Question
(a) Explain the terms allele and gene.

(b) PTC is a bitter tasting chemical that some humans can taste while others cannot. This
is controlled by a single gene with a pair of alleles.
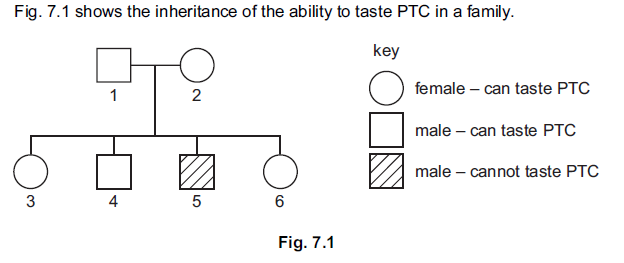
(i) The allele for tasting PTC is dominant to the allele for not tasting PTC.
State evidence shown in Fig. 7.1 that supports this fact.

(ii) Use the symbols T for the dominant allele and t for the recessive allele to state the
genotypes for individuals 2 and 5.

(iii) What are the two possible genotypes for individual 3?
![]()
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question
Some dogs have an inherited condition in which catalase is not produced. This condition is known
as acatalasia and it is caused by a mutation in the gene for catalase.
(a) Define the terms gene and gene mutation.
gene
gene mutation [2]
(b) A geneticist was asked to investigate the inheritance of acatalasia in dogs.
The normal allele is represented by B and the mutant allele is represented by b.
The geneticist made the diagram in Fig. 3.1 to show the inheritance of acatalasia in a family
of dogs. The shaded symbols indicate the dogs with acatalasia.
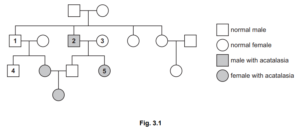
(i) State the genotypes of the dogs identified as 1, 2 and 3 in Fig. 3.1.
1
2
3 [3]
(ii) The geneticist crossed dog 4 with dog 5. Approximately half of the offspring had
acatalasia and half the offspring did not have acatalasia.
Complete the genetic diagram to show how this is possible
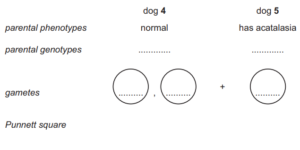
offspring genotypes
offspring phenotypes [3]
(iii) State the name given to the type of cross that you have completed in (b)(ii). [1]
[Total: 9]
Answer/Explanation
Ans
3 (a) gene a length of DNA that codes for a protein ;
gene mutation a change in base sequence of DNA ;
(b) (i) 1 Bb ;
2 bb ;
3 Bb ;
(ii) (Bb x bb)
B , b + b , (b) ;
offspring genotypes Bb and bb ;
A heterozygous and homozygous recessive
offspring phenotypes normal/ carrier and acatalasia ;
(iii) test (cross) ;
Question
(a) (i) Name the type of cell division that forms gametes (sperm cells and egg cells).
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [1]
(ii) State the difference between the number of chromosomes in gametes and the number of
chromosomes in other body cells.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [1]
(b) The sex of a human is determined by the sex chromosomes, X and Y.
State which sex chromosomes are present in a male and in a female.
male ……………………..
female ……………………..
[2]
(c) (i) Define the term allele.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [1]
(ii) The fur colour in a species of mouse can be black or white.
The allele for black fur is dominant to the allele for white fur.
Fig. 8.1 shows the cross between a mouse that is homozygous for black fur and a mouse
that is homozygous for white fur.

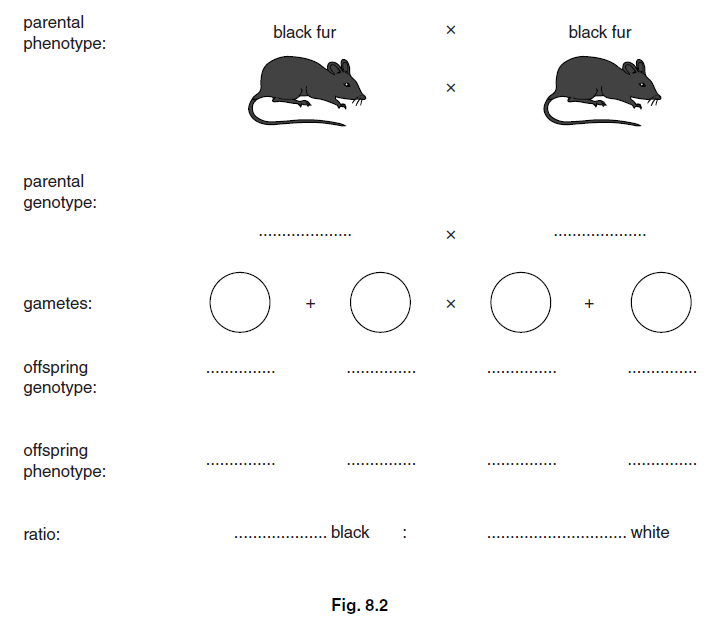
(d) In an investigation, a mouse with black fur and a mouse with white fur were mated several
times. A total of 40 offspring were produced.
There were 19 offspring with black fur and 21 with white fur.
Deduce the genotype of the parent that had black fur.
genotype …………………………….. [1]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question
(a) Define the following genetic terms.
mutation ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
heterozygous …………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
recessive allele ………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(b) People use sun-cream to protect their skin. Ultra-violet light from the sun is a type of ionising radiation.
Fig. 5.1 shows sun-cream being applied.
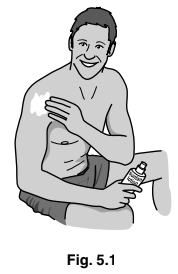
Suggest how using sun-cream reduces the damaging effect of the Sun’s rays.
(c) Fig. 5.2 shows the hand of a person who suffers from a mutation that results in people having more than five digits on each hand (polydactyly).
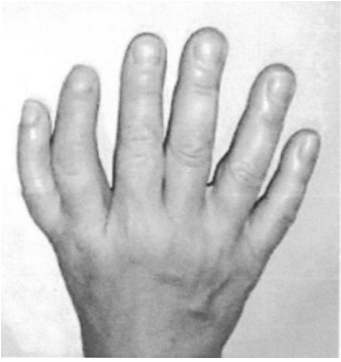
The mutation that results in this condition is dominant.
Fig. 5.3 shows how the condition is inherited in a family.
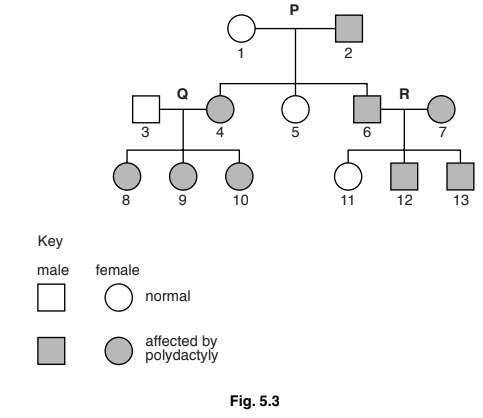
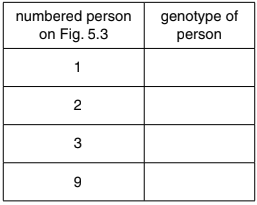
(i) State the genotype of the individuals shown in Fig. 5.3.
Use AA, Aa or aa.
Write your answers in Table 5.1.
Table 5.1
(ii) Using evidence from Fig. 5.3, state which of the couples, P, Q or R, provides proof that the mutation is not recessive.
(iii) Explain the reason for your answer.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) mutation: a change/ error ;
in a, gene/ chromosome/DNA ;
heterozygous: having, two different alleles / a dominant allele and a recessive allele ;
of a particular gene ;
recessive allele: alternative form of a gene ;
only expressed, in absence of the dominant (allele)/ if homozygous ;
(b) (sun-cream) absorbs / blocks / stops Sun’s rays ;
prevents ionising radiation/harmful Sun’s rays from reaching skin/ cells / body ;
reference to cancer/ melanoma/ mutation ;
(c) (i) 1: aa ;
2: Aa ;
3: aa ;
9: Aa ;
(ii) couple R
(iii) if it was recessive all their offspring would have shown the condition ;
but individual 11/AW is normal, so must be dominant/AW ;
