Question
Excretion is the process of removing waste products of metabolism from the body.
(a) Name the two main products of metabolism that need to be excreted from the human body.
(b) The kidney is one of the main excretory organs of the body. Its role is to filter the blood. Some substances leave the blood and are removed from the body in the urine. The concentration of
protein in the blood entering the kidneys in the renal arteries is 83 g dm^{–3}.
State the concentration of protein that you would expect in the urine of a healthy person and explain your answer.
(c) Dialysis can be used to treat people whose kidneys do not function properly.
Fig. 3.1 shows dialysis treatment.
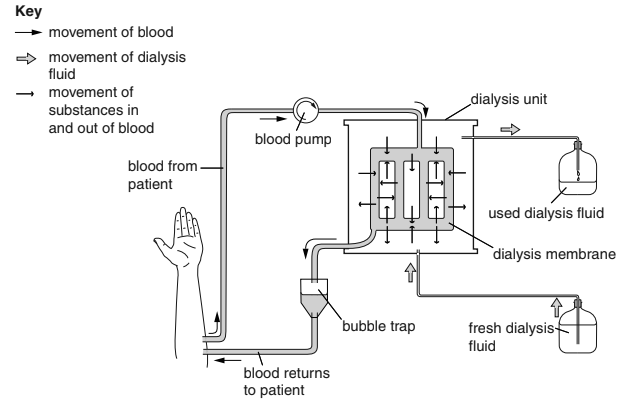
Fig. 3.1
Use Fig. 3.1 to describe the process of dialysis and explain changes that occur in a person’s blood.
(d) Some people with kidney failure are given a kidney transplant.
State one advantage and one disadvantage of having a kidney transplant instead of dialysis treatment.
(e) The liver is another excretory organ of the body. The liver breaks down hormones and drugs, such as alcohol.
(i) State one function of the liver other than the breakdown of hormones and drugs.
(ii) Describe two effects on the body of long-term, excessive consumption of alcohol.
(iii) Suggest one social implication of alcohol misuse.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) carbon dioxide ;
urea ;
(b) 0/ 0.0 (gdm^{–3}) ;
proteins too big, to pass through the capillary wall (in glomerulus)/ to be filtered (from the blood)/ out of the glomerulus ;
(c) 1 blood flows into the (dialysis) machine/blood is returned to the patient ;
2 blood passes over a dialysis membrane/ countercurrent flow described ;
3 the dialysis membrane separates the person’s blood and the dialysis fluid ;
4 dialysis fluid contains, glucose/ salts / no urea ;
5 movement (across membrane) by diffusion/ down a concentration gradient ;
6 urea leaves the blood/ enters the dialysis fluid ;
7 dialysis fluid is refreshed ;
8 excess / some salt, leaves the blood/enters the dialysis fluid ;
9 excess / some water, leaves the blood/ enters the dialysis fluid ;
10 glucose/ salts in dialysis fluid same concentration as (should be) in blood ;
11 no net loss of glucose ;
(d) advantage
no need to visit hospital ;
no need for dialysis / time not taken up with dialysis ;
no need for a restricted diet ;
no long term discomfort/ pain ;
improved quality of life/ lead a normal life ;
disadvantage
rejection of kidney ;
difficult to find suitable donor ;
risk associated with operation ;
need to take immunosuppressant drugs ;
(e) (i) breaks down/AW, dead/ damaged red blood cells ;
stores (named) vitamins /(named) minerals ;
breaks down amino acids into ammonia/ deamination ;
makes urea ;
stores glycogen ;
converts glucose to glycogen/ora ;
produces bile (salts / pigments) ;
makes cholesterol ;
makes (named) protein ;
maintains glucose concentration in blood ;
breaks down toxins ;
AVP ;
(ii) cirrhosis (of liver)/(chronic) liver disease/ kidney failure/ liver failure ;
cancer of the liver ;
brain damage ;
stomach ulcers ;
heart disease/ high blood pressure ;
oral cancer/ mouth cancer/ throat cancer/AW ;
pancreatitis ;
reduced fertility ;
depression/AW ;
addiction/dependence ;
heart failure/stroke/heart attack ;
(iii) violent crime/ domestic violence ;
road accidents /drink driving ;
(petty) crime/ vandalism ;
family breakdown/ divorce/relationship breakdown ;
impaired performance at work / unemployment/ difficulty getting a job ;
AVP ;
Question
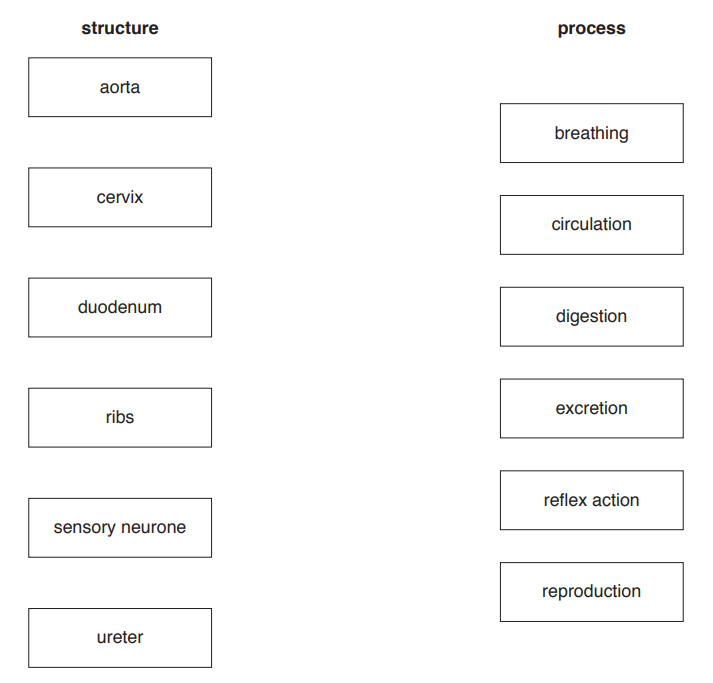
The boxes on the left contain the names of structures in the body.
The boxes on the right contain the names of processes carried out by the body.
Draw one straight line from each structure to the process in which it is involved.
Draw six lines.
Answer/Explanation
Ans
3.