Question
A wave is polarized. What must be correct about the wave?
It is a…
A. transverse wave.
B. longitudinal wave.
C. standing wave.
D. travelling wave.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
A polarized wave is a:
A. transverse wave.
Polarization refers to the orientation of the oscillations of the wave. In a transverse wave, the oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation, and this is the type of wave that can be polarized. Longitudinal waves, on the other hand, have oscillations parallel to the direction of wave propagation and cannot be polarized in the same way. Standing and traveling waves are characteristics related to the motion and behavior of waves and are not directly related to polarization.
Question
A longitudinal wave is travelling through a medium. The variation with distance d of the displacement x of the particles in the medium at time t is shown.
Which point is at the centre of a compression?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Suppose three molecule at closest to A and C.
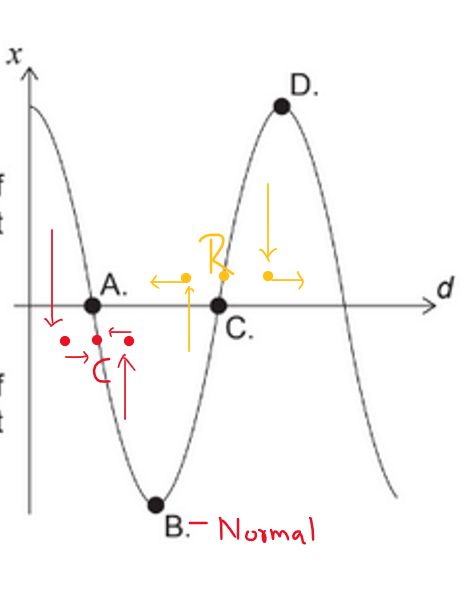
A – Compress
B- Normal pressure point
C- Rarefraction
D- Normal pressure point
Question
A transverse travelling wave is moving through a medium. The graph shows, for one instant, the variation with distance of the displacement of particles in the medium.

The frequency of the wave is 25 Hz and the speed of the wave is 100 m s–1. What is correct for this wave?
A The particles at X and Y are in phase.
B The velocity of the particle at X is a maximum.
C The horizontal distance between X and Z is 3.0 m.
D The velocity of the particle at Y is 100 m s–1.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
\(Frequency = 1 / T\)
\(25 Hz = 1 / T\)
\(T = 0.04 sec\)
\(V_{w} = 100 m /s\)
Time between X and Z is 3T / 4
Distance \(= V_{w} × 3T /4 \)
= 100 × 0.75 × 0.04
= 3 m
Which of the following gives regions of the electromagnetic spectrum in the order of decreasing frequency?
A. gamma-ray, microwave, visible
B. radio wave, infrared, microwave
C. ultraviolet, infrared, microwave
D. visible, gamma-ray, radio wave
Answer/Explanation
Answer – C
The different levels of the spectrum in order of decreasing wavelength is given below,
(1) Radio waves,
(2) Microwaves,
(3) Infrared radiation,
(4) Visible light,
(5) Ultraviolet radiation,
(6) X-rays, and
(7) Gamma rays.
Frequency and wavelength are inversely proportional to each other
So, the answer will be C
A transverse standing wave is established on a string. Consider the following phase differences.
I. 0°
II. 90°
III. 180°
Which of the following gives all the possible phase differences between the oscillations of any two particles in the standing wave?
A. I only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
Examiners report
This question concerned itself with phase difference in a standing wave. It appears not to be well known that particles within any one loop are in phase with each other and that two particles in adjacent loops differ in phase by 180°.