Question
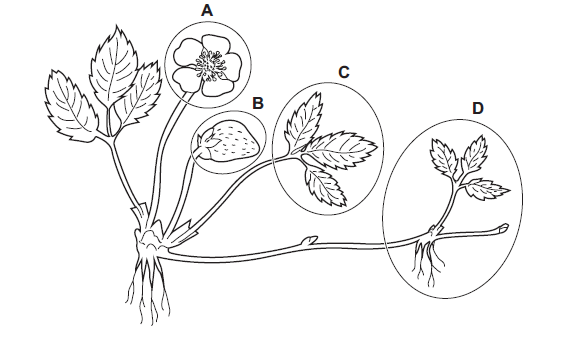
The diagram shows a strawberry plant.
Which labelled part of the plant can only be produced by asexual reproduction?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Runners (part D), also known as stolons, are the part of a strawberry plant that can only be produced by asexual reproduction. Runners are long, thin stems that grow out from the base of the strawberry plant and develop new plantlets at their nodes. These plantlets can take root in the soil and grow into new strawberry plants, creating genetically identical clones of the parent plant.
Asexual reproduction through runners is a common method of strawberry propagation, as it allows growers to easily and efficiently propagate desirable traits from a single parent plant without the genetic variation that can result from sexual reproduction (seeds). This is particularly useful for maintaining the characteristics of a specific strawberry variety.
Question
The diagram shows a plant that is producing small plantlets.
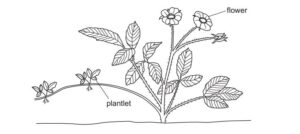
Which statement about the plantlets is correct?
A They are genetically different from the parent plant.
B They are genetically identical to the parent plant.
C They are produced as a result of the fusion of nuclei.
D They are produced by fertilising the flowers.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
The correct statement about plantlets is:
B They are genetically identical to the parent plant.
Plantlets, also known as “offshoots,” “pups,” or “clones,” are new individual plants that develop asexually from the parent plant. This means that they are produced without the involvement of sexual reproduction, which includes processes like fertilization and the fusion of nuclei.
When a plantlet forms, it usually originates from a part of the parent plant, such as a leaf, stem, or other vegetative structure. These plantlets develop through a process called vegetative propagation or asexual reproduction. In this process, a part of the parent plant undergoes cell division and growth to develop into a new individual plant that is genetically identical to the parent plant.
This genetic similarity arises because the plantlets are produced through mitosis, a type of cell division that results in identical copies of the parent cell’s genetic material being passed on to the new cells. As a result, the genetic information of the plantlets is the same as that of the parent plant. This is in contrast to sexual reproduction, where genetic diversity is introduced through the combination of genetic material from two parent plants through processes like fertilization and the fusion of nuclei.
Question
The diagram shows reproduction in a potato plant. Potato X was planted into the ground and a plant grew from it. The plant then produced potato Y.
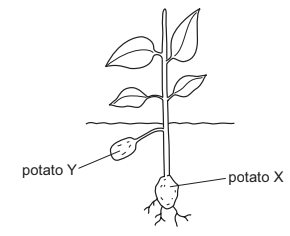
Which statement is correct?
A X and Y are genetically different.
B Y was produced by asexual reproduction.
C Y was produced by sexual reproduction.
D Y was produced by the fusion of gametes.
▶️Answer/Explanation
The correct statement is:
B. Y was produced by asexual reproduction.
In potato plant reproduction, the growth of a new plant from a planted potato (X) is a form of asexual reproduction known as vegetative propagation. This process involves the development of new plants from plant structures such as tubers, bulbs, or cuttings, without the involvement of gametes or fertilization. The resulting potato (Y) is genetically identical to the parent plant (X), which is why option A is incorrect. Since asexual reproduction doesn’t involve the fusion of gametes, options C and D are also incorrect.
Question
A gardener wants to produce many genetically identical plants from a single plant.
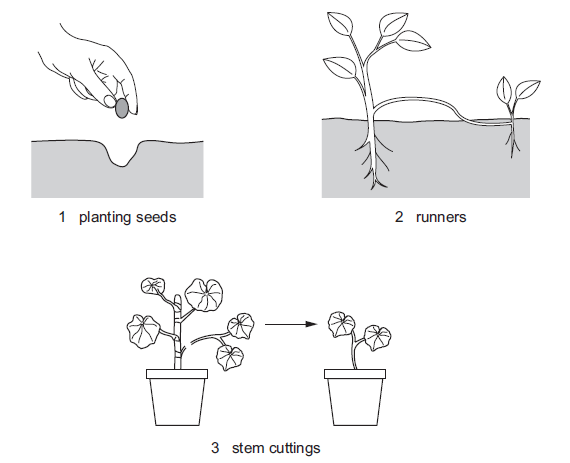
The diagram shows different methods of growing new plants.
Which methods will produce plants that are genetically identical to the parent plant?
A 1, 2 and 3
B 1 and 2 only
C 1 and 3 only
D 2 and 3 only
▶️Answer/Explanation
D
Among the methods mentioned, only method 2 (runners) and method 3 (stem cuttings) have the potential to produce genetically identical plants to the parent plant.
Runners (Stolons): Runners are specialized stems that grow horizontally above the ground, sending out roots and shoots along their length. They are produced by certain plant species (e.g., strawberries, spider plants) and can give rise to new plants at the nodes where roots and shoots develop. Because runners are a form of asexual reproduction, the new plants produced from runners will be genetically identical to the parent plant since they are essentially clones.
Stem Cuttings: Stem cuttings involve taking a piece of a plant’s stem (with leaves attached in many cases) and encouraging it to root and grow into a new plant. This method also involves asexual reproduction. The cutting develops roots and shoots, creating a new plant that is genetically identical to the parent plant. The genetic makeup of the new plant is identical to the original plant because it comes from a part of the parent plant’s tissue.
When you grow plants from seeds, there is a process called sexual reproduction involved. Seeds are the result of combining genetic material from two parent plants (pollen from one plant fertilizes the ovules of another plant). As a result, the offspring plants grown from seeds will have a combination of genetic material from both parent plants, leading to genetic variation. Therefore, plants grown from seeds will not be genetically identical to the parent plant.
