Question
What is defined as ‘a thread-like structure of DNA, carrying genetic information in the form of genes’?
allele
chromosome
protein
zygote
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
The correct answer is B: chromosome. A chromosome is defined as a thread-like structure of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) that carries genetic information in the form of genes. Chromosomes are found in the nucleus of cells and are responsible for the transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next. They consist of DNA molecules tightly coiled and wrapped around proteins called histones.
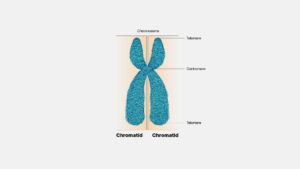
Question
A rabbit has 44 chromosomes in each of its body cells.
Which row correctly describes the gamete cells?

▶️Answer/Explanation
B
In rabbits, the gamete cells are the sperm and egg cells, which are involved in sexual reproduction. Gametes are produced through a special type of cell division called meiosis, which results in cells with half the number of chromosomes compared to the body cells. Since a rabbit has 44 chromosomes in each of its body cells, the correct row describing the gamete cells would be: Number of chromosomes in gamete cells: 22
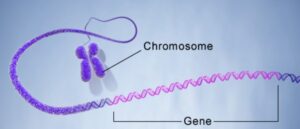
Question
What is the name of a length of DNA that codes for a protein?
A amino acid
B chromosome
C gene
D nucleus
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
The correct answer is C: gene. A gene is a specific segment or length of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) that contains the instructions or code for building a protein. Genes are the basic units of heredity and are responsible for the inheritance of traits from one generation to the next.They provide the code or sequence of nucleotides that specifies the sequence of amino acids in a protein.
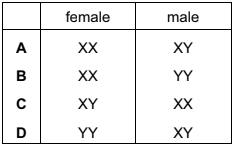
Question
What are the sex chromosomes for human females and males?
▶️Answer/Explanation
A
The sex chromosomes for human females and males are:
Human females: XX
Human males: XY
In humans, the sex chromosomes determine an individual’s biological sex. Females have two X chromosomes (XX), while males have one X chromosome and one Y chromosome (XY). The presence of the Y chromosome in males determines the development of male reproductive organs and secondary sexual characteristics. The absence of the Y chromosome in females allows for the development of female reproductive organs.
Question
A human cell contains a length of DNA that carries the code for making which substance?
A fat
B glycogen
C lipase
D starch
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
The correct answer is C: lipase. A human cell contains a length of DNA that carries the code for making lipase. Lipase is an enzyme that is involved in the breakdown and digestion of lipids (fats). It catalyzes the hydrolysis of fats into fatty acids and glycerol, allowing for their absorption and utilization in the body.
Question
What determines the sex of a baby?
A the father’s blood group
B the father’s chromosomes
C the mother’s blood group
D the mother’s chromosomes
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
The correct answer is B: the father’s chromosomes. The sex of a baby is determined by the chromosomes contributed by the parents during fertilization. Specifically, the father’s chromosomes determine the sex of the baby. Humans have two types of sex chromosomes: X and Y. Females have two X chromosomes (XX), while males have one X and one Y chromosome (XY).
Question
The diagram represents a protein molecule.
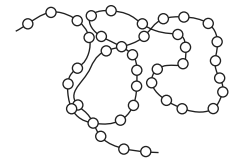
What do the small circles represent?
A amino acids
B fatty acids
C glycerol
D simple sugars
▶️Answer/Explanation
A
n a protein molecule, amino acids are the building blocks that are present. Amino acids are organic compounds that contain an amino group (-NH2) and a carboxyl group (-COOH) attached to a central carbon atom. The central carbon atom is also bonded to a hydrogen atom and a unique side chain, known as the R-group, which gives each amino acid its specific properties. There are 20 standard amino acids that are commonly found in proteins. These amino acids differ in the structure and properties of their R-groups, which can be hydrophobic, hydrophilic, acidic, or basic.

Question
What defines a diploid nucleus?
A a nucleus containing two sets of chromosomes
B a nucleus containing two unpaired chromosomes
C a nucleus with two alternative forms of a gene
D a nucleus with two separate threads of DNA
▶️Answer/Explanation
A
The correct answer is(A) a nucleus containing two sets of chromosomes. A diploid nucleus refers to a cell nucleus that contains two complete sets of chromosomes. In most organisms, including humans, diploid cells are the norm for the majority of their life cycle. The term “diploid” is derived from the Greek words “di,” meaning two, and “ploid,” meaning set or fold. Each set of chromosomes in a diploid nucleus is derived from one parent, with one set inherited from the mother and the other from the father. In humans, diploid cells contain a total of 46 chromosomes, with 23 chromosomes coming from each parent.
Question
Which sex chromosomes are present in all mature human sperm cells?
A both X and Y chromosomes
B either X or Y chromosomes
C only X chromosomes
D only Y chromosomes
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
The correct answer is B) either X or Y chromosomes. In humans, sperm cells are produced through a process called spermatogenesis. During spermatogenesis, cells called spermatogonia undergo meiosis, resulting in the formation of mature sperm cells (spermatozoa). Meiosis is a specialized cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half. Human sperm cells are haploid, meaning they contain half the number of chromosomes compared to other body cells. In the case of sex chromosomes, there are two possibilities: X and Y chromosomes.
Question
Which statement about the human sex chromosomes is correct?
A All boys have two Y chromosomes.
B Everybody has at least one X chromosome.
C Girls have a Y chromosome and an X chromosome.
D Nobody has two X chromosomes.
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
The correct answer is (B) Everybody has at least one X chromosome.The statement “Everybody has at least one X chromosome” is correct. Both males and females have at least one X chromosome. Females typically have two X chromosomes (XX), while males have one X chromosome and one Y chromosome (XY). The presence of an X chromosome is essential for the normal development and functioning of individuals. There are two types of sex chromosomes: X and Y chromosomes. The combination of these chromosomes determines whether an individual is male or female.
Question
The diagram shows part of a protein molecule.
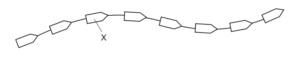
What does X represent?
A amino acid
B fatty acid
C glycerol
D sugar
▶️Answer/Explanation
A
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Proteins are essential molecules in living organisms that play a wide range of roles, including structural support, enzymatic catalysis, transportation, and signaling.
Each amino acid consists of a central carbon atom (known as the alpha carbon) bonded to four groups: an amino group (-NH2), a carboxyl group (-COOH), a hydrogen atom (-H), and a variable side chain or R-group. It’s the unique side chain of each amino acid that gives it its specific properties, such as size, charge, polarity, and reactivity.
Amino acids can link together through a process called peptide bond formation, where the carboxyl group of one amino acid reacts with the amino group of another amino acid, releasing a water molecule. This forms a linear chain of amino acids known as a polypeptide chain. Multiple polypeptide chains can then fold and interact to create the complex three-dimensional structures we observe in proteins. The specific sequence and arrangement of amino acids in a protein determine its function and properties.
Question
Which substance is coded for by a length of DNA?
A fat
B fatty acid
C glycerol
D lipase
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
The correct answer is (C) glycerol. A length of DNA does not directly code for a specific substance like a fat, fatty acid, or lipase. DNA contains the genetic information in the form of genes, which are segments of DNA that provide instructions for building proteins. Glycerol, on the other hand, is a small organic molecule that is an important component of fats and lipids. It serves as the backbone for triglycerides, which are a type of fat molecule composed of glycerol and three fatty acids.
Question
What are alleles?
A a pair of chromosomes
B different versions of the same gene
C the total number of genes on one chromosome
D two genes side by side on the same chromosome
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
The correct answer is (B) different versions of the same gene. Alleles are alternative forms or variants of a gene that occupy the same position or locus on homologous chromosomes. Genes are segments of DNA that provide instructions for the production of specific proteins or play a role in regulating various cellular processes. Each individual inherits two copies of each gene, one from each parent. These copies can have different forms or alleles. For example, a gene responsible for determining eye color may have alleles for blue eyes and brown eyes. Another gene may have alleles for tall height and short height.
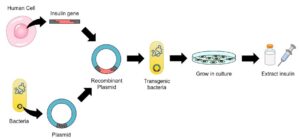
Question
A gene for insulin is taken from a human cell and placed in a bacterium.
The bacterium can then make human insulin.
What is this process called?
A artificial selection
B genetic engineering
C heterozygous inheritance
D natural selection
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
The correct answer is (B) genetic engineering. The process described, where a gene for insulin is taken from a human cell and inserted into a bacterium, is an example of genetic engineering. Genetic engineering involves manipulating an organism’s genetic material, such as DNA, to introduce specific genes or modify existing genes. In this case, the gene for insulin is isolated from a human cell, which typically produces insulin naturally. The gene is then inserted into the bacterium, which does not naturally produce insulin. By incorporating the human gene into the bacterium, it gains the ability to produce human insulin.
Question
Which identifies the chemical elements found in proteins?
▶️Answer/Explanation
A
Proteins are macromolecules composed of smaller units called amino acids. There are 20 standard amino acids that are commonly found in proteins. These amino acids differ in their side chains (also known as R-groups), which give each amino acid its unique chemical properties. The sequence of these amino acids in a protein determines its structure and function.
The chemical elements found in proteins are:
1. Carbon (C)
2. Hydrogen (H)
3. Oxygen (O)
4. Nitrogen (N)
These elements combine in various ways to form the backbone and side chains of the amino acids, resulting in the diverse structures and functions of proteins.
Question
What is the definition of an allele?
A a length of DNA that codes for a protein
B a thread-like structure, carrying genes
C a version of a gene
D the genetic make up of an organism
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
The correct answer is (C) a version of a gene. An allele is defined as a specific version or variant of a gene that exists at a particular locus or position on a chromosome. Genes are segments of DNA that contain the instructions for producing proteins or regulating specific traits or functions within an organism. Different alleles of the same gene may have slight differences in their DNA sequence, leading to variations in the specific traits or characteristics they code for. For example, there may be different alleles for eye color, hair color, or blood type, each resulting in a distinct phenotype (observable trait).
Question
Which element is found in proteins but not carbohydrates?
A carbon
B hydrogen
C nitrogen
D oxygen
▶️Answer/Explanation
The correct answer is:
C – Nitrogen
Nitrogen is an element that is found in proteins, but not typically in carbohydrates. Proteins are composed of amino acids, which contain nitrogen atoms in addition to carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Carbohydrates, on the other hand, are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, but they do not contain nitrogen.
Question
What is a gene?
A a chain of amino acids that codes for a protein
B a length of DNA that codes for a protein
C a length of protein that codes for an allele
D a structure that codes for the production of DNA
▶️Answer/Explanation
B a length of DNA that codes for a protein
A gene is a specific sequence of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) that contains the instructions for building and maintaining an organism. Genes serve as the basic units of heredity and are responsible for transmitting traits from one generation to the next. Each gene contains the information necessary to produce a specific protein or functional RNA molecule, which in turn contributes to the structure and function of cells and ultimately influences an individual’s traits and characteristics.
Question
Which sex chromosomes in the egg and the sperm will produce a male child?

▶️Answer/Explanation
B
The sex of a child is determined by the combination of sex chromosomes inherited from the parents. Typically, males have one X and one Y chromosome (XY), while females have two X chromosomes (XX).
When it comes to the production of a male child:
- The egg (ova) always carries an X chromosome. This is because females only have X chromosomes to contribute.
- The sperm can carry either an X chromosome or a Y chromosome, since males have both X and Y chromosomes.
If a sperm carrying a Y chromosome fertilizes the egg, the resulting combination will be XY, leading to the development of a male child. If a sperm carrying an X chromosome fertilizes the egg, the combination will be XX, resulting in the development of a female child.
Question
In plants, which ions are used to make amino acids?
A magnesium
B nitrates
C phosphates
D potassium
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
Plants use nitrates (NO3-) as a source of nitrogen to synthesize amino acids. Nitrogen is an essential element for plant growth and development, and it is a crucial component of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins. When plants take up nitrates from the soil through their roots, they convert them into various amino acids through a process called nitrogen assimilation. The assimilated nitrogen is then used for protein synthesis and other essential cellular processes in the plant.
Question
The graph shows the masses of two different types of tomato.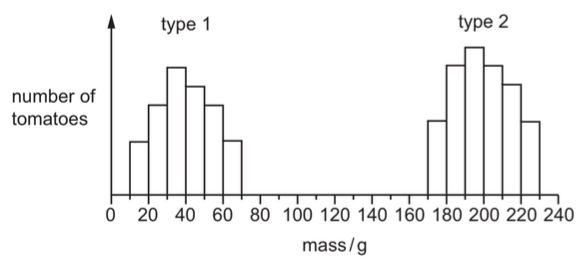
What can be concluded from the graph?
A Genes do not affect the mass of tomatoes.
B Type 1 tomatoes show continuous variation.
C Type 2 tomatoes are sometimes smaller than type 1 tomatoes.
D Type 2 tomatoes show discontinuous variation.
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
Continuous variation refers to the range of values that a trait or characteristic can take within a population, without distinct categories or breaks. In this type of variation, individuals exhibit a wide spectrum of values for a particular trait, and there are no clear-cut boundaries or discrete categories. Instead, the trait shows a smooth, gradual transition from one value to another. Here, The phrase “continuous variation” suggests that Type 1 tomatoes display a range of traits that can vary gradually and smoothly. This is often associated with quantitative traits that are influenced by multiple genes and environmental factors. This is in contrast to “discontinuous variation,” where traits fall into distinct categories with little or no overlap.
In the context of tomato plants, continuous variation could be observed in traits like plant height, leaf size, or fruit mass. This variation occurs due to the interaction of multiple genes and environmental factors, resulting in a range of values rather than distinct categories. This type of variation often follows a normal distribution, also known as a bell curve.
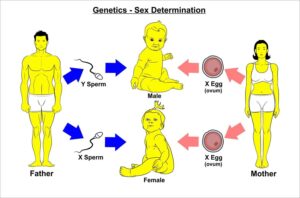
Question
The diagram shows the inheritance of sex in humans.
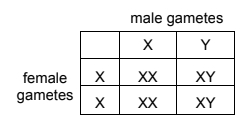
What is the chance of the couple’s next child being male?
A 25% B 50% C 75% D 100%
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
The inheritance of sex in humans is determined by the presence or absence of certain sex chromosomes. Humans typically have two sex chromosomes: X and Y. Individuals with two X chromosomes (XX) are female, while individuals with one X and one Y chromosome (XY) are male.
In the context of a couple’s child, the sex of the child is determined by which sex chromosome the father contributes. Since males have both X and Y chromosomes, they can produce two types of gametes: those containing an X chromosome and those containing a Y chromosome. On the other hand, females have two X chromosomes, so they can only produce gametes with an X chromosome.
When a couple conceives a child, the chance of having a male child is 50% and the chance of having a female child is 50%. This is because the father can contribute either an X or a Y chromosome-carrying sperm, and the mother always contributes an X chromosome-carrying egg. The combination of an X chromosome from the mother and either an X or Y chromosome from the father determines the child’s sex.
So, in simple terms, for each pregnancy, the chance of having a male child is 50%.
Question
Which term is defined as a length of DNA that codes for a protein?
A amino acid
B chromosome
C gene
D mutation
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
A gene is defined as a length of DNA that contains the instructions for building and maintaining a specific protein or set of related proteins. Genes serve as the basic functional units of heredity and play a crucial role in determining an organism’s traits, characteristics, and biological processes. The information encoded within a gene is used by the cell’s machinery to synthesize specific proteins through a process called protein synthesis.
When a gene is transcribed into a complementary RNA molecule (mRNA), which then undergoes translation, the information carried by the mRNA is used to assemble a sequence of amino acids in a specific order, ultimately forming a functional protein. These proteins are responsible for carrying out various functions within the cell and contribute to the overall structure, function, and behavior of an organism.
