Question
Option E — Leisure, tourism and sport
Answer the following question.
The graph shows visitor arrivals to Thailand from China and Malaysia between 2007 and 2019.
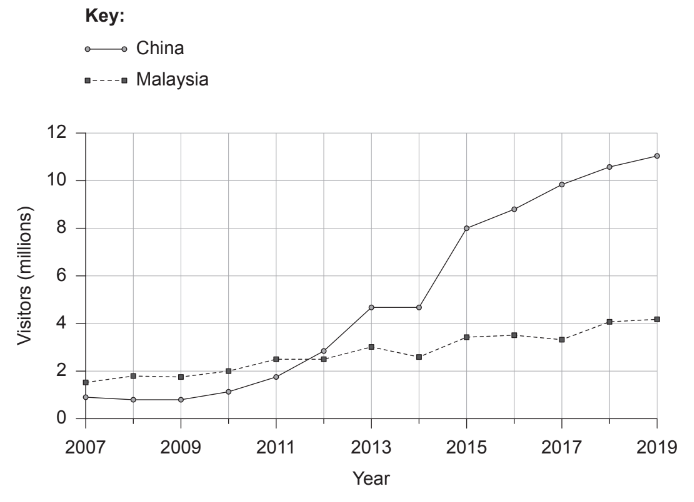
(a) (i) State the increase in visitors from Malaysia, in millions, between 2010 and 2018. [1]
(ii) State the years between which the number of visitors from China increasedthe most. [1]
(b) Outline one reason why the growth of diaspora can encourage tourists to a region. [2]
(c) Explain the effects over time on visitor numbers caused by:
(i) social media; [3]
(ii) carrying capacity being exceeded. [3]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) (i) 2 (million)
(ii) 2014-15
Award [1] for a valid reason and [1] for development/explanation/explained exemplification.
For example: The growth in diaspora encourages visitors from out of the area to visit family and friends [1] which can lead to development/expansion of local facilities such as cafes/restaurants/trails/museums – thereby attracting more tourists [1].
For example: It encourages a larger number of the diaspora to visit their home country as tourists to trace their roots [1] for example the descendants of those who came to the West Indies as indentured labourers travel as tourists to their country of origin, India [1].
Answers may relate to the region of origin of the diaspora or the region of residence
(i) social media;
Award [1] for explaining the factor/effect and up to [2] for development/explanation.
For example: Advertising/reviews/influencers on social media/internet [1] have changed the way people research trips/share experiences [1] e.g. positive reviews of hotels and good customer feedback can affect decisions, leading to an increase in visitor numbers [1].
(ii) carrying capacity being exceeded. [3]
Award [1] for explaining the factor/effect and up to [2] for development/explanation.
For example: Too many visitors to an area can cause overcrowding/environmental damage [1] such as noise and congestion from traffic/partying groups [1] which can deter people and decrease visitor numbers [1].
Question
Describe the main characteristics of sustainable tourism.[4]
Explain three different impacts of tourist developments on the environment.[3×2]
Examine how tourism has had social and economic impacts on one country.[10]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Sustainable tourism allows for continuation of activity at the same level for future generations [1 mark]. It minimizes the impact of activity on the environment; supports the livelihoods and culture of local people; manages resources to prevent depletion; and reduces the ecological footprint of industry.
Award 1 mark for each valid statement made up to a maximum of 3 marks.
If candidates define “tourism” they can receive a maximum of 1 mark.
Responses that define sustainable development and explain how it is promoted in relation to tourism should be credited.
There are a range of possible answers that include:
- increased water consumption
- increased traffic and associated pollution (water, noise, aesthetic)
- loss of habitat and biodiversity
- increased waste produced requiring disposal
- CO2 emissions (especially long-haul flights)
- consumption of local natural capital.
There are possible positives, for example, conservation, marine reserves. 1 mark should be awarded for each basic impact stated, and 1 mark for some development/explanation.
There are a wide range of valid responses that could be credited. Likely themes include positive multipliers, employment (informal and formal), effects on crime, language, cultural homogenization.
Answers are expected to provide a balanced range of both positive and negative impacts in order to gain the higher markbands. Answers that focus only on either positive or negative impacts should be restricted to band D. Answers that do not refer to a specific country should be restricted to band D. Answers that refer to the impact of a major sporting event on a named city and not tourism in general on a country should be restricted to band C. Answers that focus only on social or economic impacts should be restricted to band D.
To access bands E and F, answers should consider positive and negative impacts.
Marks should be allocated according to the markbands.
Examiners report
Many candidates scored full marks here. The characteristics of sustainability were generally well understood.
This was well answered. Some mentioned impacts on the human environment rather than the physical environment, but these candidates were in a minority.
This was generally answered very well, with a strong focus on the question. The best candidates considered positive and negative aspects of social and economic impacts, though at standard level, many responses failed to provide a balance between positive and negative impacts.
Question
Outline what is meant by the terms:
(i) primary tourist resources;
(ii) secondary tourist resources.[4]
Using examples, explain three reasons for the growth of tourism in more remote locations.[6]
To what extent do the advantages of ecotourism outweigh any disadvantages?[10]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
(i) Primary resources are pre-existing attractions [1 mark].
Award the final [1 mark] for identifying a possible pre-existing attraction: features of the natural environment (climate, landscape, and ecosystems), indigenous people, cultural resources and heritage sites, etc.
(ii) Secondary resources are purpose-built [1 mark].
Award the final [1 mark] for identifying a possible purpose-built attraction: accommodation (hotels, campsites, and guesthouses), catering, entertainment, transportation, and information, etc.
Award [1 mark] for each basic reason that is identified/stated, and a further [1 mark] for explanation of how this leads to growth of tourism in remote locations. (The concept of “remote” may depend on where the tourist’s home is. The same example can be used more than once.)
For example:
- internet tourist websites have raised awareness [1 mark] of remote locations where visitors can now go, such as Antarctica [1 mark]
- improved accessibility to remote Pacific islands [1 mark] has been helped by improvements in cruise ship designs [1 mark]
- rising incomes in developed countries [1 mark] means people have the funds for “the trip of a lifetime”, such as Europeans travelling to see South America [1 mark]
- rising incomes in emerging economies [1 mark] means more people have the funds for “the trip of a lifetime”, such as Chinese visitors to Europe [1 mark].
- over-development of some tourist areas [1 mark] has led to a desire to visit less crowded, more remote, areas such as The Maldives [1 mark].
Credit all content in line with the markbands. Credit unexpected approaches wherever relevant.
Good answers should show a sound understanding of the concept of ecotourism (responsibly supporting the environment and local communities). Accept suitable references to sustainable tourism.
Likely socio-economic themes include: positive impacts such as employment (informal and formal), infrastructure, developing facilities, reduced out-migration, reducing stereotypes. Environmental themes include maintaining biodiversity/local ecosystems, maintenance of genetic materials, climate regulation and flood control. Negative impacts might include loss of culture, clash of cultures and disrespect of local customs; also trampling and habitat loss if not done properly.
The evaluation of the statement might include multiple perspectives (external companies may benefit more from tour packages than locals do) or a temporal perspective perhaps applying a model (such as Butler or carrying capacity ie advantages/disadvantages become more evident over time as tourist incomes or visitor pressures grow.
For band D, candidates must describe one or more ecotourism/sustainable tourism schemes and some effects on communities and/or the environment.
Band E should either provide greater detail about both community and environmental advantages and disadvantages (these need not be perfectly balanced) or offer some more sophisticated evaluation of the statement (eg perspectives or timescales).
At band F, expect both elements.
Examiners report
Good answers with most able to outline primary and secondary tourist resources.
Most were aware of the basic reasons, but too many did not provide examples as required and therefore did not score the second mark in each of the three reasons.
There were a few well-considered and exemplified answers to this question, with good evaluation. However, the majority of responses were rather weak. The problem was that many candidates had an imperfect idea of the concept of ecotourism; many merely equated it with environmental protection, ignoring social and economic issues. Many answers were descriptive, and relatively few considered the advantages and disadvantages. Disadvantages were particularly not well known and tended to focus on tourism generally.
Question
Define the term tourism.[2]
State two possible reasons why not all international arrivals can be classified as tourists.[2]
Explain two strategies designed to manage the environmental damage caused by tourism in one named large town or city.[6]
Discuss the view that the economic benefits of tourism in one country you have studied outweigh its negative social and environmental impacts.[10]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Tourism involves travel away from home for at least one night [1] for the purpose of leisure [1].
Award [1] for any of the following, up to [2]:
- transit / short-term passengers, not staying at least one night
- refugees / asylum seekers
- business people
- long-term voluntary migrants (joining family/work reasons)
- research scientists
- returning residents.
Award [1] for each strategy/problem/solution, and [2] for development of how it reduces/manages environmental damage.
Possible strategies include:
- reduced vehicle emissions
- reduced noise pollution
- waste management
- control of effluent disposal into the sea.
For example: Limiting the number of tourists is one way to reduce litter problems in Venice [1]. This has been done by limiting the number of hotel beds available [1] and restricting the number/capacity of visiting cruise ships [1].
Award a maximum of [3] if there is no named town or city, or if the example is inappropriate, eg a rural location.
Answers should consider a variety of economic benefits and social/environmental impacts of tourism in a specific country.
Economic benefits might include improved employment opportunities, growth of local industry, improvements in infrastructure, increased GDP and incomes, increased standards of living.
Negative social and environmental impacts might include increases in crimerates, increasing social inequality, increases in pollution and land degradation, excessive use of groundwater supplies.
Good answers may provide a structured discussion of the different kinds of economic benefits and social/environmental costs of tourism in a particular country, and some evaluation of their relative importance.
Award a maximum of band C if the answer refers to a city (eg Venice) rather than a country.
At band D, expect some description of the economic benefits and social/environmental costs in a particular country.
At band E, expect either a more detailed explanation of the benefits and costs of tourism or some discussion of their relative overall importance in a particular country.
At band F, expect both.
Marks should be allocated according to the Paper 2 HL and SL markbands.
Question
Outline one political and one economic factor that affect participation in sport.[2+2]
Referring to a national sports league you have studied, explain the factors that have determined the home location of its teams.[6]
To what extent can tourism ever be made sustainable?[10]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Political factors could include investment in sports facilities, public health and education investment, education policies, subsidies for sporting activities and governing bodies, legislation.
Economic factors could include availability of private sports facilities, level of public investment in sports facilities, quantity of personal disposable income, cost of sporting equipment. Any single factor may have different effects at different scales (local, national, international).
In each case, award [1 mark] for identifying a valid factor and [1 mark] for a brief outline of how it affects sports participation. For example, investment in public health and education can impact participation because it raises public awareness of the personal health benefits of involvement in sport, making it more likely for people to participate. Public education also makes people more likely to participate because they are frequently prompted to participate by the public information.
Answers will vary depending upon the sport chosen and its context but must examine a sports league of national importance. Factors are likely to include population density, socio-economic factors, cultural and historical factors, government and private investment, and proximity to competing teams. There are other valid responses that should be credited.
Award up to [3 marks] for each factor that is well-explained. A wider range of factors can compensate for less depth. A generic answer, or one using an inappropriate example, should not be awarded more than [3 marks].
Answers may make use of contrasting examples, some successful, some not. Answers should show a sound understanding of the concept of sustainability (supporting local people while conserving resources for the future).
Answers are likely to make reference to the pressures resulting from tourism, efforts to minimize impact of the tourism activity, including transport, accommodation, tourist activities and resource use and waste disposal. These efforts should be evaluated rather than simply described as a success or failure in order to access the higher markbands.
Responses may evaluate the effectiveness of tourism in sustaining both societies and ecosystems in the long-term.
Marks should be allocated according to the markbands.
Examiners report
This was well done by most candidates choosing to answer the question, although some candidates focused on elite athletes rather than participation.
The question tended to be misunderstood regarding the home location of the teams. Although most could refer to a national sports league, knowledge of the location of teams was virtually non-existent. A number of obvious sports fans described where their sport was played with little reasoning.
Good knowledge of the concept of sustainable tourism was shown but descended into broad and vague discussions with few references to examples and little evaluation. Failing to draw a conclusion followed by over-generalizing were the two most common problems.
