Question
Which processes result in organisms gaining carbon compounds, and in the addition of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere?

▶️Answer/Explanation
D
Organisms gain carbon compounds through various biological processes, primarily through photosynthesis and consumption of organic matter. On the other hand, the addition of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere is mainly a result of natural processes such as respiration, volcanic activity, and human activities like burning fossil fuels.
1. Photosynthesis and Feeding: During photosynthesis, plants, algae, and some bacteria use carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to synthesize organic compounds, primarily glucose. In this process, carbon dioxide is taken in, and oxygen is released as a byproduct. The glucose and other organic compounds produced are used as energy sources for the organism’s growth and maintenance. This process removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and stores carbon in organic molecules. Animals and other heterotrophic organisms gain carbon compounds by consuming other organisms, which may have acquired their carbon through photosynthesis. When animals eat plants or other animals, they assimilate the organic carbon present in the consumed organisms’ tissues. This process transfers carbon compounds through the food chain.
2. Respiration: Respiration is a biological process that occurs in all living cells, including plants. During respiration, organisms break down organic compounds, such as glucose, to release energy for their cellular activities. This process involves the consumption of oxygen and the production of carbon dioxide as a waste product. While photosynthesis removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, respiration releases it back into the atmosphere.
In summary, photosynthesis by plants and other autotrophic organisms removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, converting it into organic compounds. On the other hand, respiration by all organisms, including plants, returns carbon dioxide to the atmosphere as a result of the breakdown of organic compounds for energy.
Question
The diagram shows part of the water cycle.
Where is osmosis occurring?
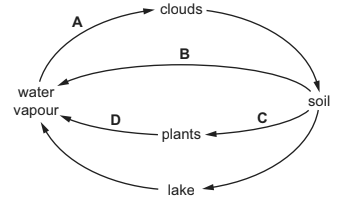
▶️Answer/Explanation
C. Soil to plants: Osmosis is a biological process involving the movement of water through a semi-permeable membrane. In the context of plants, osmosis occurs when water moves from an area of low solute concentration (usually the soil) to an area of higher solute concentration (inside the plant’s root cells). This movement of water is essential for the plant to absorb nutrients dissolved in the soil water and maintain turgor pressure in its cells.
Plant roots typically have higher solute concentrations than the surrounding soil due to various dissolved nutrients and minerals. As a result, water from the soil move into the roots through osmosis to balance the concentration gradient.
Question
The diagram shows part of the carbon cycle.
Which letter represents photosynthesis?
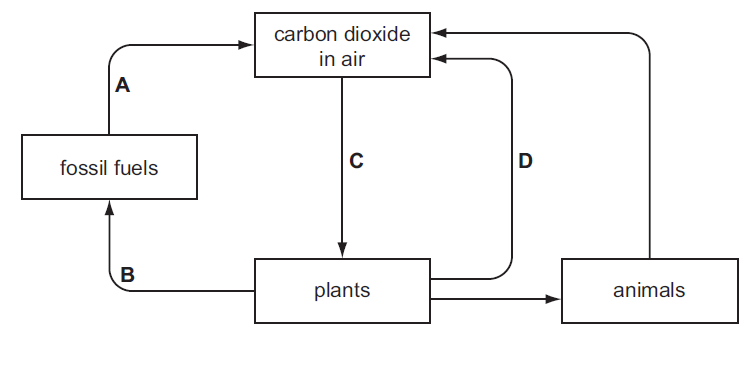
▶️Answer/Explanation
The process that represents photosynthesis is:
C. carbon dioxide in air to plants
Photosynthesis is the biological process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) into glucose (a type of sugar) and oxygen (O2) using energy from sunlight. This process takes place in the chloroplasts of plant cells and is crucial for sustaining life on Earth by producing oxygen and providing energy-rich organic molecules for organisms that consume plants.
The Letter “C” represents photosynthesis because it describes the movement of carbon dioxide from the air into plants, which is a fundamental step in the photosynthesis process. During photosynthesis, plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through tiny pores called stomata on their leaves. Inside the plant cells, carbon dioxide combines with water and sunlight to produce glucose and oxygen through the process of photosynthesis.
Question
The diagram shows part of the water cycle.
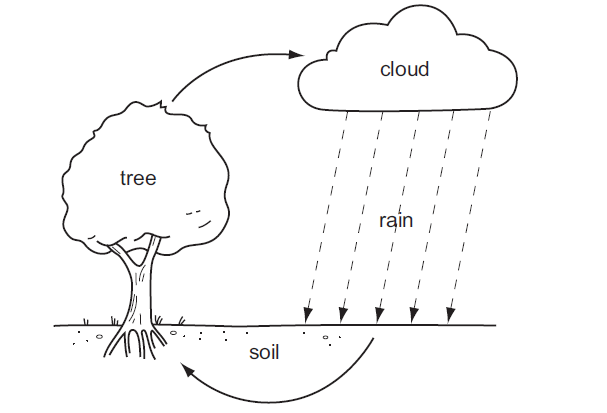
How is water lost from the tree?
A condensation
B respiration
C translocation
D transpiration
▶️Answer/Explanation
The option that represents how water is lost from the tree is:
D. Transpiration
Transpiration is the process by which water is lost from the surface of a plant, primarily through small openings called stomata on the leaves. This process is crucial for plants as it helps to transport water and nutrients from the roots to the leaves and also helps in maintaining temperature regulation within the plant. Transpiration is a significant component of the water cycle, as it contributes to the movement of water from the soil to the atmosphere.
Question
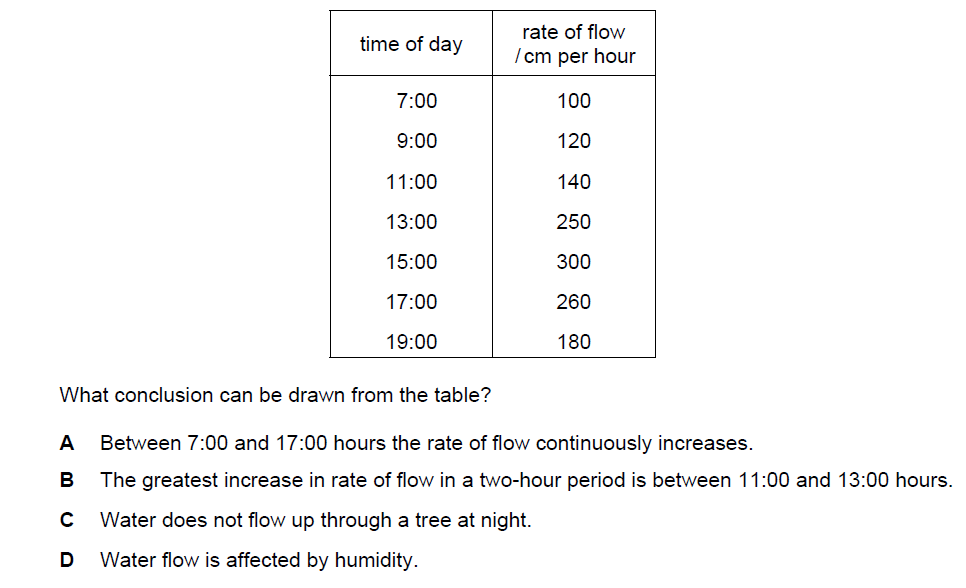
The table shows the rate of water flow through a tree over a 12 hour period.
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
It is concluded from the table that the greatest increase in rate of water flow in a two-hour period is between 11: 00 to 13: 00 hours, because this two-hour period corresponds to the tree’s peak transpiration activity. Transpiration is the process by which water is evaporated from the leaves and stems of plants and trees into the surrounding atmosphere..
During the morning hours, particularly around 11:00 AM, the environmental conditions are usually conducive to increased transpiration. Several factors contribute to this:
Solar Radiation: The sun is at a higher angle in the sky around midday, providing more direct sunlight to the tree’s leaves. This leads to higher temperatures and increased evaporation of water from the leaves.
Temperature: The air temperature usually rises during the morning hours, reaching its peak around midday. Higher temperatures cause the water in the leaves to evaporate more rapidly.
Wind Speed: Wind helps carry away the water vapor that is released through transpiration. In many places, wind speeds tend to pick up during the late morning and early afternoon hours, facilitating faster transpiration.
Stomatal Opening: Stomata are tiny pores on the surface of leaves that regulate gas exchange and water vapor release. Stomata typically open wider in response to increased light and warmth, allowing more water vapor to escape.
The combination of these factors during the 11:00 to 13:00 period leads to the greatest increase in the rate of water flow through the tree.
