- IB DP Biology 2025 SL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 1
- IB DP Biology 2025 HL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 1
- IB DP Biology 2025 SL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 2
- IB DP Biology 2025 HL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 2
D1.3 Mutations and gene editing
Types of mutation

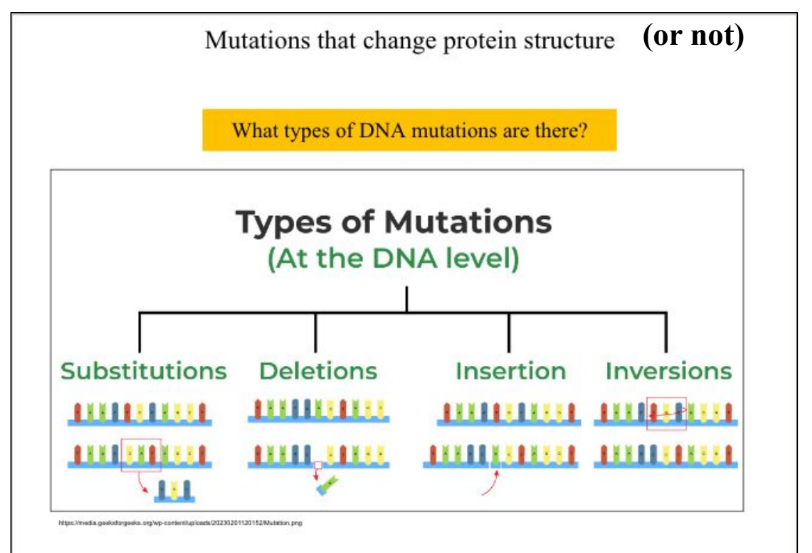

Consequences of mutations (if any)
Consequences of base substitutions (if any)

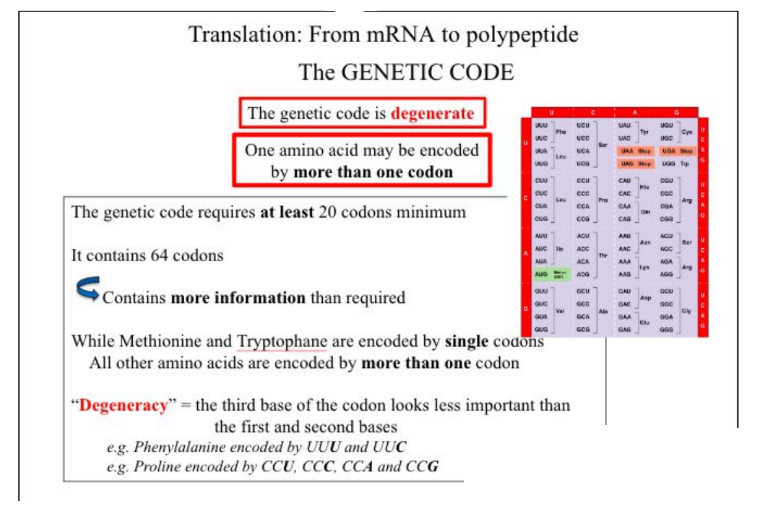
Single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) do not always change an amino acid in the polypeptide
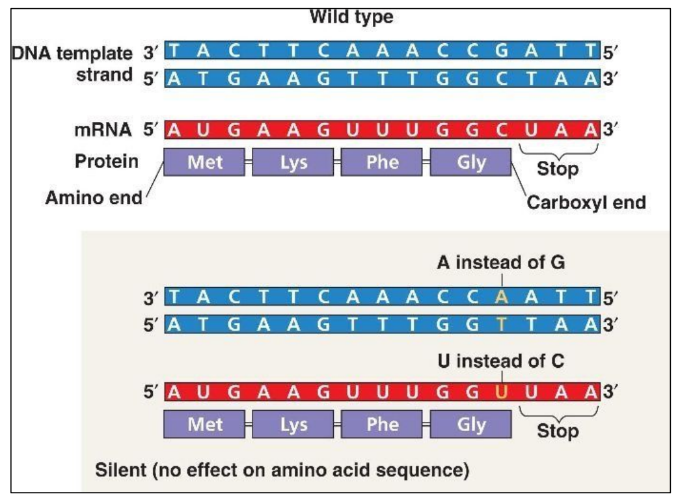
Some substitutions do not change any amino acid
“Silent mutation”
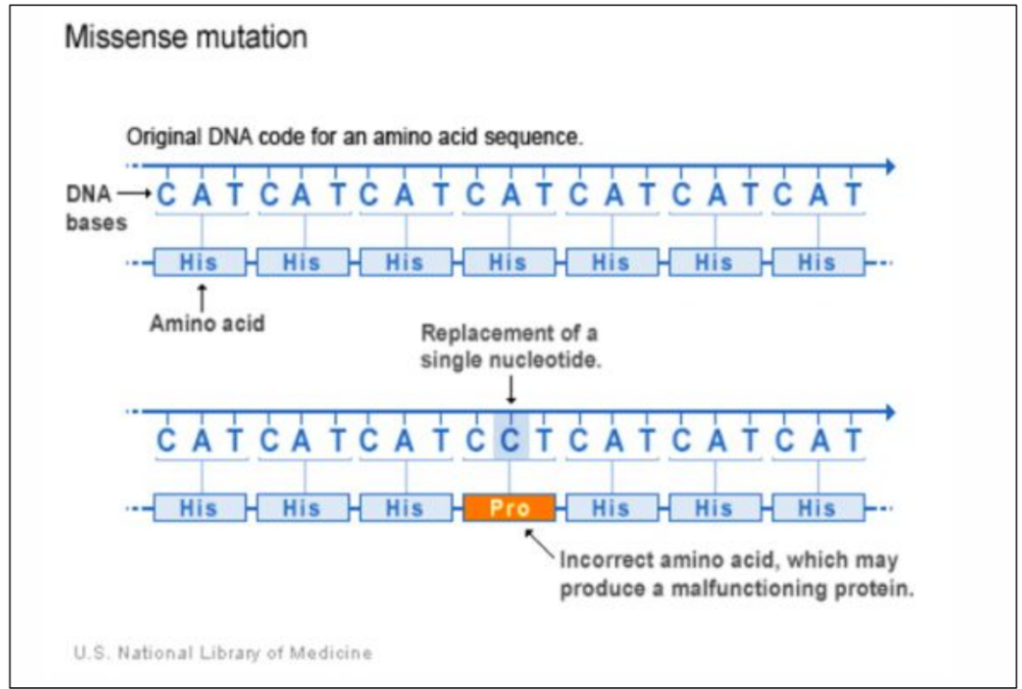
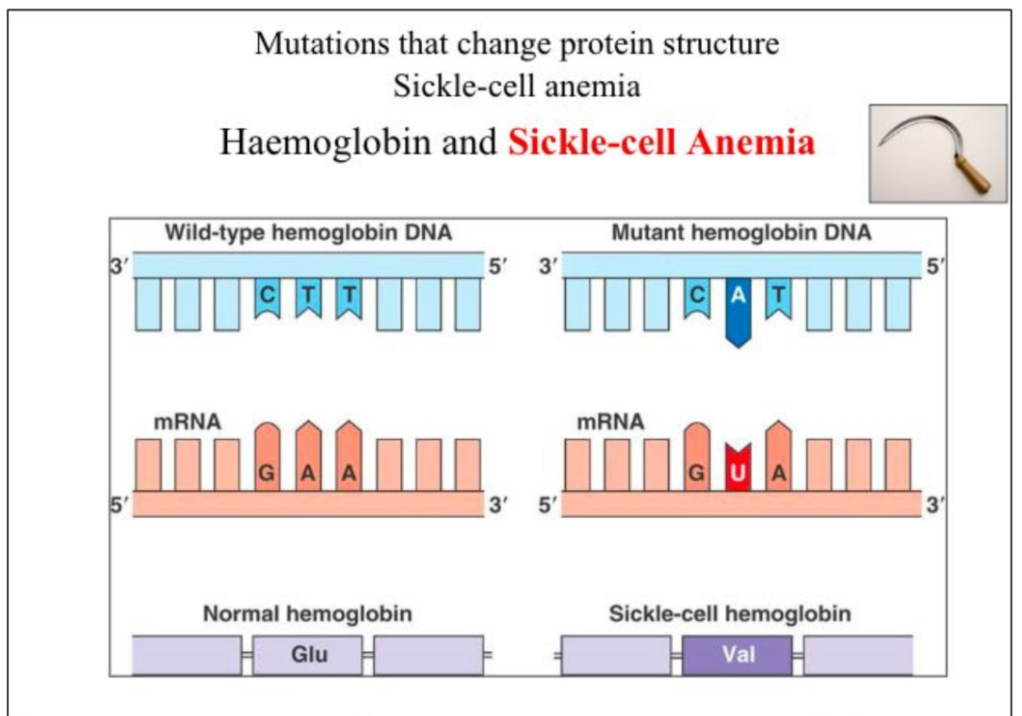
Some substitutions do change one amino acid
“Missense mutation”
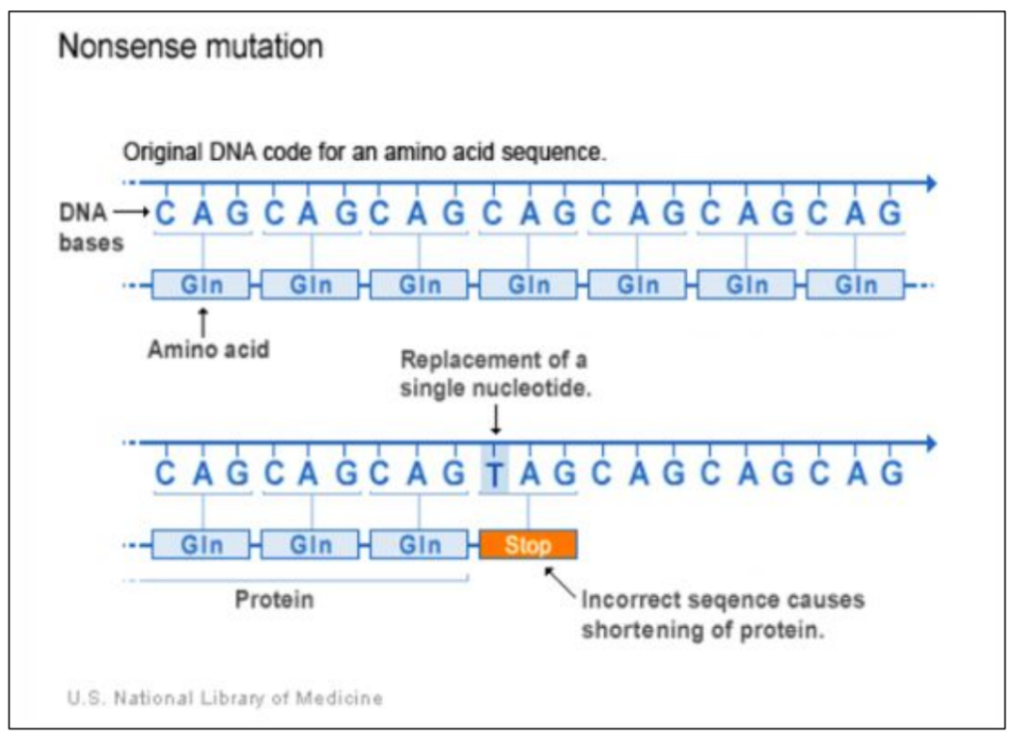
Some substitutions do change the amino acids
“Nonsense mutation”
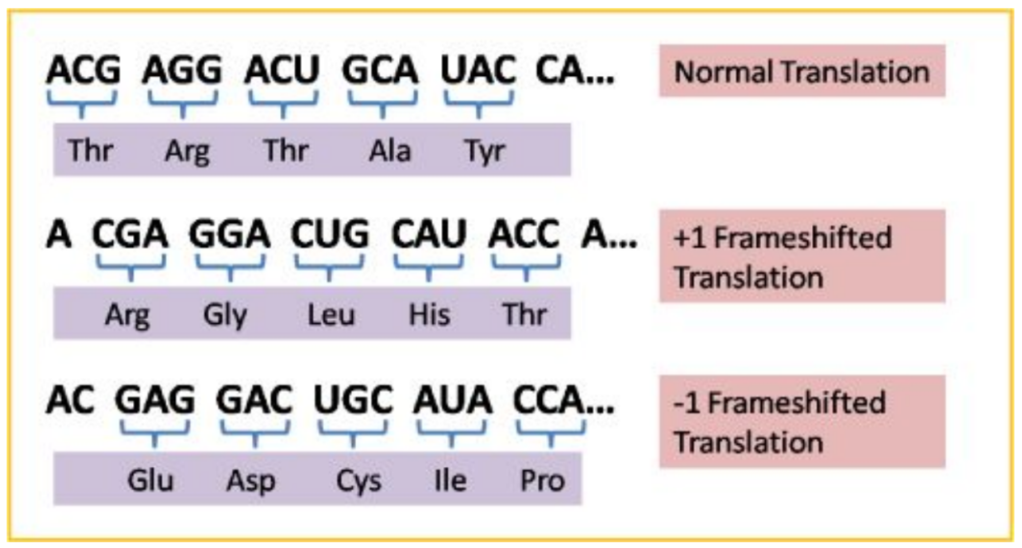
The three reading frames of mRNA

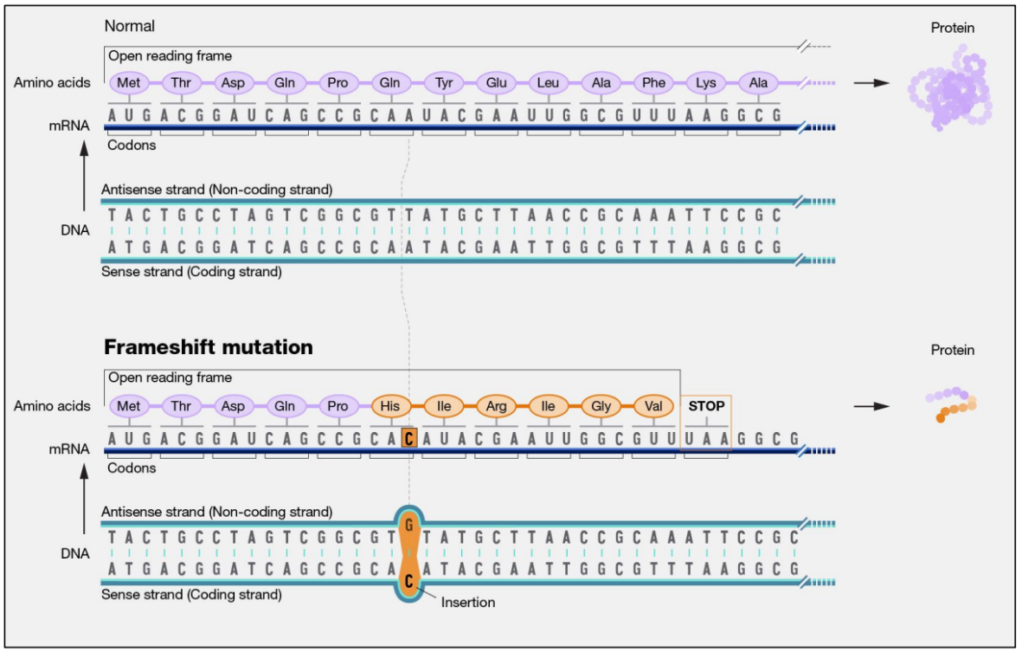
Some insertions do change the amino acids
“frameshift mutation”
Some insertions do change the amino acid(s)
“frameshift mutation” and “non-frameshift mutation”

Some insertions do change amino acids
“frameshift mutation”

“Somatic” refers to the body
“Germline” refers to gametes

All cancers = uncontrolled cell division due to gene mutation
Cancer cells continuously divide by mitosis
Tumour = mass of cancerous cells
Tumour keeps getting bigger
Cancerous cells induce development of new blood vessels around tumour
To get oxygen and nutrients transported in blood
– Healthy cells/tissues around tumour get less oxygen and nutrients
Some organs may malfunction…. fail
Metastasis = cancerous cells break away from malignant tumour
– Carried to other parts of body by bloodstream
Creation of new, secondary tumours
If not treated, cancer may cause death

Begnin tumours do NOT spread
Causes of gene mutation
DNA replication mistakes

If proofreading of gene is not perfect
– Mutation in gene DNA
Chemical mutagens: base analogs

Chemical mutagens: base altering agents

Chemical mutagens: intercalating agents

Radiations that lead to DNA mutation: Ultra-violet B rays

Radiations that lead to DNA mutation: X-rays and Gamma-Rays

Mutation as a source of genetic variation

Within groups of organisms
Even in the same species
Individuals look different from each other
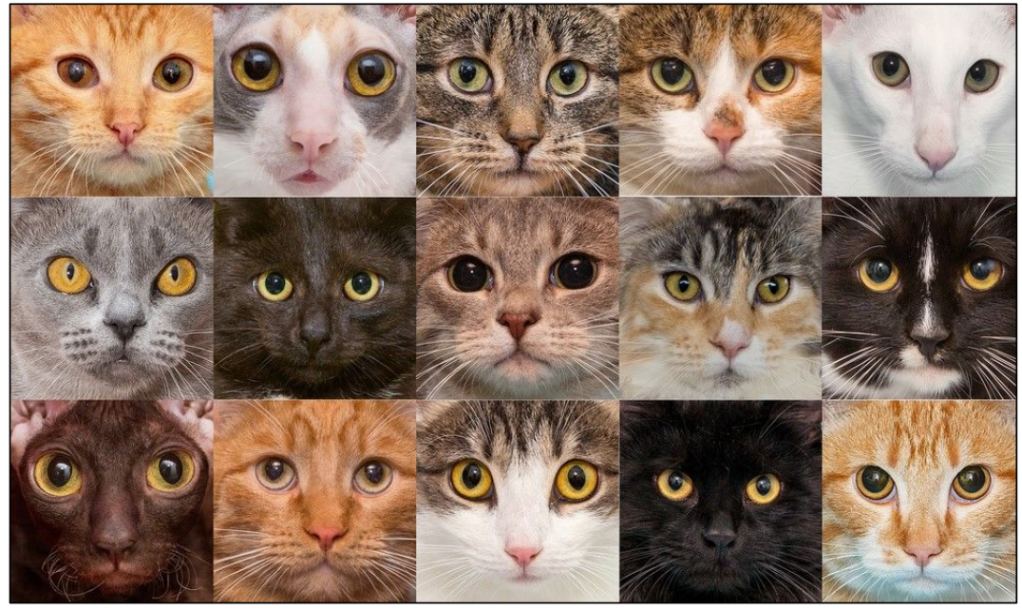


All these cats are … cats
They have the same genes
Some genes have differences in sequence
– Differences in the appearance
↑
Mutations in genes

Mutations in gene for wing colour
↓
Genetic variation in population
↓
Predators see white-winged better on dark background
Brown-winged survive more
↓
Brown-winged reproduce more
↓
Population has evolved
Mutations are essential for evolution by natural selection
Commercial genetic tests: Ancestry

Commercial genetic tests: Medicinal uses

Commercial genetic tests: Medicinal/Well-being uses

Randomness of gene mutation
“Students should understand that mutations can occur anywhere in the base sequences of a genome, although some bases have a higher probability of mutating than others. They should also understand that no natural mechanism is known for making a deliberate change to a particular base with the purpose of changing a trait. “
Knocking out genes to investigate their functions (HL only)
Whole libraries of knockout mutants have been established = Collection of individuals mutated for one gene
– Study the function of genes one by one
Viruses: Cowpox virus, Kaposi’s, Influenza, Herpes, Hepatitis B, HIV, Covid-19 …
Bacteria: E. coli , M. tuberculosis, S. pneumoniae, …
Fungi: yeast
Animals: fruit flies, zebra fish, mice, human, green monkey, …
Plants: Arabidopsis thaliana, rice…
Gene editing with CRISPR and Cas9 (HL only)

Clustered
Regularly
Interspaced
Short
Palindromic
Repeats
CRISPR
-associated protein 9
Gene editing with CRISPR and Cas9 in animals
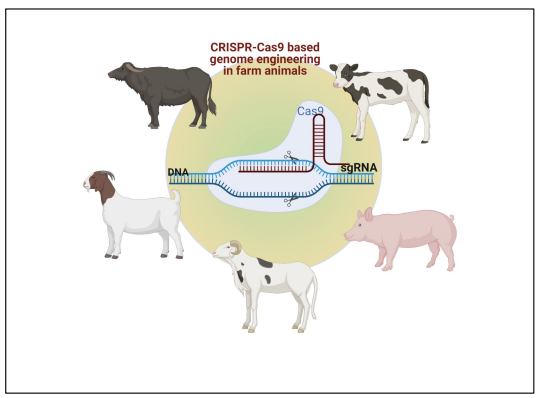
Farm animals are targets of gene editing
Improve:
– meat quantity and quality
-disease resistance
– milk quantity and quality
Gene editing with CRISPR and Cas9 in CROPS

Possible future uses for CRISPR


Opportunities and challenges for CRISPR

Conserved sequences in genes (HL only)
Using a named example, answer these questions
What are conserved sequences?
How to identify them?
What are high conserved sequences?
How to identify them
Why do they have slower rates of mutation?
Are the genes products required for organisms?