- IB DP Biology 2025 SL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 1
- IB DP Biology 2025 HL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 1
- IB DP Biology 2025 SL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 2
- IB DP Biology 2025 HL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 2
C2.2 Neural signalling
The nervous system and neurons
Sensitivity: ability to detect changes in environment (external/internal) and respond appropriately.
Sensitivity
– Individual cells (prokaryotes, unicellular animals/plants)
– Entire organisms (prokaryotes , Animals, Plants)
Changes = stimulus
Receptor detects stimulus
Response done by effector
– Receptor and effector often not close need internal communication

⮚ All neurons have cell body: Nucleus + cytoplasm
⮚ From cell body, very fine and long cytoplasmic fibres = Axon
⮚ CF specialized for transmission of information = impulses
⮚Speed of impulses = 30-120 meters per second !!!
– Nervous coordination extremely FAST
– Response to stimuli almost instantaneous
Reflex arc

Neurons – structure and function

Dendrons and axons
⮚ Dendrons carry nerve impulse from dendrite to cell body
⮚ Axons carry nerve impulse from cell body to dendrite




Myelin sheath and Nodes of Ranvier

Myelin is a lipid that prevents ions to go in/out of axon
Speeds up conduction of nerve impulse along axon
Motor neurons

Reflex arcs and reflex action
Reflex arcs
The pathway
Connects sense cell/organ (receptor)
with muscle or gland (effector)
Via neurones
Reflex action
The response
Rapid, automatic, short-lived response to stimulus
Involuntary (reflex)
Does not involve brain

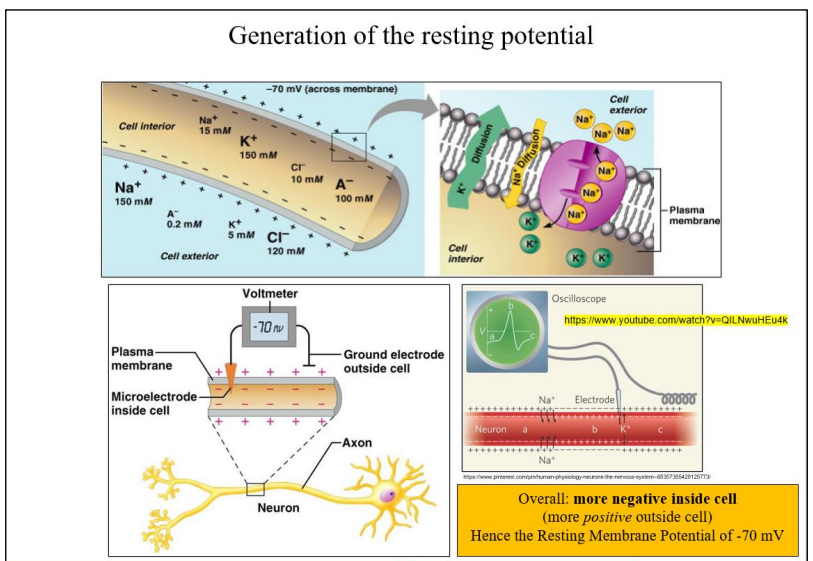
Generation of the resting potential
\(Na^{+}/K^{+}\) pump: Active transport Na+ and K+ across cell membrane
\(Na^{+}\) OUT \(3 Na^{+}\) out
\(K^{+}\) IN 2 \(K^{+}\) in
Overall: more negative inside cell
(more positive outside cell)
Hence the RMP.
“Resting potential”
Potential of the membrane when neuron not conducting impulse


The nerve impulse as action potential
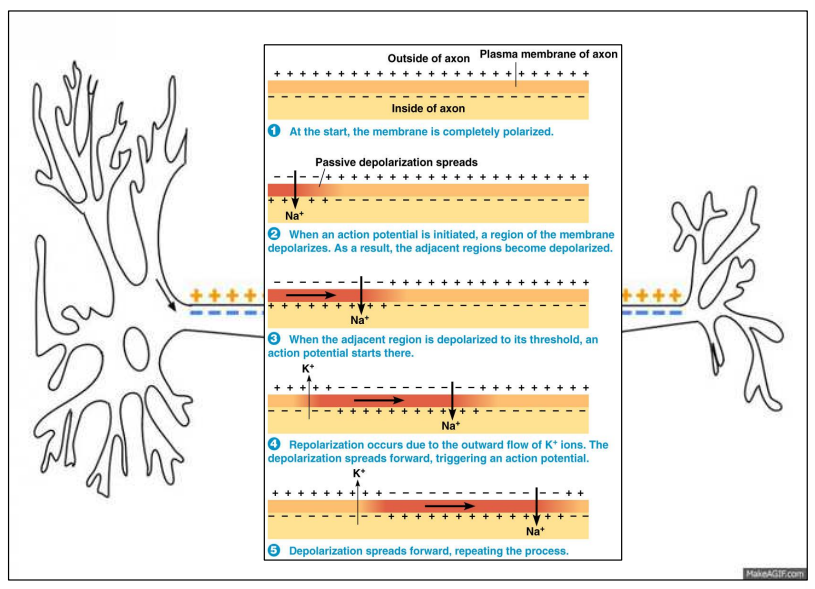
The nerve impulse (arrow) involves the movement of cations \(Na^{+}\) and \(K^{+ inside and across the membrane of the neuron
– It is electrical in nature
-Action potential
Transmission of impulse
Impulse transmitted along nerve fibers
NOT electrical current
Rather momentary reversal in electrical potential
difference across membrane of nerve fibers
=
Change in amounts of anions/cations inside/outside membrane of neurons
Reversal travels along axon in milliseconds
Variation in the speed of nerve impulses
Neurons – structure and function
– Motor neurons
Reminder 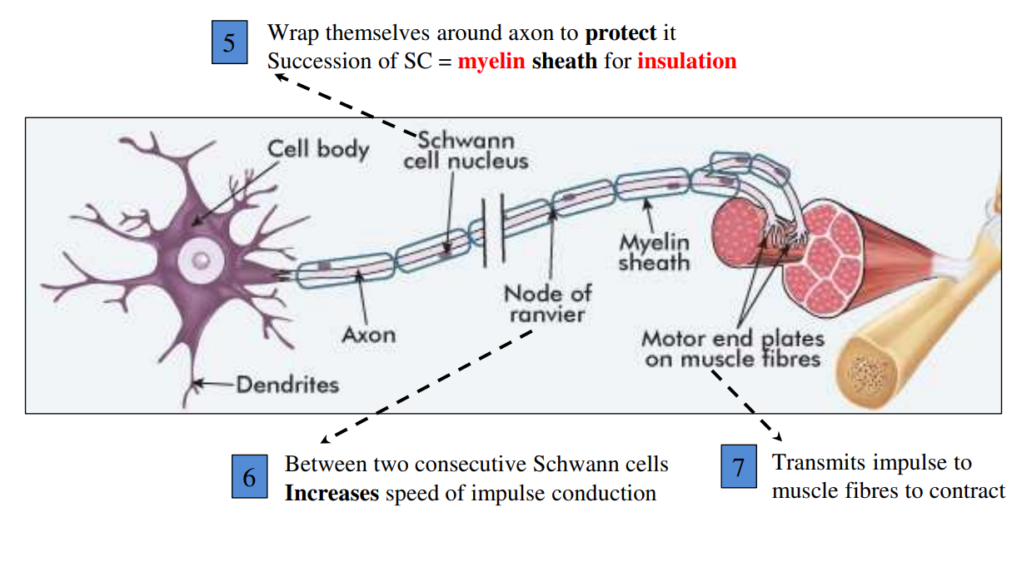

Fewer leaks of cations
– Faster speed
Many more leaks of cations
– Lower speed

What can you observe from these data?
Myelinated axons conduct action potentials faster than non-myelinated axons
Axons with a greater diameter conduct action potentials faster than those with a smaller diameter
 Positive correlation
Positive correlation
Strong
Weak
No correlation
Negative correlation
Strong
Weak

Correlation is not causation(Needs a scientific reasoning)
Scientific reasoning: This finding is in line with cable theory (Goldstein and Rall, 1974) as axons of increased diameter have less internal electrical resistance, which facilitates the spread of action potential.
Synapses and transmission of nerve impulses
⮚ Where two neurons meet, they do not actually touch
⮚ Junction between neurons or between neuron and effector cell = synapse
Synapse = synaptic knob (swollen tip) of axon of a neuron = pre-synaptic neuron + dendrite or cell body of another neuron = post-synaptic neuron
⮚ Gap of 20 nm between two neurons = synaptic cleft

⮚ Gap between neurons = synapse
Action potential is across the membrane of the pre-synaptic neuron
Post-synaptic neuron is another cell
Pre- and post-synaptic neurons do not share their cell membranes
– Action potential from pre-synaptic neuron cannot be passed on to the post-synaptic neuron
⮚ Transmission uses chemicals = neurotransmitters
Produced by pre-synaptic neuron
In vesicles from Golgi apparatus
Neurotransmitters
- Skeletal muscles
Brain
Acetylcholine
Neurons releasing ACh = cholinergic neurons

- Heart
Noradrenaline = norepinephrine
Neurons releasing NorA = adrenergic neurons

- Brain
– Glutamic acid (amino acid)

– Dopamine

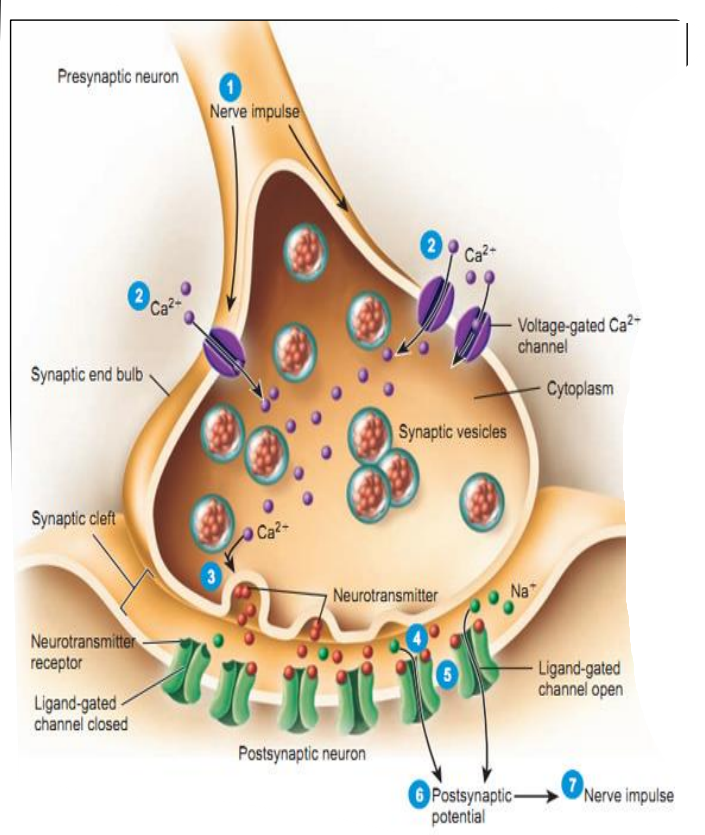
- Action potential travels along axon of pre-synaptic neuron
- – Voltage-gated \(Ca^{2+}\) channels open when AP reaches them
-\( Ca^{2+}\) flows into pre-synaptic neuron - – \( Ca^{2+}\) triggers exocytosis of neurotransmitter in Golgi vesicles
– Neurotransmitter diffuses into synaptic cleft - Neurotransmitter binds its receptor on post-synaptic neuron
- – Ligand-gated channel coupled to neurotransmitter channel opens
– \(Na^{+}\) ions flow into post-synaptic neuron = depolarisation - – If depolarisation reaches/above threshold
Generation of action potential in post-synaptic neuron
= Transmission of impulse between two neurons - Impulse conducted along post-synaptic neuron’s membrane
Acetylcholine cycle
⮚ Acetylcholine has to be removed from its receptor on post-synaptic neuron
If not removed, post-synaptic neuron will keep on transmitting impulse
e.g. effector = muscle will keep on contracting = seizures in epilepsy
⮚ Acetylcholinesterase breaks down acetylcholine
Products of reaction: – re-uptaken into pre-synaptic neuron
– reassembled into acetylcholine using ATP
No need to synthesise acetylcholine from “scratch”

⮚ Concentration acetylcholine kept low around its receptor
– Diffusion from region of exocytosis to receptor favored
⮚ Concentration of products of breaking down kept low in pre-synaptic neuron
– Diffusion from synaptic cleft to pre-synaptic neuron favored
The action potential in details (HL only)
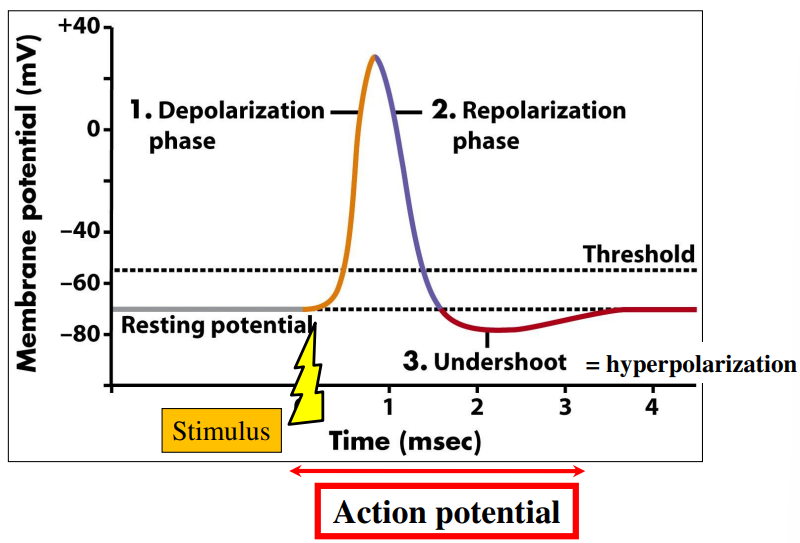


Let see this in 9 steps…….
Step 1: At resting potential -70mV
VGSC closed
VGKC closed

Step 2: ⮚ Depolarization by stimulus reaches membrane threshold potential
⮚ VGSC open
Action potential generated
VGSC open
VGKC closed

Step 3:⮚ Na+ enters the cell down gradient
⮚ Depolarization near VGSC
VGSC opened
VGKC closed

Step 4:⮚ Na+ enters the cell down its concentration gradient
⮚ Depolarization increases
VGSC opened
VGKC closed

Step 5:
⮚ Action potential
Peaks
+30mV
⮚ VGSC close
⮚ VGSC cannot respond to stimulus
Refractory period
⮚ VGKC open
VGSC close
VGKC open

Step 6: ⮚ \(K^{+}\) exits the cell down its concentration gradient
⮚ Repolarization stars
VGSC closed
VGKC opened

Step 7: ⮚ \(K^{+}\) leaves the cell down gradient
⮚ Repolarization ends
VGSC closed
VGKC opened

Step 8: Hyperpolarization
VGSC closed
VGKC close

Step 9: ⮚ \(Na^{+} /K^{+}\) pump against gradients
⮚ Membrane potential returns to
Resting potential
⮚ VGSC responsive again
Ready for new stimulus
VGSC closed
VGKC closed

Transmission of impulse
Impulse transmitted along nerve fibers
NOT electrical current
Rather momentary reversal in electrical potential
difference across membrane of nerve fibers
=
Change in amounts of anions/cations inside/outside membrane of nerve fibers
Reversal travels along axon in milliseconds
Review


Propagation of the action potential along an axon (HL only)
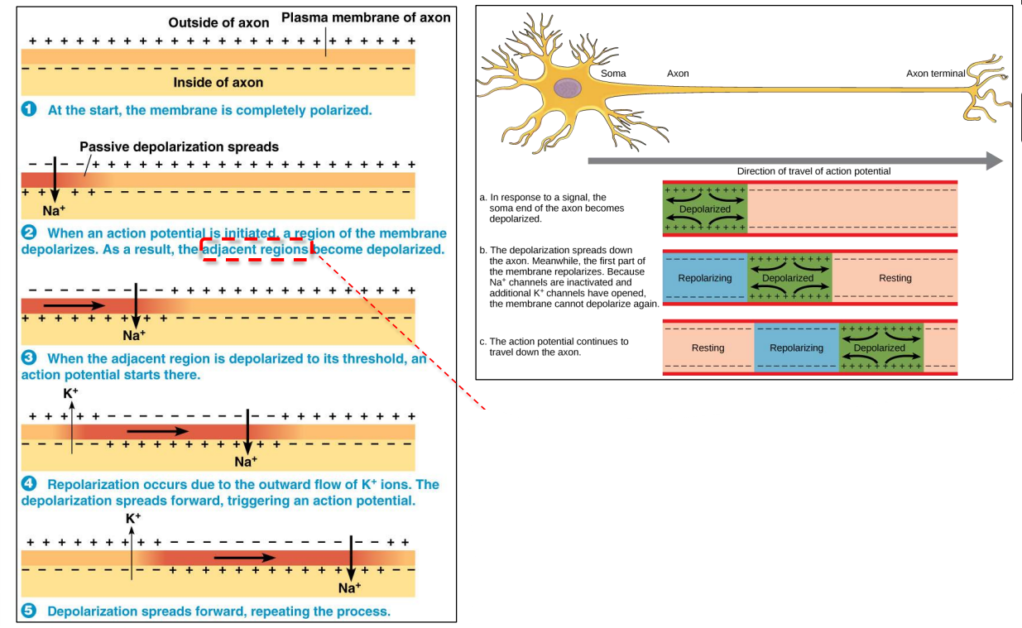
Adjacent regions: Higher concentration \(Na^{+}\) in region where VGSC opened
Lower concentration Na+ around
– Concentration gradient of Na+
– \(Na^{+}\) ions diffuse on both sides of opened VGSC
“Local current” of \(Na^{+}\)
Oscilloscopes (HL only)
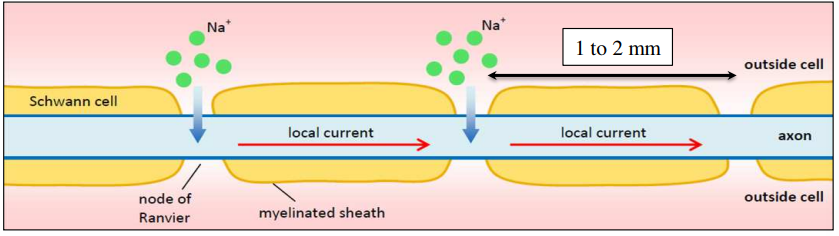
Saltatory conduction of nerve impulses (HL only)
Presence of myelin sheath speeds up transmission of action potential
⮚ Myelin insulates membrane of axon from any electrical activity
– Myelin prevents any influx/efflux of ions across the axon’s membrane
– Influx/efflux of ions only between Schwann cells = nodes of Ranvier
– Action potential “jumps” from node to node
Thanks to diffusion of \(Na^{+}\) ions
“Saltatory conduction”
“saltation” = leaping, jumping
– Conduction of impulse greatly sped up

Axolemma = cell membrane around axon
⮚ Myelinated neurons:
– Action potentials cannot be generated out of cell body or outside nodes of Ranvier
– Have a faster impulse conduction than non-myelinated neurons
– Look white: Make up “white matter” in central nervous system
⮚ Non-myelinated neurons:
– Are frequent in invertebrates: conduction much slower
– Larger diameter increases speed of conduction
– Make up “grey matter” in central nervous system: relay neurons are non-myelinated

Factors influencing synapses (HL only)
Ability of EOs to inhibit acetylcholinesterase (AChE), thereby increasing levels and duration of acetylcholine in the brain and assisting with memory retention.

Some pesticides block synaptic transmission in insects
e.g. neonicotinoids
Block contraction signals to muscles, leading to death

What neurotransmitter is affected by cocaine?
What is the mechanism of action of cocaine?
What are the consequences of cocaine use?
Dopamine Blocks reuptake of dopamine

The refractory period
⮚ Refractory period is the time when neuron cannot respond to stimulus during action potential
VGSC cannot respond to additional stimulus when membrane potential is between +30 mV and -70 mV
VGSC are closed and stay closed until membrane potential returns to resting potential = -70 mV
Neurone unresponsive during action potential when membrane potential between +30 mV and -70 mV
Time between +30 mV and -70 mV = Refractory period = around 3 ms
⮚ VGSC becomes responsive again to stimulus when membrane potential = resting potential = -70 mV

⮚ During the refractory period the neuron:
– recovers from the action potential
– restores the correct balance of ions on either side of the membrane
The sodium-potassium pump actively transports \(K^{+}\) in and \(Na^{+}\) out across the membrane
⮚ The refractory period is beneficial because:
– Another action potential cannot be triggered so soon after the first
– It ensures that action potentials are being transmitted in one single direction only


The “all-or-nothing” principle
To trigger an action potential, stimulus has to depolarise membrane potential at least up to threshold

⮚ Sub-threshold stimulus: influx of Na+ quickly reversed by Na+ / K+ pump
– Action potential not triggered
– Resting potential restored

⮚ Stimulus above threshold and continuously reaching the neuron
1. Action potential triggered
Neuron rests during refractory period
2. After refractory period
New action potential triggered
– Frequency of action potentials only limited by refractory period
– Effector (or brain) measures intensity of stimulus from frequency of action potentials


Frequency of action potentials only limited by refractory period
Excitatory and Inhibitory synapses and neurotransmitters

“To trigger an action potential, stimulus has to depolarise membrane potential at least up to threshold”

Extension: Why have synapses between neurones?
Since synapses have the disadvantages of very slightly slowing down the transmission of action potentials, we may assume they also provide distinct advantages to the operation of nervous communication in organisms too. In fact there are a number of advantages. Synapes allow:
- the filtering out of low level stimuli of limited importance
- the protection of effectors (muscles and glands) from over stimulation , since continous transmission of action potentials eventually temporarily exhausts the supply of transmitter substances (that is,it causes synapse fatigue)
- flexibility of response by the central nervous system, particularly by the brain
Excitatory synapse: post-synaptic N \(Na^{+}\) channels: depolarisation of post-synaptic neuron
Inhibitory synapse: post-synaptic N \(Cl^{-}\) channels: hyperpolarisation of post-synaptic neuron
- integration of information , since the post-synaptic neurons may receive action potentials from both excitatory and inhibitory pre- synaptic neurons – the post – synaptic neurons summates all the action potentials, thereby integrating impulses from more than one source neurons or sense organ , for example.
Spatial and temporal summation

- Spatial summation occurs where multiple neurons can fire impulses to one receiving neuron, where one of those action potentials alone will not be sufficient to produce an action potential on the other side , but if they all fire simultaneously , the impulse will continue along the post- synaptic membrane ,however , not all neurons will send excitory post – synaptic potentials . EPSPs ( to generate an impulse) some will send inhibitory post- synaptic potentials) and- an ISPS can override incoming EPSP signals from adjacent neurones.
- Temporal summation occurs where one neurons fires multiple impulses from the same place , which with pauses in between will not be sufficient to generate an impulse on the receiving neurone, but when fired within rapid succession of each other , it will be enough to produce an action potential on the post- synaptic membrane
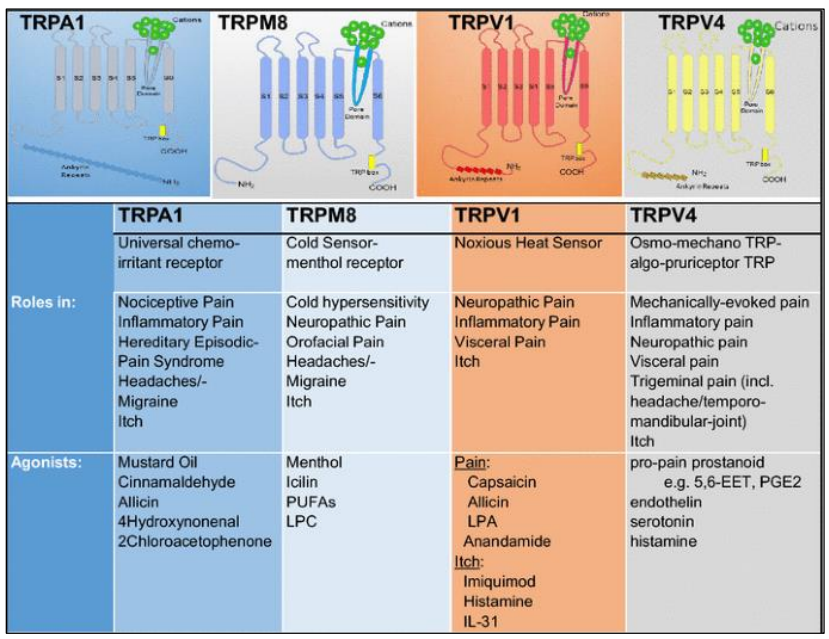
Perception of pain in the skin (HL only)
Stimuli are sensed by sensory receptors
Stimuli are changes in the environment (inside or outside)
e.g. temperature, pressure, chemicals

Nociceptors sense pain
Caused by chemicals, temperature, acids
Example = receptor of capsaicin, contained in chili peppers