Question
In humans, what is an example of a secondary sexual characteristic in both males and females?
A hair grows on face
B hips widen
C fat is deposited on hips and thighs
D sexual organs grow
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
Fat is deposited on hips and thighs.
In both males and females, the deposition of fat on specific body parts is considered a secondary sexual characteristic. During puberty, as sex hormones like estrogen and testosterone increase, they influence the distribution of fat in the body. In females, estrogen leads to the accumulation of fat in the hips, buttocks, and thighs, giving rise to a curvier shape. This is often referred to as the “pear-shaped” body. In males, testosterone contributes to a more central distribution of fat, often resulting in a more “apple-shaped” body.
Secondary sexual characteristics are traits that develop during puberty and are not directly related to reproductive organs themselves but rather play a role in sexual attraction and differentiation between the sexes. While options A and D also involve changes associated with puberty, they are not examples of secondary sexual characteristics shared by both males and females.
Question
The diagram shows some changes which take place during a woman’s menstrual cycle.
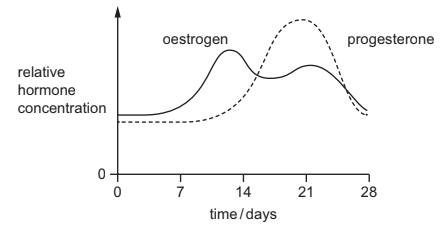
Assuming ovulation occurs on day 14, what is occurring at the time of ovulation?
A a fall in the levels of oestrogen and progesterone
B a fall in the level of progesterone only
C a rise in the level of oestrogen
D a rise in the level of progesterone and fall in the level of oestrogen
▶️Answer/Explanation
During a woman’s menstrual cycle, assuming ovulation occurs on day 14, the correct answer is:
D. a rise in the level of progesterone and fall in the level of oestrogen
Ovulation is the process in which a mature egg is released from the ovary and becomes available for fertilization. This event is triggered by a surge in luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) from the pituitary gland. This surge in LH causes the ovarian follicle to rupture, releasing the mature egg.
Leading up to ovulation, there is an increase in the level of estrogen produced by the developing follicles in the ovaries. Estrogen plays a role in preparing the uterine lining for potential implantation and also contributes to the LH surge that triggers ovulation.
After ovulation, the ruptured follicle transforms into the corpus luteum, which secretes progesterone. Progesterone helps maintain the uterine lining, making it conducive for implantation of a fertilized egg. However, if fertilization doesn’t occur, the corpus luteum eventually degenerates, leading to a decrease in progesterone levels, and the menstrual cycle starts anew.
Question
The following statements are about some hormones in the human body.
V causes changes in the ovaries during the menstrual cycle
W promotes the development of stronger muscles
X causes the voice to deepen at puberty
Y produced by the pancreas
Which statements are correct for testosterone?
A V and W B V and Y C W and X D X and Y
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
The correct answer is C. W and X.
- Statement W: Testosterone promotes the development of stronger muscles. Testosterone is a male sex hormone that plays a significant role in the growth and maintenance of muscle mass in both males and females.
- Statement X: Testosterone causes the voice to deepen at puberty. During puberty, the increase in testosterone levels in males leads to the growth of the larynx (voice box), causing the vocal cords to lengthen and thicken, resulting in a deeper voice
