Question
Fig. 1.1 shows a pyramid of biomass and part of the carbon cycle.
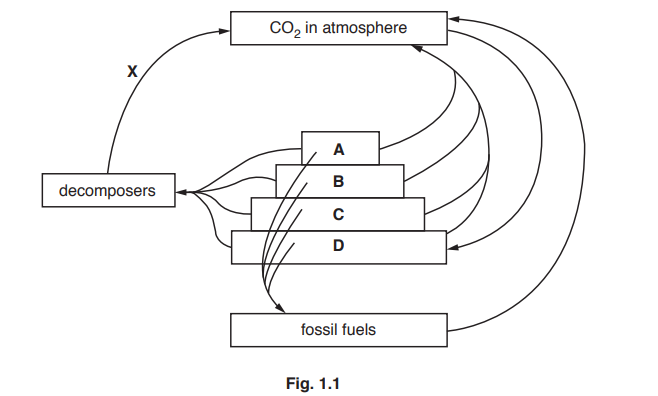
(a) (i) State the principal source of energy required for trophic level D of the pyramid of biomass
in Fig. 1.1.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………[1]
(ii) State the letter that represents the primary consumers in Fig. 1.1.
……………………………………. [1]
(iii) State how carbon is transferred from producers to primary consumers.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………[1]
(iv) Explain why trophic level A is smaller than trophic level B in the pyramid of biomass in
Fig. 1.1.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………[3]
(b) Some fungi and bacteria are decomposers.
(i) Define the term decomposer.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………[1]
(ii) Arrow X on Fig. 1.1 indicates the transfer of carbon from decomposers to the atmosphere.
State the name of process X.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………[1]
(c) Describe how human activities are affecting the carbon cycle.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..[5]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question
Fig. 7.1 shows part of the nitrogen cycle.
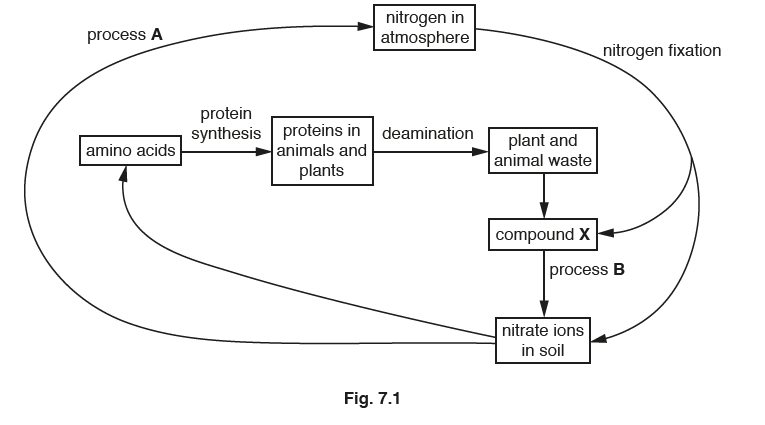
(a) (i) State two ways that nitrogen fixation can occur.
1 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
2 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
[2]
(ii) State the names of processes A and B in Fig. 7.1.
process A …………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
process B …………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
[2]
(iii) State the name of compound X in Fig. 7.1.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [1]
(iv) Define the term deamination.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [2]
(b) State the name of the structure in a cell where protein synthesis occurs.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1]
(c) State the name of an enzyme that digests proteins.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question
(a) Baker’s yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is a single-celled organism that is classified in the
kingdom Fungi.
Fig. 1.1 is a drawing of a section through a yeast cell.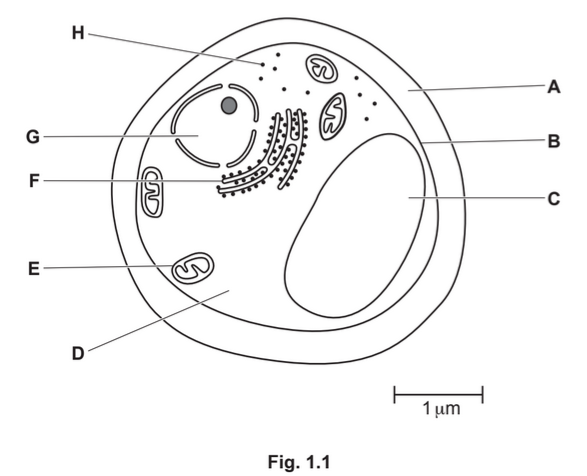
(i) State one other kingdom that contains organisms that all have structure A.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(ii) Table 1.1 shows some cell functions.
Complete Table 1.1 by naming the cell structure responsible for each cell function and
give the letter that identifies each cell structure in Fig. 1.1.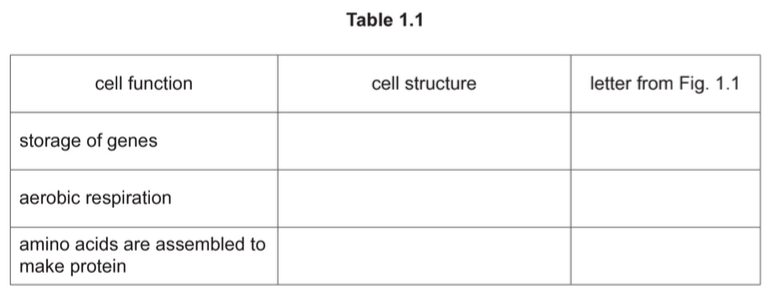
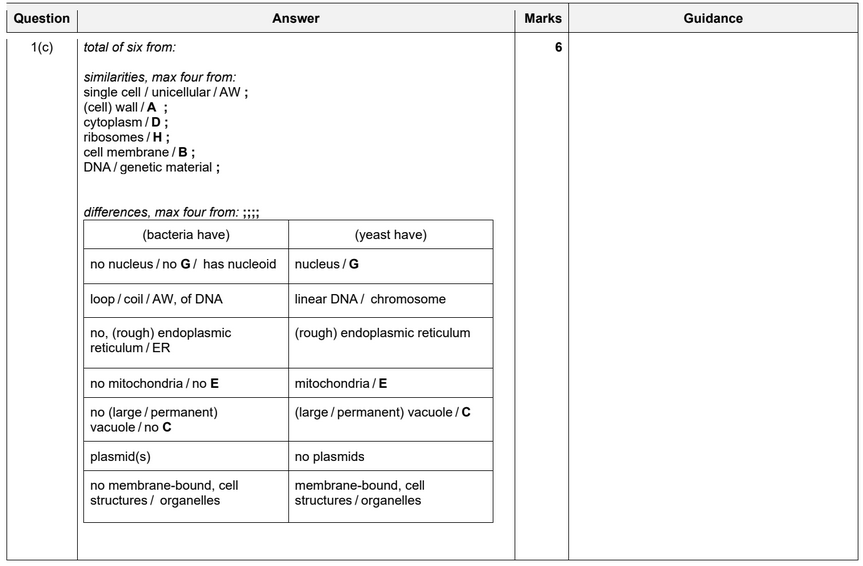
(b) A student made a drawing of one Escherichia coli bacterium. Fig. 1.2 shows the student’s
drawing.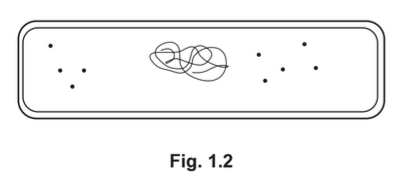
The actual length of the bacterial cell is 2 μm.
(i) Convert the actual length of the cell to millimetres.
…………………………………………… mm
(ii) State the other information that the student needs in order to calculate the magnification
of the drawing in Fig. 1.2.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(c) Describe the similarities and differences between the structure of the yeast cell and the
structure of the bacterial cell.
Use the information in Fig. 1.1 and Fig. 1.2 in your answer.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
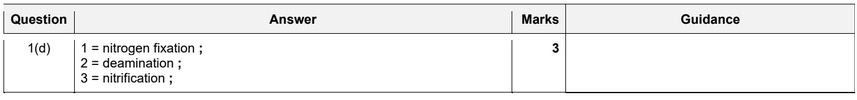
(d) Some bacteria are involved in the nitrogen cycle.
Fig. 1.3 shows part of the nitrogen cycle.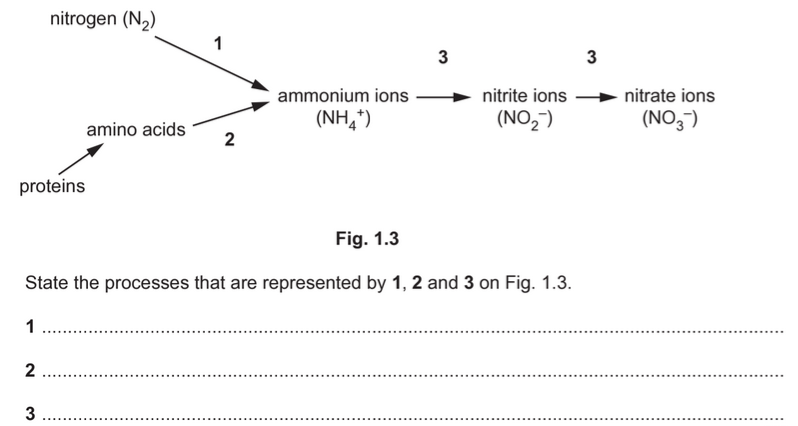
Answer/Explanation
Ans: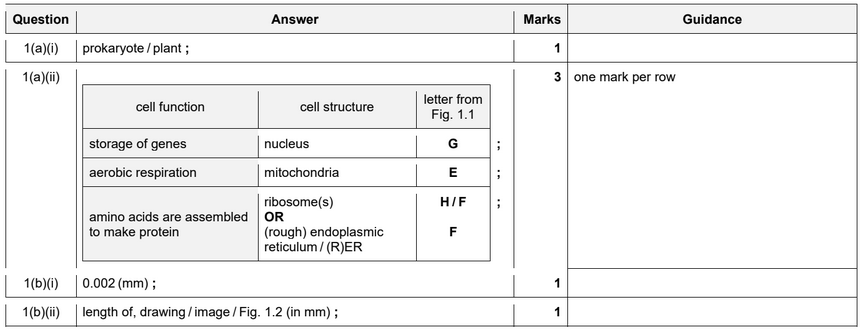
Question
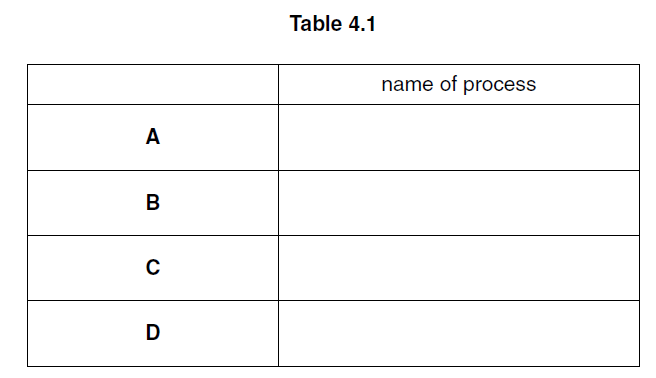
Fig. 4.1 shows part of the carbon cycle.
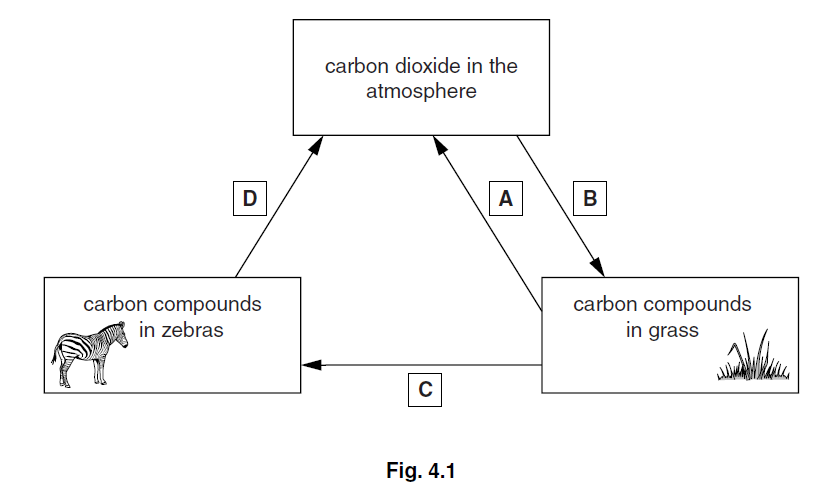
(a) Name the processes labelled A, B, C and D in Fig. 4.1.
Write your answers in Table 4.1.
[4]
(b) Name a compound containing carbon:
(i) that is found in grass,
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………[1]
(ii) that is found in zebras.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [1]
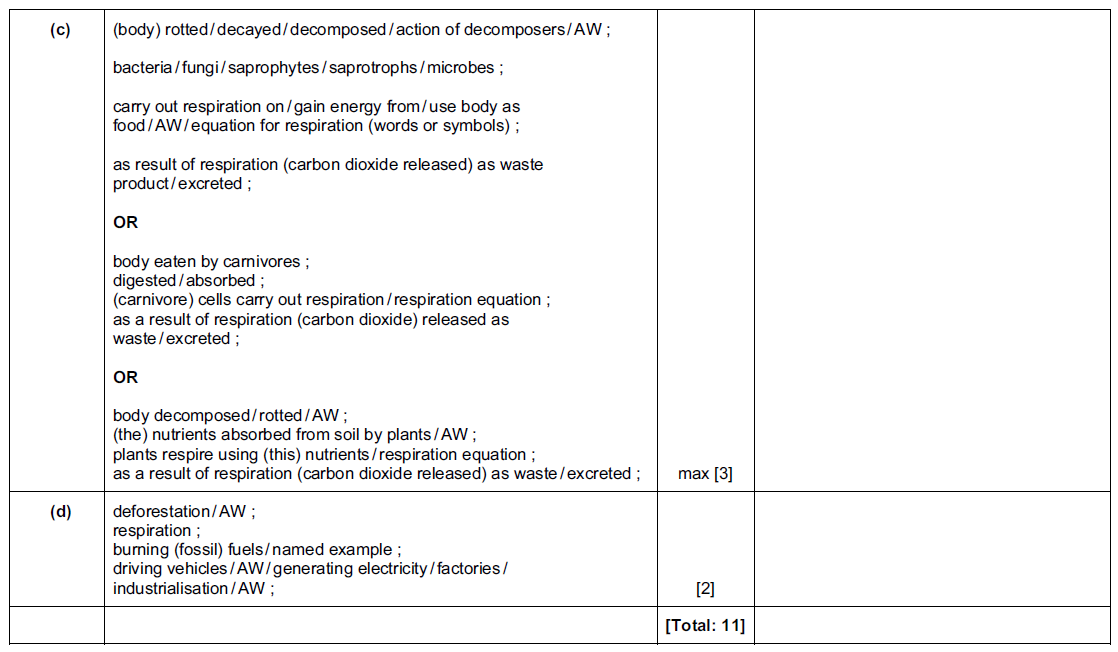
(c) When a zebra dies, the carbon in its body is eventually returned to the atmosphere in the form
of carbon dioxide.
Explain how this happens.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [3]
(d) State two human activities that are increasing the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
1 ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
2 ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
[2]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:

Question
Fig. 5.1 shows a carbon cycle.
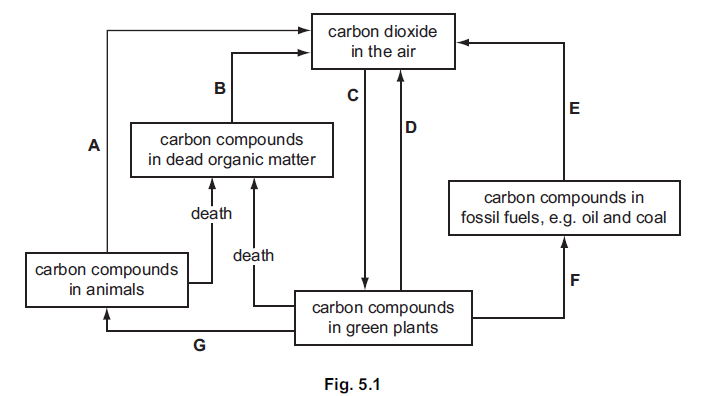

(d) In an ecosystem the flow of carbon can be drawn as a cycle but the flow of energy
cannot be drawn as a cycle.
Explain this difference.

Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question
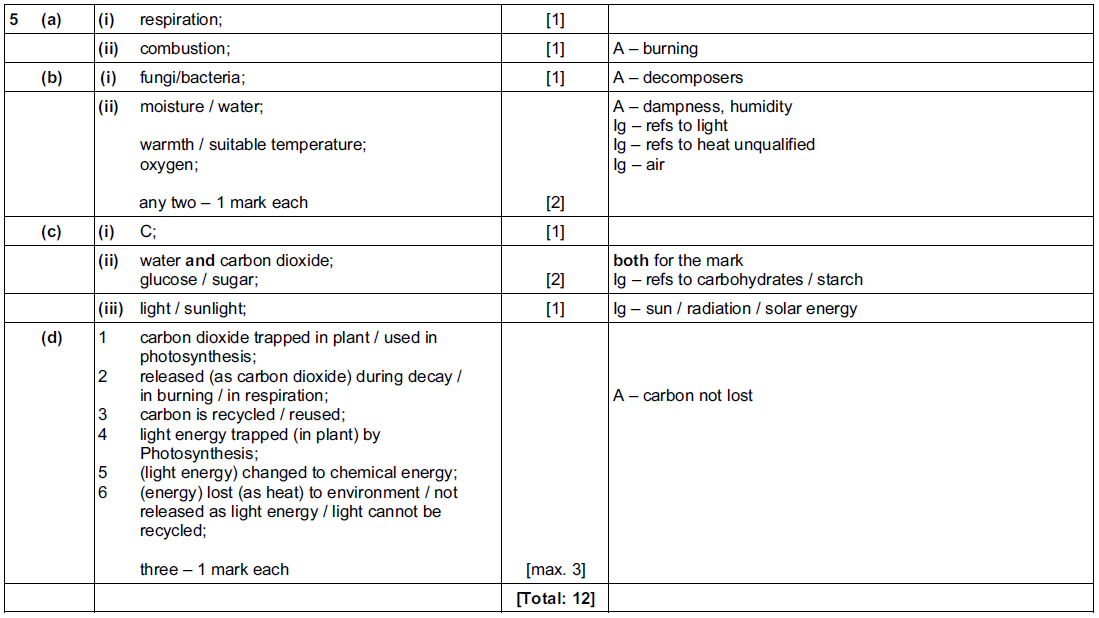
(a) Fig. 7.1 shows a carbon cycle.
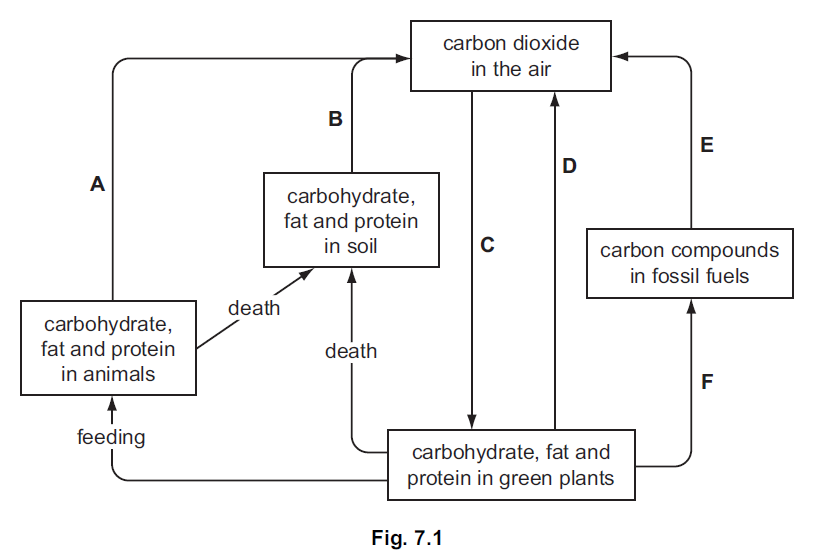
(i) Write the letter of an arrow, A, B, C, D, E, or F as shown in Fig. 7.1, that
represents each of the following processes.

(ii) Many of the world’s governments are concerned that the carbon dioxide
concentration in the atmosphere keeps rising.
Explain why they are concerned about the rise in carbon dioxide concentration.

(b) Gazelles are herbivores that eat grass.
Oxpecker birds feed on ticks that live on the skin of gazelles.
Ticks suck blood from the gazelles.
(i) Draw a food chain to represent these feeding relationships.
[2]
(ii) State what the arrows represent in a food chain.
![]()
(iii) Explain why a food chain is not considered to be a cycle like the carbon cycle.

Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question
Fig. 7.1 shows part of the carbon cycle.
The arrows represent the processes that take place in the carbon cycle.
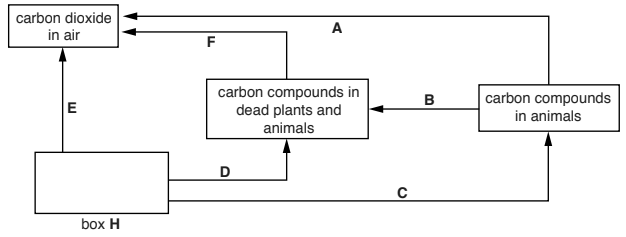
Fig. 7.1
(a) (i) Complete Fig. 7.1 by filling in box H.
(ii) State the process represented by letter C.
(iii) Draw a line with an arrow on Fig. 7.1 to represent photosynthesis Label this line G.
(iv) State the process represented by letter B.
(b) (i) State which two letters represent respiration.
(ii) Write the word equation for aerobic respiration.
(iii) Explain why every living cell has to carry out respiration.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) (i) (carbon compounds in) plants ;
(ii) feeding/ eating/nutrition/ digestion/AW ;
(iii) arrow drawn in opposite direction to E/ from CO2 in air to box H ;
(iv) death ;
(b) (i) A ;
E ;
(ii) glucose + oxygen ; ———-→
carbon dioxide + water ;
(iii) releases energy ;
example of use of energy( in cells or organisms) ;
