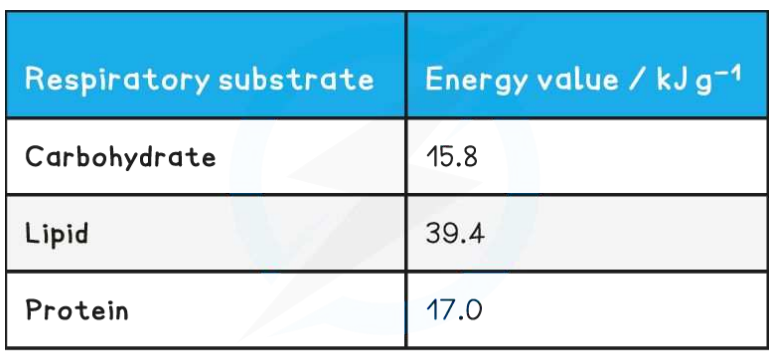
Lipids contain twice more energy than carbohydrates
(WHY)
Glucose \(C_6H_{12}O_6\) \(C_nH_{2n}O_n\)
Saturated fatty acids \(C_nH_{2n}O_2\)
In proportion per molecule,
Lipids contain more carbon and hydrogen than carbohydrates
↓
Provide more acetyl to the Krebs cycle
↓
Provide more ATP
Anaerobic respiration in yeast in brewing and baking (HL only)
- Bread is made by adding water to flour, kneading the mixture to make dough and then baking it. Usually an ingredient is added to the dough to create bubbles of gas, so that the baked bread has a lighter texture (e.g. yeast).
- After kneading (mixing) the dough is kept warm to encourage the yeast to respire.
- Yeast can respire aerobically or anaerobically, but oxygen in the dough is soon used up so the yeast is forced to respire anaerobically.
- The carbon dioxide produced by anaerobic cell respiration cannot escape from the dough and forms bubbles causing the dough to swell and rise.
- Ethanol is also produced by anaerobic cell respiration, but it evaporates during baking.


Compare and contrast lactic and ethanol acid fermentations

Substrate Product(s)
- Humans
– Glucose
– Ethanol
– CO2
- Yeast
– Glucose
– Lactic acid