- IB DP Biology 2025 SL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 1
- IB DP Biology 2025 HL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 1
- IB DP Biology 2025 SL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 2
- IB DP Biology 2025 HL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 2
D2.2 Gene expression (HL only)
Steps of gene expression (HL only)


What are these steps?
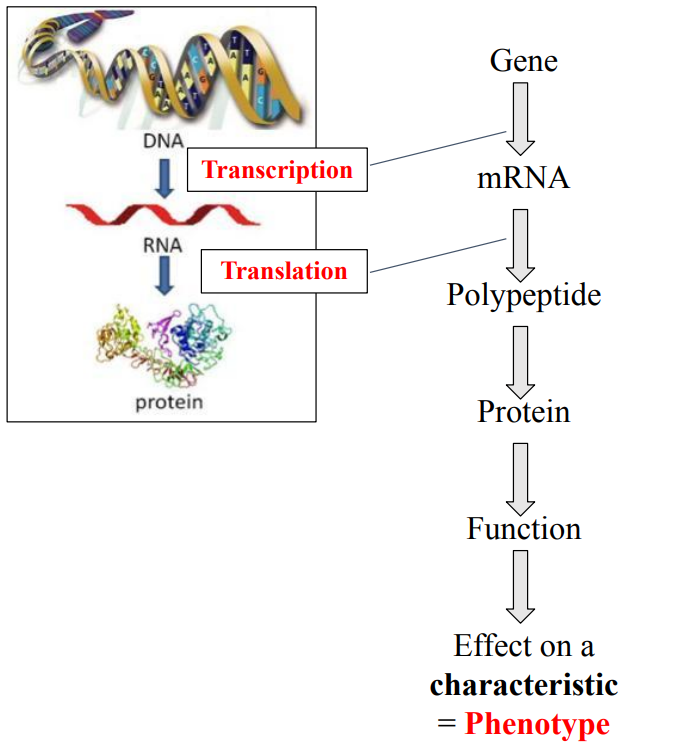

What is this step?
This step is known as Folding

Examples of protein function?
Enzymes

Effect on a characteristic
ex. Iris pigment Eye colour

Genome, transcriptome and proteome (HL only)



Genome
All genes of a cell + Non-coding DNA
Genome
= sum of all genetic information
= all DNA
= all chromosome(s)
Is the genome the same for all cells of an organism?
YES
Transcriptome

All RNAs = products of transcription called “transcripts”
Sum of all RNAs of a cell = Transcriptome
Is the transcriptome the same for all cells of an organism?
NO

Proteome

All proteins = products of translation
Sum of all proteins of a cell = Proteome
Is the proteome the same for all cells of an organism?
NO
Compare and contrast

Regulation of gene expression at the genomic level (HL only)

Cells start to differentiate
– variety of tissues and organs


Differentiation into a type of cell depends on several processes
Including changes in the DNA chemistry but NOT in the DNA sequence

Histones and nucleosomes

Euchromatin and heterochromatin

| Euchromatin | Heterochromatin | |
| DNA is | loose | tightly packed |
| Genes are | easy to access for proteins | hard to access for proteins |
| Genes are | expressed (transcribed | not expressed |
Methylation of cytosines in gene promoter
Methylation and Acetylation of histones


Acetylation of histones and Methylation of promoter cytosines

Methylation of DNA and histones causes nucleosomes to pack tightly together. Transcription factors cannot bind the DNA, and genes are not expressed.

Histones acetylation results in loose packing of nucleosomes. Transcription factors can bind the DNA and genes are expressed.

Effect of the environment on epigenetic tags
Factors affecting Methylation patterns

Effect of the environment on epigenetic tags
Fetus’ methylation patterns created during pregnancy

Figure . The effects of prenatal air pollution exposure on placental DNA methylation patterns and its implications on fetal development and future disease susceptibility. Maternal exposure to air pollution, including heavy metals, can reach the placenta, where they alter DNA methylation patterns at both the global and gene promoter level. The aberrant methylation of genes affects fetal growth (HSD11B2, BID, D-loop, PCDHAC1, LOC284276) and increases the risk of developing
cancer (p53, APEX1, OGG1, ERCC4), neurobehavioral abnormalities (NR3C1, EMID2), and atopic dermatitis (AHRR, DPP10, HLA-DRB1) in later life.
Inheritance of epigenetic tags
Epigenetic tags can be passed on to offspring by parents
ONLY if they are not erased during mitosis and meiosis, or in embryo

What is a species?
A group of individuals that share common characteristics and can produce fertile offspring


All male ligers and tigons are sterile
Why are ligers bigger than tigons?

Lions and tigers have different DNA imprinting strategies. Male lions want their cubs to grow as big as possible. But a lioness wants all the cubs to be the same size, so her imprinting counteracts his.

Gene “big size” 3 types of epigenetic tags

weak expression, medium size

Strong expression , bigger size

no expression, smaller size
Monozygotic twins studies and evolution of epigenetic tags

The epigenome and twins

- identical twins begin life with similar epigenomes
- epigenetic tags of one twin are labelled green , and red for the another
- yellow areas indicate shared epigenetic tags

- over time environmental influences differ
- yellow regions indicate shared epigenetic tags
- epigenome of twins has diverged

Regulation of gene expression at the transcriptional level (HL only)


External factors impacting the pattern of gene expression

Regulation of gene expression at the translational level (HL only)

One way to control level of translation = control how fast mRNA are degraded
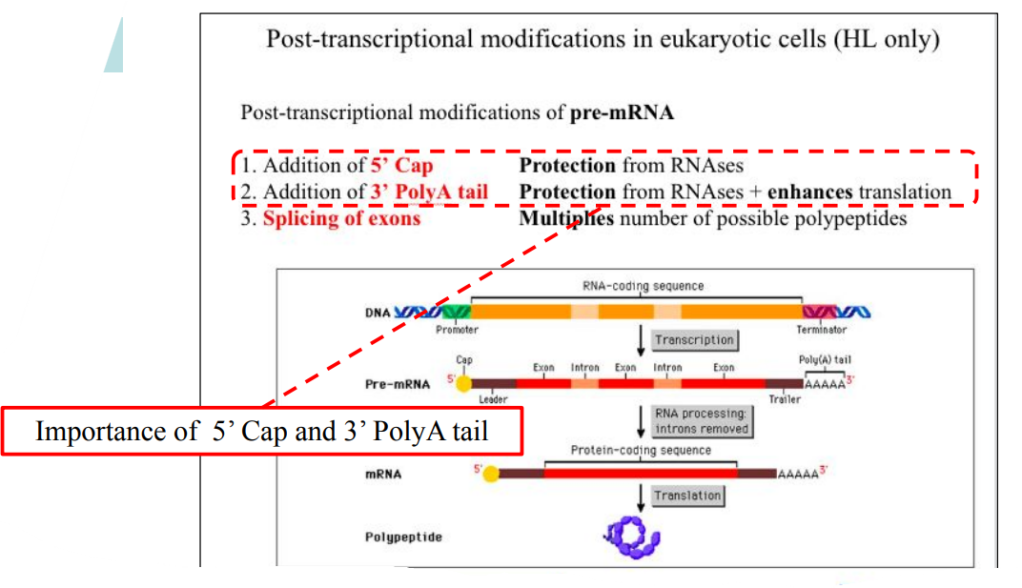
Importance of 5’ Cap and 3’ PolyA tail
When removed, mRNA is quickly degraded by exonucleases
5’ to 3’ and 3’ to 5’
